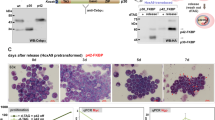
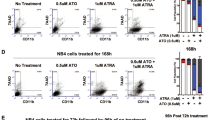
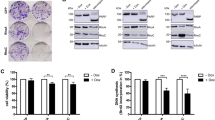
Abstract
Retinoic Acid (RA) treatment induces disease remission of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemias (APL) by triggering differentiation of neoplastic cells. Differentiation is mediated by the APL-specific transforming protein PML/RARα and involves its activity as ligand-dependent enhancer factor on RA-target genes. We report here the identification of p21 as a transcriptional target of PML/RARα during RA-induced differentiation of APL cells. We found that RA-treated APL cells undergo two rounds of cell division before entering post mitotic G1, that progression through the G1-S is indispensable for differentiation and coincides with the duration of commitment. RA-treatment induced two peaks of p21 synthesis: early (from the 2nd to the 6th hour), dependent on PML/RARα expression and associated with G1-S transition and high CDK activity; late (from 3rd to the 4th day), independent from PML/RARα and associated with G1 block and low CDK activity. Increased p21 in PML/RARα cells during G1-S had no effect on the cell cycle while an antisense p21 prevented RA-induced differentiation without altering G1-S transition and the late G1 block. These results demonstrate that p21 is an effector of the activity of PML/RARα on differentiation and suggest that p21 exerts a function in G1-S connected to differentiation-commitment and uncoupled from cell cycle and CDK inhibition.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloch A. . 1993 Leukemia 7: 1219–1224.
Brown D, Kogan S, Lagasse E, Weissman I, Alcalay M, Pelicci PG, Atwater S and Bishop JM. . 1997a PNAS 94: 2551–2556.
Brown JP, Wei W and Sedivy JM. . 1997b Science 277: 831–834.
Chambon P. . 1996 FASEB J. 10: 940–954.
Chuang LS-H, Ian H-I, T-W, K, Ng H-H, Xu G and Li BFL. . 1997 Science 277: 1996–2000.
Deng C, Zhang P, Harper JW, Elledge SJ and Leder P. . 1995 Cell 82: 675–684.
Di Cunto F, Topley G, Calautti E, Hsiao J, Ong L, Seth PK and Dotto GP. . 1998 Science 280: 1069–1072.
Dynlacht B. . 1997 Cell Cycle Control 283 Methods in Enzymology. E William G Dunphy (ed).. Academic Press, New York, NY.
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B. . 1993 Cell 75: 817–825.
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Waldman T, Velculescu VE, Burrell M, Hill DE, Healy E, Rees JL, Hamilton SR, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B. . 1995 Cancer Res. 55: 2910–2919.
Grignani F, Ferrucci PF, Testa U, Talamo G, Fagioli M, Alcalay M, Mencarelli A, Grignani F, Peschle C, Nicoletti I and Pelicci PG. . 1993 Cell 74: 1–20.
Grignani F, Fagioli M, Alcalay M, Longo L, Pandolfi PP, Donti E, Biondi A, Lo Coco F, Grignani F and Pelicci PG. . 1994 Blood 83: 10–25.
Grignani F, Testa U, Rogaia D, Ferrucci PF, Samoggia P, Pinto A, Aldinucci D, Gelmetti V, Fagioli M, Alcalay M, Seeler J, Grignani F, Nicoletti I, Peschle C and Pelicci PG. . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 4949–4958.
Grignani F, De Matteis S, Nervi C, Tomassoni L, Gelmetti V, Cioce M, Fanelli M, Ruthardt M, Ferrara FF, Zamir I, Seiser C, Grignani F, Lazar MA, Minucci S and Pelicci PG. . 1998a Nature 391: 815–818.
Grignani F, Kinsella T, Mencarelli A, Valtieri M, Riganelli D, Grignani F, Lanfrancone L, Peschle C, Nolan GP and Pelicci PG. . 1998b Cancer Res. 58.
Grisolano JL, Wesselschmidt RL, Pelicci PG and Ley TJ. . 1997 Blood 89: 376–387.
Grunstein M. . 1997 Nature 389: 349–352.
Gu Y, Rosenblatt J and Morgan DO. . 1992 EMBO J. 11: 3995–4005.
Gu Y, Turek CW and Morgan DO. . 1993 Nature 366: 707–710.
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K and Elledge SJ. . 1993 Cell 75: 805–816.
LaBaer J, Garrett MD, Stevenson LF, Slingerland JM, Sandhu C, Chou HS, Fattaey A and Harlow E. . 1997 Genes & Dev. 11: 847–862.
Li-Zhen H, Tribioli C, Rivi C, Peruzzi D, Pelicci PG, Soares V, Cattoretti G and Pandolfi PP. . 1997 PNAS 94: 5302–5307.
Lin RJ, Nagy L, Inoue S, Shao W, Miller WH and Evans RM. . 1998 Nature 391: 811–814.
Liu M, Iavarone A and Freedman L. . 1996a J. Biol. Chem. 271: 31723–31728.
Liu M, Lee M-H, Cohen M, Bommakanti M and Freedman L. . 1996b Genes & Dev. 10: 142–153.
Lübbert M, Herrmann F and Koeffler PH. . 1991 Blood 77: 909–924.
Macleod KF, Sherry N, Hannon G, Beach D, Tokino T, Kinzler K, Vogelstein B and Jacks T. . 1995 Genes Dev. 9: 935–944.
Matsumura I, Ishikawa J, Nakajima K, Oritani K, Tomiyama Y, Miyagawa J-I, Kato T, Miyazaki H, Matsuzawa Y and Kanakura Y. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 2933–2943.
McConnell SK and Kaznowski CE. . 1991 Science 254: 282–285.
Miller AM and Nasmyth KA. . 1984 Nature 312: 247–251.
Missero C, Di Cunto F, Kiyokawa H, Koff A and Dotto GP. . 1996 Genes Dev. 10: 3065–3075.
Parker SB, Eichele G, Zhang P, Rawls A, Sands AT, Bradley A, Olson EN, Harper JW and Elledge SJ. . 1995 Science 267: 1024–1027.
Raelson JV, Nervi C, Rosenauer A, Benedetti L, Monczak Y, Pearson M, Pelicci PG and Miller WH, Jr. . 1996 Blood 88: 2826–2832.
Rovera G, Olashaw N and Meo P. . 1980 Nature 284: 69–70.
Ruthardt M, Testa U, Nervi C, Grignani F, Puccetti E, Peschle C and Pelicci PG. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 4859–4869.
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. . 1995 Genes & Dev. 9: 1149–1163.
Skapek SX, Rhee J, Spicer DB, Lassar AB. . 1995 Science 267: 1022–1024.
Spriggs LL, Hill SM and Jeter JR J. . 1992 Biochem. Cell Biol. 70: 555–564.
Tsai S, Bartelmez S, Sitnicka E and Collins S. . 1994 Genes & Dev. 8: 2831–2841.
Xiong Y, Hannon GJ, Zhang H, Casso D, Kobayashi R and Beach D. . 1993 Nature 366: 701–704.
Yoshida H, Kitamura K, Tanaka K, Omura S, Miyazaki T, Hachiya T, Ohno R and Naoe T. . 1996 Cancer Res. 56: 2945–2948.
Zhang H, Hannon GJ and Beach D. . 1994 Genes & Dev. 8: 1750–1758.
Ziebold U, Bartsch O, Marais R, Ferrari S and Klempnauer K-H. . 1997 Curr. Biol. 7: 253–260.
Acknowledgements
We thank C Matteucci for excellent technical assistance, H Müller for his generous help with the elutriator and G Draetta, K Helin, PP di Fiore, S Minucci and H Müller for many helpful discussions and critical reading of the manuscript. We are also grateful to C Mercurio and M Pearson for hints and suggestions on experiments. M Lafage-Pochitaloff kindly provided the APL blasts and the CP74 α-p21 antibody was a gift from E Harlow. This work was supported by grants from AIRC and EC (Biomed II programme).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casini, T., Pelicci, P. A function of p21 during promyelocytic leukemia cell differentiation independent of CDK inhibition and cell cycle arrest. Oncogene 18, 3235–3243 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202630
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202630
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Development of functional dendrisomes based on a single molecule of polyesterbenzylether dendrimer and their application in cancer stem cell therapy
NPG Asia Materials (2019)
-
Repression of CDKN2C caused by PML/RARα binding promotes the proliferation and differentiation block in acute promyelocytic leukemia
Frontiers of Medicine (2016)
-
Biology of the cell cycle inhibitor p21CDKN1A: molecular mechanisms and relevance in chemical toxicology
Archives of Toxicology (2015)
-
The Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p27Kip1 is a Positive Regulator of Schwann Cell Differentiation In Vitro
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2011)
-
Acute promyelocytic leukaemia: novel insights into the mechanisms of cure
Nature Reviews Cancer (2010)