Abstract
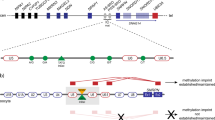
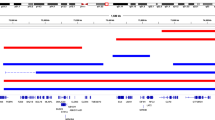
Genetic studies indicate that chromosome 7q is likely to contain an autism susceptibility locus (AUTS1). We have followed a positional candidate gene approach to identify the relevant gene and report the analysis of four adjacent genes localised to a 800 kb region in 7q32 that contains an imprinted domain: PEG1/MEST, COPG2, CPA1 and CPA5—a previously uncharacterised member of the carboxypeptidase gene family. Screening these genes for DNA changes and association analysis using intragenic single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) provided no evidence for an etiological role in IMGSAC families. We also searched for imprinting mutations potentially implicated in autism: analysis of both DNA methylation and replication timing indicated a normal imprinting regulation of the PEG1/COPG2 domain in blood lymphocytes of all patients tested. The analysis of these four genes strongly suggests that they do not play a major role in autism aetiology, and delineates our strategy to screen additional candidate genes in the AUTS1 locus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Gottesman I, Bolton P, Simonoff E, Yuzda E et al. Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study Psychol Med 1995 25: 63–77
Bolton P, Macdonald H, Pickles A, Rios P, Goode S, Crowson M et al. A case-control family history study of autism J Child Psychol Psychiatr 1994 35: 877–900
Pickles A, Bolton P, Macdonald H, Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Sim C-H et al. Latent-class analysis of recurrence risk for complex phenotypes with selection and measurement error: a twin and family history study of autism Am J Hum Genet 1995 57: 717–726
International Molecular Genetic Study of Autism Consortium. A full genome screen for autism with evidence for linkage to a region on chromosome 7q Hum Mol Genet 1998 7: 571–578
Philippe A, Martinez M, Bataille-Guillot M, Gillberg C, Rastam M, Sponheim E et al. Genome-wide scan for autism susceptibility genes Hum Mol Genet 1999 8: 805–812
Risch N, Spiker D, Lotspeich L, Nouri N, Hinds D, Hallmeyer J et al. A genomic screen of autism: evidence for a multilocus etiology Am J Hum Genet 1999 65: 493–507
Collaborative-Linkage-Study-of-Autism Barrett S, Beck JC, Bernier R, Bisson E, Braun TA et al. An autosomal genomic screen for autism Am J Med Genet 1999 88: 609–615
Ashley-Koch A, Wolpert CM, Menold MM, Zaeem L, Basu S, Donnelly SL et al. Genetic studies of autistic disorder and chromosome 7 Genomics 1999 61: 227–236
Buxbaum JD, Silverman JM, Smith CJ, Kilifarski M, Reichert J, Hollander E et al. Evidence for a susceptibility gene for autism on chromosome 2 and for genetic heterogeneity Am J Hum Genet 2001 68: 1514–1520
Vincent JB, Herbrick JA, Gurling HMD, Bolton PF, Roberts W, Scherer SW . Identification of a novel gene on chromosome 7q31 that is interrupted by a translocation breakpoint in an autistic individual Am J Hum Genet 2000 67: 510–514
Kobayashi S, Kohda T, Miyoshi N, Kuroiwa Y, Aisaka K, Tsutsumi O et al. Human PEG1/MEST, an imprinted gene on chromosome 7 Hum Mol Genet 1997 6: 781–786
Riesewijk AM, Hu L, Schulz U, Tariverdian G, Hoglund P, Kere J et al. Monoallelic expression of human PEG1/MEST is paralleled by parent-specific methylation in fetuses Genomics 1997 42: 236–244
Blagitko N, Schulz U, Schinzel AA, Ropers HH, Kalscheurer VM . γ2-COP, a novel imprinted gene on chromosome 7q32, defines a new imprinting cluster in the human genome Hum Mol Genet 1999 8: 2387–2396
Keverne EB . Genomic imprinting in the brain Curr Opin Neurobiol 1997 7: 463–468
International Molecular Genetic Study of Autism Consortium. Further characterization of the autism susceptibility locus AUTS1 on chromosome 7q Hum Mol Genet 2001 9: 973–982
Kaneko-Ishino T, Kuroiwa Y, Miyoshi N, Kohda T, Suzuki R, Yokoyama M et al. Peg1/Mest imprinted gene on chromosome 6 identified by cDNA subtraction hybridization Nat Genet 1995 11: 52–59
Lefebvre L, Viville S, Barton SC, Ishino F, Keverne EB, Surani MA . Abnormal maternal behaviour and growth retardation associated with loss of the imprinted gene Mest Nat Genet 1998 20: 163–169
Kosaki K, Kosaki R, Craigen W, Matsuo N . Isoform-specific imprinting of the human PEG1/MEST gene Am J Hum Genet 2000 66: 309–312
Gillberg C, Trygstad O, Foss I . Childhood psychosis and urinary excretion of peptides and protein-associated peptide complexes J Autism Dev Disord 1982 12: 229–241
Israngkun PP, Newman HA, Patel ST . Potential biochemical markers for infantile autism Neurochem Pathol 1986 5: 51–70
Pedersen OS, Liu Y, Reichelt KL . Serotonin uptake stimulating peptide found in plasma of normal individuals and in some autistic urines J Peptide Res 1999 53: 641–646
Le Couteur A, Trygstad O, Evered C, Gillberg C, Rutter M . Infantile autism and urinary excretion of peptides and protein-associated peptide complexes J Autism Dev Disord 1988 18: 181–190
Normant E, Gros C, Schwartz J-C . Carboxypeptidase A isoforms produced by distinct genes or alternative splicing in brain or other extrapancreatic tissues J Biol Chem 1995 270: 20543–20549
Falls JG, J PD, Wylie AA, Jirtle RL . Genomic imprinting: implications for human disease Am J Pathol 1999 154: 635–647
Reik W, Walter J . Genomic imprinting: parental influence on the genome Nat Rev Genet 2001 2: 21–32
Kitsberg D, Selig S, Brandelis M, Simon I, Keshet I, Driscoll RD et al. Allele-specific replication timing of imprinted gene regions Nature 1993 364: 459–463
Simon I, Tenzen T, Reubinoff BE, Hillman D, McCarrey JR, Cedar H . Asynchronous replication of imprinted genes is established in the gametes and maintained during development Nature 1999 401: 929–932
Selig S, Okumura K, Ward DC, Cedar H . Delineation of DNA replication time zones by fluorescence in situ hybridization EMBO J 1992 11: 1217–1225
International Molecular Genetic Study of Autism Consortium (IMGSAC). A genomewide screen for autism: strong evidence of linkage to chromosomes 2q, 7q and 16p Am J Hum Genet 2001 69: 570–581
Sham PC, Curtis D . An extended transmission/disequilibrium test (TDT) for multi-allele marker loci Ann Hum Genet 1995 59: 323–336
Hinds D, Risch N . The ASPEX package: affected sib-pair mapping 1996 ftp://lahmed.stanford.edu/pub/aspex
Dudbridge F, Eaves IA, Koeleman PC, Todd JA . Software for multilocus TDT analysis Available from ftp://ftp-gene.cimr.cam.ac.uk
Martin ER, Kaplan NL, Weir BS . Tests for linkage and association in nuclear families Am J Hum Genet 1997 61: 439–448
Monk D, Wakeling E, Proud V, Hitchins M, Abu-Amero S, Stanier P et al. Duplication of 7p11.2–p13, including GRB10, in Silver–Russell Syndrome Am J Hum Genet 2000 66: 36–46
Tanke HJ, Florijn RJ, Wiegant J, Raap AK, Vrolijk J . CCD microscopy and image analysis of cells and chromosomes stained by fluorescence in situ hybridization Histochem J 1995 27: 4–14
Hayashida S, Yamasaki K, Asada Y, Soeda E, Niikawa N, Kishino T . Construction of a physical and transcript map flanking the imprinted MEST/PEG1 region at 7q32 Genomics 2000 66: 221–225
Nielsen HJE, Brunak S, von Heijne G . Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and prediction of their clevage sites Prot Engin 1997 10: 1–6
Dobson-Stone C, Cox R, Lonie L, Southam L, Fraser M, Wise C et al. Comparison of fluorescent single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis and denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography for detection of EXT1 and EXT2 mutations in hereditary multiple exostoses Eur J Hum Genet 2000 8: 24–32
Spence JE, Perciaccante RG, Greig GM, Willard HF, Ledbetter DH, Hejtmancik JF et al. Uniparental disomy as a mechanism for human genetic disease Am J Hum Genet 1988 42: 217–226
Maestrini E, Paul A, Monaco AP, Bailey A . Identifying autism susceptibility genes Neuron 2000 28: 19–24
Roberts SB, MacLean CJ, C NM, Eaves LJ, Kendler KS . Replication of linkage studies of complex traits: an examination of variation in location estimates Am J Hum Genet 1999 65: 876–884
Risch N, Merikangas K . The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases Science 1996 273: 1516–1517
Ashley-Koch A, Menold M, Joyner K, Mason S, Poole C, Donnelly S et al. Examination of epigenetic factors and gene–gene interactions influencing genetic susceptibility at chromosomes 7 and 15 for autistic disorder Am J Hum Genet 2000 67: Abstract Nr. 177
Yamasaki K, Hayashida S, Miura K, Masuzaki H, Ishimaru T, Niikawa N et al. The novel gene, γ2-COP (COPG2), in the 7q32 imprinted domain escapes genomic imprinting Genomics 2000 68: 330–335
Acknowledgements
This work would not have been possible without the co-operation of both the subjects and their families and the many referring professionals. We would like to thank Zoe Docherty from Guy's Hospital for providing samples from blood lymphocytes, Pat Scudder for technical support, Janine A Lamb, Gabrielle Barnby and Anthony Bailey for helpful discussions and critical comments on the manuscript, and Lorne Lonie for assistance on DHPLC. This study is funded by support from the UK Medical Research Fund, The Wellcome Trust and Telethon, Italy (E.1007). APM is a Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonora, E., Bacchelli, E., Levy, E. et al. Mutation screening and imprinting analysis of four candidate genes for autism in the 7q32 region. Mol Psychiatry 7, 289–301 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001004
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001004
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Advances in autism research, 2021: continuing to decipher the secrets of autism
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Quantitative trait locus analysis identifies Gabra3 as a regulator of behavioral despair in mice
Mammalian Genome (2010)
-
High-density SNP association study and copy number variation analysis of the AUTS1 and AUTS5 loci implicate the IMMP2L–DOCK4 gene region in autism susceptibility
Molecular Psychiatry (2010)
-
Mutation screening and association analysis of six candidate genes for autism on chromosome 7q
European Journal of Human Genetics (2005)
-
Association of the homeobox transcription factor, ENGRAILED 2, 3, with autism spectrum disorder
Molecular Psychiatry (2004)