Abstract
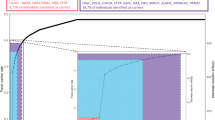
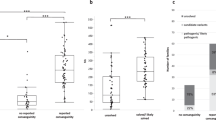
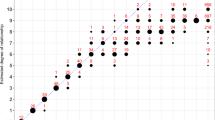
Founder effect and linkage disequilibrium have been successfully exploited to map single gene disorders1, and the study of isolated populations is emerging as a major approach to the investigation of genetically complex diseases2. In the search for genetic isolates ranging from Pacific islands to Middle East deserts, the 10 million Gypsies resident in Europe3 have largely escaped the attention of geneticists. Because of their geographical ubiquity, lack of written history and the presumed social and cultural nature of their isolation, Gypsies are construed as not meeting the criteria for a well defined founder population. Gypsy society has a complex structure with subdivisions and stratifications that are incomprehensible to the surrounding populations. Marginalization by the health care systems in most countries results in a lack of information on causes of morbidity and mortality and little is known about hereditary disorders or the population genetic characteristics of Gypsies. This study is the first example of mapping a disease gene in endogamous Gypsy groups. Using lod score analysis and linkage disequilibrium, we have located a novel demyelinating neuropathy to a narrow interval on chromosome 8q24. We show that the disease, occuring in Gypsy groups of different identity and history of migrations, is caused by a single mutation whose origin predates the divergence of these groups.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de la Chapelle, A. Disease gene mapping in isolated human populations: the example of Finland. J. Med Genet. 30, 857–865 (1993).
Risch, N. & Botstein, D. A manic depressive history. Nature Genet. 12, 351–353 (1996).
Liegeois, J.-P., Travellers. (Council of Europe Press, 1994).
Marushiakova, E. & Popov, V. Gypsies in Bulgaria. (Club '90 Publishing House, Sofia, 1993).
Fraser, A., The Gypsies (Blackwell, Oxford, UK & Cambridge, USA, 1995).
Houwen, R.H.J. et al. Genome screening by searching for shared segments: mapping a gene for benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Nature Genet. 8, 380–386 (1994).
Terwilliger, J.D. A powerful likelihood method for the analysis of linkage disequilibrium between trait loci and one or more polymorphic marker loci. Am. J. Hum. Genet 56, 777–785 (1995).
Ionasescu, V.V. et al. A Dejerine-Sottas neuropathy family with a gene mapped on chromosome 8. Muscle and Nerve 19, 319–323 (1996).
Pott, A., Zigeuner in Europen und Asien. (1884), quoted in San Roman, T. Vecinosgitanos(Akal, Madrid, 1976).
Kenrick, D. & Paxton, C., Destiny of Europe's Gypsies. (Cox & Wyman, London, 1972).
Cornell, J., Sellars, S. & Beighton, P. Autosomal-recessive inheritance of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease associated with sensorineural deafness. Clin. Genet. 25, 163–165 (1984).
Gyapay, G. et al. The 1993–94 Généthon human linkage map. Nature Genet. 7, 246–339 (1994).
Murray, J.C. et al. A comprehensive human linkage map with centimorgan density. Science 265, 2049–2054.
Cottingham, R.W. et al. Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 53, 252–263 (1993).
Schaffer, A.A. et al. Avoiding recomputation in linkage analysis. Hum. Hered. 44, 225–237 (1994).
Lathrop, G. & Lalouel, J.-M. Easy calculations of LOD scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 36, 460–465 (1984).
O'Connel, J.R. & Weeks, D.E. The VITESSE algorithm for rapid exact multiiocus linkage analysis via genotype set-recording and fuzzy inheritance. Nature Genet. 11, 402–408 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalaydjieva, L., Hallmayer, J., Chandler, D. et al. Gene mapping in Gypsies identifies a novel demyelinating neuropathy on chromosome 8q24. Nat Genet 14, 214–217 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1096-214
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1096-214
This article is cited by
-
A splice altering variant in NDRG1 gene causes Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 4D
Neurological Sciences (2022)
-
HMSN Lom in 12 Czech patients, with one unusual case due to uniparental isodisomy of chromosome 8
Journal of Human Genetics (2017)
-
Significant interethnic differencies in functional variants of PON1 and P2RY12 genes in Roma and Hungarian population samples
Molecular Biology Reports (2015)
-
Genetik der Neuropathien
Der Nervenarzt (2013)
-
NDRG1/Cap43 overexpression in tumor tissues and serum from lung cancer patients
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2012)