Abstract
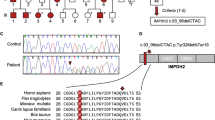
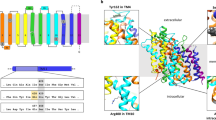
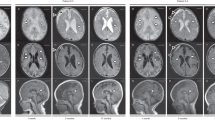
Canavan disease, an autosomal recessive leukodystrophy, is caused by deficiency of aspartoacylase and accumulation of N–acetylaspartic acid in brain. We have cloned the human aspartoacylase (ASP) cDNA spanning 1,435 basepairs, and show that the isolated cDNA expresses aspartoacylase activity in bacteria. Furthermore, an A to C base change, at nucleotide 854, has been found in 85% of the 34 Canavan alleles tested so far. This base change results in a missense Glu285Ala mutation that is predicted to be part of the catalytic domain of aspartoacylase. The data suggest that the catalytic centre of aspartoacylase involves a triad of Ser, His and Glu residues. Our findings have implications for diagnosis and screening of Canavan disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Globus, J.H. & Strauss, I. Progressive degenerative subcortical encephalopathy (Schilder's disease). Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. 20, 1190–1228 (1928).
Canavan, M.M. Schilder's encephalitis periaxialis diffusa. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat 25, 299–308 (1931).
van Bogaert, L. & Bertrand, I. Sur une idiotie familiale avec degerescence sponglieuse de neuraxe (note preliminaire). Acta. Neurol. Belg. 49, 572–587 (1949).
Adachi, M., Torii, J., Schneck, L. & Volk, B.W. Electron microscopic and enzyme histochemical studies of the cerebellum in spongy degeneration (van Bogaert and Bertrand type). Acta. Neuropath. 20, 22–31 (1972).
Adornato, B.T., O'Brien, J.S., Lamport, P.W., Roe, T.F. & Neustein, H.B. Cerebral spongy degeneration of infancy: a biochemical and ultrastructural study of affected twins. Neurology 22, 202–210 (1972).
Matalon, R., Michals, K., Sebasta, D., Deanching, M., Gashkoff, P. & Casanova, J. Aspartoacylase deficiency and N-acetylaspartic aciduria in patients with Canavan Disease. Am. J. med. Genet. 29, 463–471 (1988).
Bimbaum, S.M. Amino acid acylases I and II from hog kidney. Meth. Enzymol. 2, 115–119 (1955).
Bimbaum, S.M., Levinton, L., Kingsley, R.B. & Greenstein, J.P. Specificity of amino acid acylases. J. biol. Chem. 194, 455–462 (1952).
Matalon, R. et al. Aspartoacylase deficiency: the enzyme defect in Canavan Disease. J. inher. met. Dis. 12, 329–331 (1989).
Matalon, R., Kaul, R. & Michals, K. Canavan disease: biochemical and molecular studies. J. inher. metab. Dis. (in the press).
Grodd, W., Krägeloh-Mann, I., Petersen, D., Trefz, F.K. & Harzer, K. In vivo asessment of N-acetylaspartate in brain in spongy degeneration (Canavan disease) by proton spectroscopy. Lancet 336, 437–438 (1990).
Matalon, R., Kaul, R. & Michals, K. . In The Molecular Biology and Genetic Basis of Neurological Disease (eds Rosenberg, R.N. et al.) 541–546 (Butterworth-Heineman, Boston, 1993).
Ozand, P.T., Gascon, G. & Dhalla, M. Aspartoacylase deficiency and canavan disease in Saudi Arabia. Am. J. med. Genet. 35, 266–268 (1990).
Michelakakis, H., Giouroukos, S., Divry, P., Katsarou, E., Rolland, M.O. & Skardoutsow, A., Canavan Disease: findings in four new cases. J. inher. metab. Dis. 14, 267–268 (1991).
Matalon, R., Michals, K., Gashkoff, P. & Kaul, R. Prenatal diagnosis of Canavan disease. J. inher. metab. Dis. 15, 392–394 (1992).
Kaul, R., Casanova, J., Johnson, A., Tang, P. & Matalon, R. Purification, characterization and localization of aspartoacylase from bovine brain. J. Neurochem. 56, 129–135 (1991).
Proudfoot, N.J. & Brownlee, G.G. 3′ Non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature 263, 211–214 (1976).
Birnstiel, M.L., Busslinger, M. & Strub, K. Transcription termination and 3′ processing: the end is in site! Cell 41, 349–359 (1985).
Cygler, M. et al. Relationship between sequence conservation and three-dimentional structure in a large family of esterases, lipases, and related proteins. Protein Sci. 2, 366–382 (1993).
Lemeur, M.A., Galliot, B. & Geriinger, P. Termination of the ovalbumin gene transcription. EMBO J. 3, 2779–2786 (1984).
Miller, Y.R., Drabkin, H., Jones, C. & Fisher, J.H. Human aminoacylase-1: cloning, regional assignment to distal chromosome 3p21.1, and identification of a cross-hybridizing sequence on chromosome 18. Genomics 8, 149–154 (1990).
Goldstein, F.B. Biosynthesis of N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid. J. biol. Chem. 234, 2702–2706 (1959).
Goldstein, F.B. The enzymatic synthesis of N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid by subcellular preparations of rat brain. J. biol. Chem. 244, 4257–4260 (1969).
Moffett, J.R., Namboodiri, M.A., Cangro, C.B. & Neale, J.H. Immunohistochemical localization of N-acetylaspartate in rat brain. NeuroReport 2, 131–134 (1991).
Urenjak, J., Williams, S.R., Gadian, D.G. & Noble, M. Specific expression of N-acetylaspartate in neurons, oligodendrocyte-type-2 astrocyte progenitors, and immature oligodendrocytes in vitro. J. Neurochem. 59, 55–61 (1992).
Moffett, J.R., Namboodiri, M.A. & Neale, J.H. Enhanced carbodiimide fixation for immunohistochemistry: application to the comparative distributions of N-acetylaspartylglutamate and N-acetylaspartate immunoreactivities in rat brain. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 31, 559–570 (1993).
Tallan, H.H., Moore, S. & Stein, W.H. N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid in brain. J. biol. Chem. 219, 257–264 (1956).
Jacobson, K.B. Studies on the role of N-acetylaspartic acid on mammalian brain. J. gen. Physiol. 43, 323–333 (1957).
Mclntosh, J.M. & Cooper, J.R. Studies on the function of N-acetylaspartic acid in the brain. J. Neurochem. 12, 825–835 (1965).
Shigematsu, H. et al. Purification and characterization of the heat stable factors essential for conversion of lignoceric acid to cerebronic acid and glutamic acid: identification of N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid. J. Neurochem. 40, 814–620 (1983).
Cangro, C.B., Namboodiri, M.A.A., Sklae, L.A., Corigliano-Murphy, A. & Neale, J.H. Immunocytochemistry and biosynthesis of N-acetylaspartylglutamate in spinal sensory ganglia. J. Neurochem. 49, 1579–1588 (1987).
Ory-Lavollee, L., Blakely, R.D. & Coyle, J.T. Neurochemical and immunocytochemical studies on the distribution of N-acetylaspartylglutamate and N-acetyl-aspartate in rat spinal cord and some peripheral nervous tissues. J. Neurochem. 48, 895–899 (1987).
Birken, D.L. & Oldendorf, W.H. N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid: A literature review of a compount prominent in 1H-NMR spectroscopic studies on brain. Neurosci. Behavioral Rev. 13, 23–31 (1989).
Grood, W., Krägeloh-Mann, I., Klose, U. & Sauter, R. Metabolic and destructive brain disorders in children: Finding with localized proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 181, 173–181 (1991).
Dunlop, D.S., McHale, D.M. & Lajtha, A. Decreased brain N-acetylaspartate in Huntingdon's disease. Brain Res. 580, 44–48 (1992).
Meyerhoff, D.J. et al. Reduced brain N- acetylaspartate suggests neuronal loss in cognitively impaired human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive individuals: In vivo 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Neurology 43, 509–515 (1993).
Gideon, P. et al. Early time course of N-acetylspartate, creatine and phosphocreatine, and compounds containing choline in the brain after acute stroke-a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Stroke 23, 1566–1572 (1992).
Marcucci, F., Colombo, L., De Ponte, G. & Mussini, E. Decrease in N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid in brain of myodystrophic mice. J. Neurochem. 43, 1484–1486 (1984).
Bell, J.D. et al. In vivo detection of metabolic changes in a mouse model of scrapie using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. gen. Virology 72, 2419–2423 (1991).
Kaul, R., Murthy, S.N.P., Reddy, A.G., Steck, T.L. & Kohler, H. Amino acid sequence of the N-terminal 201 residues of human erythrocyte membrane band 3. J. biol. Chem. 258, 7981–7990 (1983).
Saiki, R.K. et al. Enzymatic amplification of β-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science 230, 1350–1354 (1985).
Orita, M., Suzuki, Y., Sekiya, T. & Hayashi, K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics 5, 874–879 (1989).
Feinberg, A.P. & Vogelstein, B. Technique for radio labelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal. Biochem. 137, 266–267 (1984).
Kaul, R., Hidebrand, B., Roberts, S. & Jagadeeswaran, P. Isolation and characeterization of human blood coagulation factor X cDNA. Gene 41, 311–314 (1986).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A laboratory manual 2nd edn (Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory, New York, 1989).
Sanger, F.S., Nicklen, I. & Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Chomczynski, P. & Sacchi, N. Single step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidiniumthiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162, 156 (1987).
Lowry, O.H., Rosenbroug, N.J., Farr, A.L. & Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaul, R., Ping Gao, G., Balamurugan, K. et al. Cloning of the human aspartoacylase cDNA and a common missense mutation in Canavan disease. Nat Genet 5, 118–123 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1093-118
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1093-118
This article is cited by
-
Uncoupling N-acetylaspartate from brain pathology: implications for Canavan disease gene therapy
Acta Neuropathologica (2018)
-
The state of treatment approach and diagnostics in Canavan disease with focus on the determination of N-acetylasparic acid
Chemical Papers (2017)
-
Comparative computational assessment of the pathogenicity of mutations in the Aspartoacylase enzyme
Metabolic Brain Disease (2017)
-
The neuronal metabolite NAA regulates histone H3 methylation in oligodendrocytes and myelin lipid composition
Experimental Brain Research (2017)
-
Cytotoxic edema and diffusion restriction as an early pathoradiologic marker in canavan disease: case report and review of the literature
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2016)