Abstract
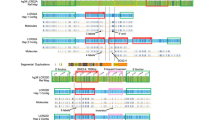
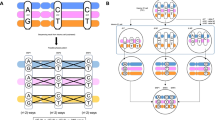
We have developed a 32–interval deletion panel for human chromosome Xp22 spanning about 30 megabases of genomic DNA. DNA samples from 50 patients with chromosomal rearrangements involving Xp22 were tested with 60 markers using a polymerase chain reaction strategy. The ensuing deletion map allowed us to confirm and refine the order of previously isolated and newly developed markers. Our mapping panel will provide the framework for mapping new sequences, for orienting chromosome walks in the region and for projects aimed at isolating genes responsible for diseases mapping to Xp22.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McKusick, V.A. Mendelian Inheritance in Man. 10th edn (Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, 1992).
Schmickel, R.D. Contiguous gene syndromes: a component of recognizable syndromes. J. Pediatr. 109, 231–241 (1986).
Ballabio, A. et al. Contiguous gene syndromes due to deletions in the distal short arm of the human X chromosome. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 10001–10006 (1989).
Ballabio, A. Contiguous deletion syndromes. Curr. Op. Genet. Devel. 1, 25–29 (1991).
Read, A.P. et al. Mapping of the human X-linked hypophosphataemia rickets by multilocus linkage analysis. Hum. Genet. 73, 267–270 (1986).
Brown, C.J., Mahtani, M.M. & Willard, H.F. Genetic mapping of four DNA markers (DXS16, DXS43, DXS85, and DXS143) from the p22 region of the human X chromosome. Hum. Genet. 80, 296–298 (1988).
Alitalo, T. et al. Genetic mapping of 12 marker loci in the Xp22.3-p21.2 region. Hum. Genet. 86, 599–603 (1991).
Johnson, C.L., Charmley, P., Yen, P.H. & Shapiro, L.J. A multipoint linkage map of the distal short arm of the human X chromosome. Am. J. hum. Genet. 49, 261–266 (1991).
Weissenbach, J. et al. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature 359, 794–801 (1992).
Vollrath, D. et al. The human Y chromosome: a 43-interval map based on naturally occuring deletions. Science 258, 52–59 (1992).
Foote, S., Vollrath, D., Hilton, A. & Page, D. The human Y chromosome: overlapping DNA clones spanning the euchromatic region. Science 258, 60–66 (1992).
Davies, K.E., Mandel, J.-L., Monaco, A.P., Nussbaum, R.L. & Willard, H.F. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X chromosome. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 58, 853–966 (1991).
Koenig, M., Camerino, G., Heilig, R. & Mandel, J.L. A DNA fragment from the human X chromosome short arm which detects a partially homologous sequence on the Y chromosome long arm. Nucl. Acids Res. 12, 4097–4109 (1984).
Kunkel, L.M. et al. Identification and isolation of transcribed human X chromosome DNA sequences. Nucl. Acids Res. 11, 7961–7979 (1983).
Franco, B. et al. A gene deleted in Kallmann's syndrome shares homology with neural cell adhesion and axonal path-finding molecules. Nature 353, 529–536 (1991).
Legouis, R. et al. The candidate gene for the X-linked Kallmann syndrome encodes a protein related to adhesion molecules. Cell 67, 423–435 (1991).
Yen, P.H. et al. Cloning and expression of steroid sulfatase cDNA and the frequent occurance of deletions in STS defiency: implications for X-Y interchange. Cell 49, 443–454 (1987).
Ballabio, A. et al. Isolation and characterization of a steroid sulfatase cDNA clone: genomic deletions in patients with X-linked ichthyosis. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 4519–4523 (1987).
Yen, P.H. et al. Frequent deletions of the human X chromosome distal short arm result from recombination between low-copy repetitive elements. Cell 61, 603–610 (1990).
Ellis, N.A. et al. The pseudoautosomal boundary in man is defined by an Alu repeat sequence inserted on the Y chromosome. Nature 337, 81–84 (1989).
Dorkins, H. et al. Segregation analysis of a marker localised Xp21.2-Xp21.3 in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy families. Hum. Genet. 71, 103–107 (1985).
Carrozzo, R. et al. Isolation and characterization of a yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) contig around the human steroid sulfatase gene. Genomics 12, 7–12 (1992).
Wapenaar, M.C. et al. The genes for X-linked ocular albinism (OA1) and microphtalmia with linear skin defects (MLS): cloning and characterization of the critical regions. Hum. mol. Gen. (in the press).
Lagerstrom, M., Dahl, N., Iselius, L., Backman, B. & Pettersson, U. Mapping of the gene for amelogenesis imperfecta by linkage analysis. Am. J. hum. Genet. 46, 120–125 (1990).
Bailey, D.M.D., Affara, N.A. & Ferguson-Smith, M.A. The X-Y homologous gene amelogenin maps to the short arms of both the X and Y chromosomes and is highly conserved in primates. Genomics 14, 203–205 (1992).
Becker, M.A. et al. Cloning of the cDNAs for human phosphoribo-sylpyrophosphate synthetases 1 and 2 and X chromosome localization of PRPS1 and PRPS2 genes. Genomics 8, 555–561 (1990).
Ellison, J. et al. Directed isolation of human genes that escape X-inactivation. Som. Cell molec. Genet. 18, 259–268 (1992).
Dahl, H.H., Hutchison, W.M., Guo, Z., Forrest, S.M. & Hansen, L.L. Polymorphisms in the human X-linked pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 alpha gene. Hum. Genet. 87, 49–53 (1991).
Kere, J. et al. Mapping human chromosomes by walking with sequence-tagged sites from end fragments of yeast artificial chromosome inserts. Genomics 14, 241–248 (1992).
Ballabio, A., Bardoni, B., Guioli, S., Basler, E. & Camerino, G. Two families of low-copy repeats are interspersed on Xp22.3: implications for the high frequency of deletions in this region. Genomics 8, 263–270 (1990).
Petit, C. et al. Isolation of sequences from Xp22.3 and deletion mapping using sex chromosome rearrangements from human X-Y interchange sex reversals. Genomics 6, 651–658 (1990).
Wapenaar, M.C. et al. Physical mapping of 14 new DNA markers isolated from the human distal Xp region. Genomics 13, 167–175 (1992).
Bergen, A.A.B. et al. Localization of the X-linked ocular albinism gene (OA1) between DXS278/DXS237 and DXS143/DXS16 by linkage analysis. Ophthalmic paediat. Genet. 11, 165–170 (1990).
Bergen, A.A.B. et al. Multipoint linkage analysis in X-linked ocular albinism of the Nettleship-Falls type. Hum. Genet. 88, 162–166 (1991).
Schnur, R.E. et al. Linkage analysis in X-linked ocular albinism. Genomics 9, 605–613 (1991).
Charles, S.J., Moore, A.T. & Yates, J.R.W. Genetic mapping of X-linked ocular albinism: linkage analysis in British families. J. med. Genet. 29, 552–554 (1992).
Aicardi, J., Lefebvre, J. & Lerique-Koechlin, A. A new syndrome: spasms in flexion, callosal agenesis, ocular abnormalities. Electroencephalogr. clin. Neurophysiol. 19, 609–610 (1965).
Goltz, R.W., Peterson, W.C., Gorlin, R.J. & Ravits, H.G. Focal dermal hypoplasia. Arch. Dermatol. 86, 708–717 (1962).
Yen, P.H. et al. Cloning and expression of steroid sulfatase cDNA and the frequent occurence of deletions in STS deficiency: implications for X-Y interchange. Cell 49, 443–454 (1987).
Ballabio, A. et al. Molecular heterogeneity of steroid sulfatase deficiency: a multicenter study on 57 unrelated patients, at DNA and protein levels. Genomics 4, 36–40 (1989).
Ballabio, A. et al. Molecular characterization of human X/Y translocation suggests their aetiology through aberrant exchange between homologous sequences on Xp and Yq. Ann. Hum. Genet. 53, 9–1 (1989).
Yen, P.H. et al. X/Y translocations resulting from recombination between homologous sequences on Xp and Yq. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 8944–8948 (1991).
Guioli, S. et al. Kallmann syndrome due to a translocation resulting in an X/Y fusion gene. Nature Genet. 1, 337–34 (1992).
Ballabio, A. & Andria, G. Deletions and translocations involving the distal short arm of the human X chromosome: review and hypotheses. Hum. molec. Genet. 1, 221–227 (1992).
Ballabio, A., Parenti, G., Napolitano, E., Di Natale, P. & Andria, G. Genetic complementation of steroid sulfatase after somatic cell hybridization of X-linked ichthyosis and multiple sulfatase deficiency. Hum. Genet. 70, 315–317 (1985).
Zoghbi, H.Y. et al. Assignment of autosomal dominant spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA1) centromeric to the HLA region on the short arm of chromosome 6, using multilocus linkage analysis. Am. J. hum. Genet. 44, 255–263 (1989).
Ellison, K.A. et al. Examination of X chromosome markers in Rett syndrome: exclusion mapping with a novel variation on multilocus linkage analysis. Am. J. hum. Genet. 50, 278–287 (1992).
Zoghbi, H.Y., McCall, A.E. & LeBorgne-DeMarquoy, F. Sixty-five radiation hybrids for the short arm of chromosome 6: their value as a mapping panel and as a source for rapid isolation of new probes using repeat element-mediated PCR. Genomics 9, 713–720 (1991).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual 2nd edn (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1989).
Ledbetter, D.H., Airhardt, S.D. & Nussbaum, R.L. Somatic cell hybrid studies of fragile X expression in a carrier female and transmitting male. Am. J. med. Genet. 23, 429–443 (1986).
Joslyn, G. et al. Identification of deletion mutations and three new genes at the familial polyposis locus. Cell 66, 601–613 (1991).
Breukel, C. et al. Vector-Alu PCR: a rapid step in mapping cosmids and YACs. Nucl. Acids Res. 18, 3097 (1990).
Zoghbi, H.Y. & Chinault, A.C. Generation of YAC contigs by walking. YACs: A user's guide eds B.H. Browning, D. Nelson & W.H. Freeman (in the press).
Lagerstrom, M. et al. A deletion in the amelogenin gene (AMG) causes X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta (AIH1). Genomics 10, 971–975 (1991).
Barker, D.F. et al. Further isolation, characterization, and physical localization of X chromosome RFLP markers, comparing VNTR-directed and random isolation strategies. Cytogenet.Cell Genet. 51, 958 (1989).
Yen, P.H., Marsh, B., Mohandas, T.K. & Shapiro, L.J. Isolation of genomic clones homologous to transcribed sequences from the human X chromosome. Som. Cell molec. Genet. 10, 561–571 (1984).
Schneider-Gadicke, A. et al. Putative transcription activator with alternative isoforms encoded by human ZFX gene. Nature 342, 708–711 (1989).
Bardoni, B. et al. Isolation and characterization of a family of sequences dispersed on the human X chromosome. Genomics 3, 32–38 (1988).
Gillard, E.F. et al. Deletion of a DNA sequence in eight of nine families with X-linked ichthyosis (steroid sulfatase deficiency). Nucl. Acids Res. 15, 3977–3985 (1987).
Gibbs, R., Nguyen, P.N., McBride, L.J., Koepf, S.M. & Caskey, C.T. Identification of mutations leading to the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome by automated direct DNA sequencing of in vitro amplified DNA. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 1919–1923 (1989).
Ropers, H.H., Zimmer, J., Strobl, G. & Goodfellow, P., The MIC2X (12E7) locus maps distally from STS on Xp. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 40, 736 (1985).
Wieacker, P., Voiculescu, J., Muller, C.R. & Ropers, H.H. An XX male with a sigle STS gene dose. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 35, 72–74 (1983).
Ballabio, A. et al. Deletion of the distal short arm of the X chromosome (Xp) in a patient with short stature, chondrodysplasia punctata, and X-linked ichthyosis due to steroid sulfatase deficiency. Am. J. med. Genet. 41, 184–187 (1991).
Nishimura, S. et al. Two cases of steroid sulfatase deficiency with complex phenotype due to a contiguous gene deletions. Am. J. med. Genet. 40, 260–263 (1991).
Ballabio, A. et al. X/Y translocation in a family with X-linked ichthyosis, chondrodysplasia punctata, and mental retardation: DNA analysis reveals deletion of the steroid sulfatase gene and translocation of its Y pseudogene. Clin. Genet. 34, 31–37 (1988).
Tiepolo, L. et al. Assignment by deletion mapping of the steroid sulfatase X-linked ichthyosis locus to Xp22.3. Hum. Genet. 54, 205–206 (1980).
Metaxotou, C. et al. A familial X/Y translocation in a boy with ichthyosis, hypogonadism, and mental retardation. Clin. Genet. 24, 380–383 (1983).
Wulfsberg, E.A., Curtis, J. & Jayne, C.H. Chondrodysplasia punctata: A boy with X-linked recessive chondrodysplasia punctata due to an inherited X-Y translocation with a current classification of these disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. 43, 823–828 (1992).
Ballabio, A. et al. X-linked ichthyosis, due to steroid sulfatase deficiency, associated with Kallmann syndrome (hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and anosmia): linkage relationships with Xg and cloned DNA sequences from the distal short arm of the X chromosome. Hum. Genet. 72, 237–240 (1986).
Curry, C.J.R. et al. Inherited chondrodysplasia punctata due to a deletion of the terminal short arm of an X chromosome. New Engl. J. Med. 311, 1010–1014 (1984).
Bick, D. et al. Male infant with ichthyosis, Kallmann syndrome, chondrodysplasia punctata, and an Xp chromosome deletion. Am. J. med. Genet. 33, 100–107 (1989).
Sunohara, N., Sakuragawa, N., Satoyoshi, E., Tanae, A. & Shapiro, L.J. A new syndrome of anosmia, ichthyosis, hypogonadism, and various neurological manifestations with deficiency of steroid sulfatase and arylsulfatase C. Ann. Neurol. 19, 174–181 (1986).
Johnston, K. et al. De novo X;Y translocation associated with imperforate anus and retinal pigmentary abnormalities. Am. J. med. Genet. 27, 603–611 (1987).
Thies, U., Gopal Rao, V.V.N., Engel, W. & Schmidtke, J. Physical mapping of two Xp markers DXS16 and DXS143. Hum. Genet. 86, 418–420 (1990).
Temple, I.K., Hurst, J.A., Hing, S., Butler, L. & Baraitser, M. De novo deletion of Xp22.2-pter in a female with linear skin lesions of the face and neck, microphthalmia, and anterior chamber eye anomalies. J. med. Genet. 27, 56–58 (1990).
Donnenfeld, A.E. et al. Microphthalmia and chorioretinal lesions in a girl with Xp22.2-pter deletion and partial 3p trisomy: clinical observations relevant to Aicardi syndrome gene localization. Am. J. med. Genet. 37, 182–186 (1990).
Al Gazali, L.I. et al. Two 46,XX,t(X;Y) females with linear skin defects and congenital microphthalmia: A new syndrome at Xp22.3. J. med. Genet. 27, 59–63 (1990).
Naritomi, K. et al. Combined Goltz and Aicardi syndromes in a terminal Xp deletion: Are they a contiguous gene syndrome? Am. J. med. Genet. 43, 839–843 (1992).
Ropers, H.H., Zuffardi, O., Bianchi, E. & Tiepolo, L. Agenesis of the corpus callosum, ocular, and skeletal anomalies (X-linked dominant Aicardi's syndrome) in a girl with balanced X/3 translocation. Hum. Genet. 61, 364–368 (1982).
Wang, J.C. et al. Physical mapping of loci in the distal half of the short arm of the human X chromosome: Implications for the spreading of X-chromosome inactivation. Som. Cell molec. Genet. 18, 195–200 (1992).
Couvreur, J.M. et al. Cathepsin E: assignment to chromosome 1 by in situ hybridization and somatic cell hybrid analysis. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 53, 137–139 (1990).
Piombo, G. et al. “Spreading” of inactivation in a case of trisomy 4q from t(Xp;4q)mat. 2nd Natn.Congress of the Italian Federation for the Study of Inherited Disease (FISME). p. 151 (1987).
Worley, K.C. et al. Identification of markers in Xp21 between DXS28 (C7) and DMD. Genomics 13, 957–961 (1992).
Pillers, D.M. et al. Aland island eye disease (Forsius-Eriksson Ocular albinism) and an Xp21 deletion in a patient with Duchenne muscular dystrophy, glycerol kinase deficiency, and congenital adrenal hypoplasia. Am. J. med. Genet. 36, 23–28 (1990).
Towbin, J.A. et al. Characterization of patients with glycerol kinase deficiency utilizing cDNA probes for the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Hum. Genet. 83, 122–126 (1989).
Francke, U. et al. Congenital adrenal hypoplasia, myopathy and glycerol kinase deficiency: molecular genetic evidence for deletions. Am. J. hum. Genet. 40, 212–227 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schaefer, L., Ferrero, G., Grillo, A. et al. A high resolution deletion map of human chromosome Xp22. Nat Genet 4, 272–279 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0793-272
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0793-272
This article is cited by
-
SHOX gene in Leri-Weill syndrome and in idiopathic short stature
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2001)
-
Deletion Pattern of the STS Gene in X-linked Ichthyosis in a Mexican Population
Molecular Medicine (2001)
-
Pseudoautosomal deletions encompassing a novel homeobox gene cause growth failure in idiopathic short stature and Turner syndrome
Nature Genetics (1997)
-
Opitz G/BBB syndrome, a defect of midline development, is due to mutations in a new RING finger gene on Xp22
Nature Genetics (1997)
-
High-resolution mapping by YAC fragmentation of a 2.5-Mb Xp22 region containing the human RS, KFSD and CLS disease genes
Mammalian Genome (1997)