Abstract
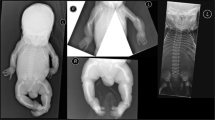
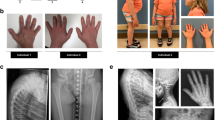
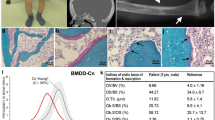
Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome (SGBS) is an X-linked condition characterized by pre-and postnatal overgrowth with visceral and skeletal anomalies. To identify the causative gene, breakpoints in two female patients with X;autosome translocations were identified. The breakpoints occur near the 5′, and 3′, ends of a gene, GPC3, that spans more than 500 kilobases in Xq26; in three families, different microdeletions encompassing exons cosegregate with SGBS. GPC3 encodes a putative extracellular proteoglycan, glypican 3, that is inferred to play an important role in growth control in embryonic mesodermal tissues in which it is selectively expressed. Initial western- and ligand-blotting experiments suggest that glypican 3 forms a complex with insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2), and might thereby modulate IGF2 action.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simpson, J.L., Landey, S., New, M. & German, J. A previously unrecognized X-linked syndrome of dysmorphia.Birth Defects Orig. Art. Ser. XI, 18–24 (1975).
Golabi, M. & Rosen, L. A new X-linked mental retardation-overgrowth syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 17, 345–358 (1984).
Behmel, A., Plochl, E. & Rosenkranz, W. A new X-linked dysplasia gigantism syndrome: identical with the Simpson dysplasia syndrome. Hum. Genet. 67, 409–413 (1984).
Neri, G., Marini, R., Cappa, M., Borrelli, P. & Opitz, J.M. Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome: an X-linked encephalo-trophoschisis syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 30, 287–299 (1988).
Hughes-Benzie, R.M., Hunter, A.G., Allanson, J.E. & MacKenzie, A.E. Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome assoicated with renal dysplasia and embryonal tumors: localization of the gene to Xqcen–q21. Am. J. Med. Genet. 43, 428–435 (1994).
Garganta, L.C. & Bodurtha, J.N. Report of another family with Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome and a review of the literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. 44, 129–135 (1992).
Cohen, M.M., Jr. A comprehensive and critical assessment of overgrowth and overgrowth syndromes. Adv. Hum. Genet. 18, 181–303, 373–376 (1989).
Hughes-Benzie, R.M., Allanson, J., Hunter, A. & Cole, T. The importance of differentiating Simpson-Golabi-Behmel and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndromes. J. Med. Genet. 29, 928 (1992).
Punnett, H.H. Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome (SGBS) in a female with an X-autosome translocation. Am. J. Med. Genet. 50, 391–393 (1994).
Verloes, A., Massart, B., Dehalleux, I., Langhendries, J.P. & Koulischer, L. Clinical overlap of Beckwith-Wiedemann, Periman and Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndromes – a diagnostic pitfall. Clin. Genetics 47, 257–262 (1995).
Collins, F.S. Positional cloning moves from perditional to traditional. Nature Genet. 9, 347–350 (1995).
Little, R.D. et al. Yeast artificial chromosomes spanning 8 Mb and 10–15 centimorgans of human cytogenetic band Xq26(1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.USA 89, 177–181 (1992).
Orth, U. et al. Gene for Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome is linked to HPRT in Xq26 in two European families. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 50, 388–390 (1994).
Xuan, J.Y., Besner, A., Ireland, M., Hughes-Benzie, R.M. & MacKenzie, A.E. Mapping of Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome to Xq25–q27. Hum. Mol. Genet. 3, 133–137 (1994).
Olson, M.V., Hood, L., Cantor, C. & Botstein, D. A common language for physical mapping of the human genome. Science 245, 1434–1435 (1989).
Antequera, F. & Bird, A. Number of CpG islands and genes in human and mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 11995–11999 (1993).
Uberbacher, E.C. & Mural, R.J. Locating protein-coding regions in human DNA sequences by a multiple sensor-neural network approach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 11261–11265 (1991).
D'Esposito, M. et al. PCR-based immortalization and screening of hierarchical pools of cDNAs. Nucl. Acids Res. 22, 4806–4809 (1994).
Kozak, M. An analysis of 5′–noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucl. Acids Res. 15, 8125–6148 (1987).
Pearson, W.R. & Lipman, D.J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 2444–2448 (1988).
Altschul, S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W. & Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403–410 (1990).
Filmus, J., Church, G. & Buick, R.N. Isolation of a cDNA corresponding to a devlopmentally regulated transcript in rat intestine. Mol. Cell. Biol. 8, 4243–4249 (1988).
Stipp, C.S., Litwack, E.D. & Lander, A.D. Molecular cloning of a glypican-related heparan sulfate proteioglycan expressed in the developing rat brain. Mol. Biol. Cell 3, 65a (1992).
David, G. Integral membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans. FASEB J. 7, 1023–1030 (1993).
Mannens, M. et al. Parental imprinting of human chromosome region 11p15.3-pter involved in the Beckwith-Weidemann Syndrome and various human neoplasia. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2, 3–23 (1994).
Hossenlopp, P., Seurin, D., Segovia-Quinson, B., Hardouin, S. & Binoux, M. Analysis of serum insulin-like growth factorbinding proteins using Western blotting: use of the method for trtration of the binding proetins and competitive binding studies. Anal. Biochem. 154, 138–143 (1986).
Shimasaki, S., Shimonaka, M., Zhang, H.-P. & Ling, N. Identification of five different insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) from adult rat serum and molecular cloning of a novel IGFBP-5 in rat and human. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 10646–10653 (1991).
Lories, V., De Boeck, H., David, G., Cassiman, J.J. & Van Den Berghe, H. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans of human lung fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 854–859 (1987).
Willard, H.F. et al. Report of the Fifth International Workshop on Human X Chromosome Mapping. Cytogenet. Cell Genet 67, 295–358 (1994).
Vermeesch, J.R., Mertens, G., David, G. & Marynen, P. Assignment of the human glypican gene (GPC1) to 2q35–q37 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genomics 25, 327–329 (1995).
Lindlof, M. et al. Gene deletions in X-linked muscular dystrophy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 44, 496–503 (1989).
Schlessinger, J., Lax, I. & Lemmon, M. Regulation of growth factor activation by proteoglycans: what is the role of the low affintiy receptors? Cell 83, 357–360 (1995).
Green, P.J., Ferguson, M.A.J., Robinson, P.J. & Feizi, T. The cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor binds to soluble GPI-linked proteins via mannose-6-phosphate. FEBS Lett. 360, 384–389 (1995).
Baker, J., Liu, J.-P., Robertson, E.J. & Efstratiadis, A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell 75, 73–82 (1993).
Lau, M.M.H. et al. Loss of the imprinted IGF2/cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor results in fetal overgrowth and perinatal lethality. Genes Dev. 8, 2953–2963 (1994).
Wang, Z.-Q., Fung, M.R., Barlow, D.P. & Wagner, E.F. Regulation of embryonic growth and lysosomal targeting by the imprinted Igf2/Mpr gene. Nature 372, 464–467 (1994).
Blanchard, M.M., Taillon-Miller, P., Nowotny, P. & Nowotny, V. PCR-buffer optimization with uniform temperature regimen to facilitate automation. PCR Meth. Appl. 2, 234–240 (1992).
Burke, D.T., Carle, G.F. & Olson, M.V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science 236, 806–812 (1987).
Chen, E.Y. et al.Sequence of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase cloned in plasmids and a yeast artificial chromosome (YAC). Genomics 10, 792–600 (1991).
Ledbetter, S.A., Schwartz, C.E., Davies, K.E. & Ledbetter, D.H. New somatic cell hybrids for physical mapping in distal Xq and the Fragile X region. Am. J. Med. Genet. 38, 418–420 (1991).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, L. & Maniatis, T., l, 2nd ed. (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, 1989).
Posnett, D.N., McGrath, H. & Tam, J.P. A novel method for producing anti-peptide antibodies Production of site-specific antibodies to the T cell antigen receptor beta-chain. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 1719–1725 (1988).
Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685 (1970).
Program Manual for the GCG Package, Version 7,575 Science Drive, Madison, Wisconsin, USA 53711. (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pilia, G., Hughes-Benzie, R., MacKenzie, A. et al. Mutations in GPC3, a glypican gene, cause the Simpson-Golabi-Behmel overgrowth syndrome. Nat Genet 12, 241–247 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0396-241
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0396-241
This article is cited by
-
Precocious puberty in a case of Simpson–Golabi–Behmel syndrome with a de novo 240-kb deletion including GPC3
Human Genome Variation (2022)
-
The Treatment Landscape of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Current Oncology Reports (2022)
-
GPC3 affects the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma
BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2021)
-
Overexpression of Annexin A2 promotes proliferation by forming a Glypican 1/c-Myc positive feedback loop: prognostic significance in human glioma
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Rapamycin inhibits lung squamous cell carcinoma growth by downregulating glypican-3/Wnt/β-catenin signaling and autophagy
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2021)