Abstract
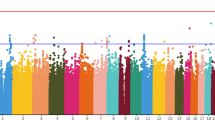
A whole genome association study was performed in a phase 3 clinical trial conducted to evaluate a novel antipsychotic, iloperidone, administered to treat patients with schizophrenia. Genotypes of 407 patients were analyzed for 334 563 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). SNPs associated with iloperidone efficacy were identified within the neuronal PAS domain protein 3 gene (NPAS3), close to a translocation breakpoint site previously observed in a family with schizophrenia. Five other loci were identified that include the XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 4 gene (XKR4), the tenascin-R gene (TNR), the glutamate receptor, inotropic, AMPA 4 gene (GRIA4), the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor receptor-alpha2 gene (GFRA2), and the NUDT9P1 pseudogene located in the chromosomal region of the serotonin receptor 7 gene (HTR7). The study of these polymorphisms and genes may lead to a better understanding of the etiology of schizophrenia and of its treatment. These results provide new insight into response to iloperidone, developed with the ultimate goal of directing therapy to patients with the highest benefit-to-risk ratio.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, 2000.
Bondy B, Spellmann I . Pharmacogenetics of antipsychotics: useful for the clinician? Curr Opin Psychiatry 2007; 20: 126–130.
Reynolds GP, Templeman LA, Godlewska BR . Pharmacogenetics of schizophrenia. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2006; 7: 1429–1440.
Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, Perkins DO et al. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1209–1223.
Kane JM, Malhotra A . The future of pharmacotherapy for schizophrenia. World Psychiatry 2003; 2: 81–86.
Kalkman HO, Subramanian N, Hoyer D . Extended radioligand binding profile of iloperidone: a broad spectrum dopamine/serotonin/norepinephrine receptor antagonist for the management of psychotic disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001; 25: 904–914.
Kalkman HO, Feuerbach D, Lotscher E, Schoeffter P . Functional characterization of the novel antipsychotic iloperidone at human D2, D3, alpha 2C, 5-HT6, and 5-HT1A receptors. Life Sci 2003; 73: 1151–1159.
Richelson E, Souder T . Binding of antipsychotic drugs to human brain receptors focus on newer generation compounds. Life Sci 2000; 68: 29–39.
Ichikawa J, Meltzer HY . Relationship between dopaminergic and serotonergic neuronal activity in the frontal cortex and the action of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 1999; 249 (Suppl 4): 90–98.
Jain KK . An assessment of iloperidone for the treatment of schizophrenia. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2000; 9: 2935–2943.
Cutler AJ, Kalali AH, Weiden P, Hamilton J, Wolfgang CD . Four-week, double-blind, placebo- and ziprasidone-controlled trial of iloperidone in patients with acute exacerbations of schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2008; 28 (Suppl 1): S20–S28.
Weiden PJ, Cutler A, Polymeropoulos MH, Wolfgang CD . Safety profile of iloperidone: a pooled analysis of 6-week acute-phase pivotal trials. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2008; 28 (Suppl 1): S12–S19.
Baroldi P, Wolfgang C . A Pharmacokinetic (PK)-Pharmacodynamic (PD) Relationship Exists for Efficacy of Iloperidone, a Novel Investigational Atypical Antipsychotic Agent. American Psychiatric Association 2007 Meeting POSTER NR507—available at: http://www.psych.org/edu/other_res/lib_archives/archives/meetings/AMN/2007nra.pdf.
Verbeke G, Molenberghs G . Linear Mixed Models for Longitudinal Data. Springer: New York, 2000.
Little RJA, Rubin DB . Statistical Analysis with Missing Data, 2nd edn. Wiley: New York, 2003.
Molenberghs G, Thijs H, Jansen I, Beunckens C, Kenward MG, Mallinck-rodt C et al. Analyzing incomplete longitudinal clinical trial data. Biostatistics 2004; 5: 445–464.
Cook RJ, Zeng L, Yi Y . Marginal analysis of incomplete longitudinal binary data: a cautionary note on LOCF imputation. Biometrics 2004; 60: 820–828.
Mallinckrodt CH, Clark WS, David SR . Accounting for dropout bias using mixed-effects models. J Biopharm Stat 2001; 11: 9–21.
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P . Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000; 2: 945–959.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y . Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc 1995; 57: 289–300.
Kukreti R, Tripathi S, Bhatnagar P, Gupta S, Chauhan C, Kubendran S et al. Association of DRD2 gene variant with schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 2006; 392: 68–71.
Bishop JR, Ellingrod VL, Moline J, Miller D . Association between the polymorphic GRM3 gene and negative symptom improvement during olanzapine treatment. Schizophr Res 2005; 77: 253–260.
Fallin MD, Lasseter VK, Avramopoulos D, Nicodemus KK, Wolyniec PS, McGrath JA et al. Bipolar I disorder and schizophrenia: a 440-single-nucleotide polymorphism screen of 64 candidate genes among Ashkenazi Jewish case-parent trios. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 77: 918–936.
Lee HJ, Song JY, Kim JW, Jin S-Y, Hong MS, Park JK et al. Association study of polymorphisms in synaptic vesicle-associated genes, SYN2 and CPLX2, with schizophrenia. Behav Brain Funct 2005; 1: 15.
Hamajima N, Matsuo K, Tajima K, Mizutani M, Iwata H, Iwase T et al. Limited association between a catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) polymorphism and breast cancer risk in Japan. Int J Clin Oncol 2001; 6: 13–18.
Ronai Z, Barta C, Guttman A, Lakatos K, Gervai J, Staub M et al. Genotyping the –521C/T functional polymorphism in the promoter region of dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4) gene. Electrophoresis 2001; 22: 1102–1105.
Huang YY, Battistuzzi C, Oquendo MA, Harkavy-Friedman J, Greenhill L, Zalsman G et al. Human 5-HT1A receptor C(–1019)G polymorphism and psychopathology. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2004; 7: 441–451.
Joober R, Benkelfat C, Brisebois K, Toulouse A, Turecki G, Lal S et al. T102C polymorphism in the 5-HT2A gene and schizophrenia: relation to phenotype and drug response variability. J Psychiatry Neurosci 1999; 24: 141–146.
Di X, Matsuzaki H, Webster TA, Hubbell E, Liu G, Dong S et al. Dynamic model based algorithms for screening and genotyping over 100 K SNPs on oligonucleotide microarrays. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 1958–1963.
BRLMM: an improved genotype calling method for the GeneChip® Human Mapping 500 K Array Set. Affymetrix Web site. Available at: http://www.affymetrix.com/support/technical/whitepapers/brlmm_whitepaper.pdf (accessed 26 July).
Murabito JM, Rosenberg CL, Finger D, Kreger BE, Levy D, Splansky GL et al. A genome-wide association study of breast and prostate cancer in the NHLBI's Framingham Heart Study. BMC Med Genet 2007; 8 (Suppl 1): S6.
Newton-Cheh C, Guo CY, Wang TJ, O’donnell CJ, Levy D, Larson MG . Genome-wide association study of electrocardiographic and heart rate variability traits: the Framingham Heart Study. BMC Med Genet 2007; 8 (Suppl 1): S7.
Gottlieb DJ, O’Connor GT, Wilk JB . Genome-wide association of sleep and circadian phenotypes. BMC Med Genet 2007; 8 (Suppl 1): S9.
Arking DE, Pfeufer A, Post W, Kao WHL, Newton-Cheh C, Ikeda M et al. A common genetic variant in the NOS1 regulator NOS1AP modulates cardiac repolarization. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 644–651.
Kamnasaran D, Muir WJ, Ferguson-Smith MA, Cox DW . Disruption of the neuronal PAS3 gene in a family affected with schizophrenia. J Med Genet 2003; 40: 325–332.
Calenda G, Peng J, Redman CM, Sha Q, Wu X, Lee S . Identification of two new members, XPLAC and XTES, of the XK family. Gene 2006; 370: 6–16.
Jung HH, Haker H . Schizophrenia as a manifestation of X-linked McLeod-Neuroacanthocytosis syndrome. J Clin Psychiatry 2004; 65: 722–723.
Wu C-Y, Chiu C-C . Usher syndrome with psychotic symptoms: two cases in the same family. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2006; 60: 626–628.
Carnemolla B, Leprini A, Borsi L, Querze G, Urbini S, Zardi L . Human tenascin-R: complete primary structure, pre-mRNA alternative splicing and gene localization on chromosome 1q23-q24. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 8157–8160.
Leprini A, Gherzi R, Siri A, Querze G, Viti F, Zardi L . The human tenascin-R gene. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 31251–31254.
Wei J, Hemmings GP . TNXB locus may be a candidate gene predisposing to schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2004; 125B: 43–49.
Makino C, Fujii Y, Kikuta R, Hirata N, Tani A, Shibata A et al. Positive association of the AMPA receptor subunit GluR4 gene (GRIA4) haplotype with schizophrenia: linkage disequilibrium mapping using SNPs evenly distributed across the gene region. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2003; 116B: 17–22.
Blaveri E, Kalsi G, Lawrence J, Quested D, Moorey H, Lamb G et al. Genetic association studies of schizophrenia using the 8p21-22 genes: prepronociceptin (PNOC), neuronal nicotinic cholinergic receptor alpha polypeptide 2 (CHRNA2) and arylamine N-acetyltransferase 1 (NAT1). Eur J Hum Genet 2001; 9: 469–472.
Blouin JL, Dombroski BA, Nath SK, Lasseter VK, Wolyniec PS, Nestadt G et al. Schizophrenia susceptibility loci on chromosomes 13q32 and 8p21. Nat Genet 1998; 20: 70–73.
Stefansson H, Sigurdsson E, Steinthorsdottir V, Bjornsdottir S, Sigmundsson T, Ghosh S et al. Neuregulin 1 and susceptibility to schizophrenia. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 877–892.
Michelato A, Bonvicini C, Ventriglia M, Scassellati C, Randazzo R, Bignotti S et al. 3′ UTR (AGG)n repeat of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) gene polymorphism in schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 2004; 357: 235–237.
Ikeda M, Iwata N, Kitajima T, Suzuki T, Yamanouchi Y, Kinoshita Y et al. Positive association of the serotonin 5-HT7 receptor gene with schizophrenia in a Japanese population. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006; 31: 866–871.
Moises HW, Yang L, Kristbjarnarson H, Wiese C, Byerley W, Macciardi F et al. An international two-stage genome-wide search for schizophrenia susceptibility genes. Nat Genet 1995; 11: 321–324.
Pieper AA, Wu X, Han TW, Estill SJ, Dang Q, Wu LC et al. The neuronal PAS domain protein 3 transcription factor controls FGF-mediated adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 14052–14057.
Erbel-Sieler C, Dudley C, Zhou Y, Wu X, Estill SJ, Han T et al. Behavioral and regulatory abnormalities in mice deficient in the NPAS1 and NPAS3 transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 13648–13653.
Goldberger C, Gourion D, Leroy S, Schurhoff F, Bourdel M-C, Leboyer M et al. Population-based and family-based association study of 5′UTR polymorphism of the reelin gene and schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2005; 137B: 51–55.
Impagnatiello F, Guidotti AR, Pesold C, Dwivedi Y, Caruncho H, Pisu MG et al. A decrease of reelin expression as a putative vulnerability factor in schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 15718–15723.
Guo S, Shi Y, Zhao X, Duan S, Zhou J, Meng J et al. No genetic association between polymorphisms in the AMPA receptor subunit GluR4 gene (GRIA4) and schizophrenia in the Chinese population. Neurosci Lett 2004; 369: 168–172.
Stone JM, Morrison PD, Pilowsky LS . Glutamate and dopamine dysregulation in schizophrenia—a synthesis and selective review. J Psychopharmacol 2007; 21: 440–452.
Semba J, Akanuma N, Wakuta M, Tanaka N, Suhara T . Alterations in the expressions of mRNA for GDNF and its receptors in the ventral midbrain of rats exposed to subchronic phencyclidine. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2004; 124: 88–95.
Kongsamut S, Roehr JE, Cai J, Hartman HB, Weissensee P, Kerman LL et al. Iloperidone binding to human and rat dopamine and 5-HT receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 1996; 317: 417–423.
Forton JT, Udalova IA, Campino S, Rockett KA, Hull J, Kwiatkowski DP . Localization of a long-range cis-regulatory element of IL13 by allelic transcript ratio mapping. Genome Res 2007; 17: 82–87.
Woolfe A, Goodson M, Goode DK, Snell P, McEwen GK, Vavouri T et al. Highly conserved non-coding sequences are associated with vertebrate development. PLoS Biol 2005; 3: e7.
Washietl S, Hofacker IL, Lukasser M, Huttenhofer A, Stadler PF . Mapping of conserved RNA secondary structures predicts thousands of functional noncoding RNAs in the human genome. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 1383–1390.
Arranz MJ, de Leon J . Pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics of schizophrenia: a review of last decade of research. Mol Psychiatry 2007; 8: 707–747.
Acknowledgements
We thank all of the patients who participated in this study. We also thank Michael Di Marino and Ingeborg Holt for their assistance in the statistical analysis and Kelly Greer for her technical support. We are grateful to Dr Yoav Benjamini and Chip Clark for their critical reviews of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interests
All authors are employees of Vanda Pharmaceuticals Inc. and have no additional affiliations or financial interests to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lavedan, C., Licamele, L., Volpi, S. et al. Association of the NPAS3 gene and five other loci with response to the antipsychotic iloperidone identified in a whole genome association study. Mol Psychiatry 14, 804–819 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2008.56
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2008.56
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Ethnic Differences in Antipsychotic Response: What Genetic Variation Does and Does Not Tell Us
Current Behavioral Neuroscience Reports (2023)
-
Family-effects in the epigenomic response of red blood cells to a challenge test in the European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.)
BMC Genomics (2021)
-
Gene expression and response prediction to amisulpride in the OPTiMiSE first episode psychoses
Neuropsychopharmacology (2020)
-
De novo single-nucleotide and copy number variation in discordant monozygotic twins reveals disease-related genes
European Journal of Human Genetics (2019)
-
Pathogenic variants in E3 ubiquitin ligase RLIM/RNF12 lead to a syndromic X-linked intellectual disability and behavior disorder
Molecular Psychiatry (2019)