Abstract
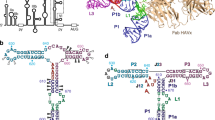
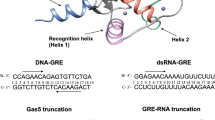
The family of interferon regulatory factor (IRF) transcription factors is important in the regulation of interferons in response to infection by virus and in the regulation of interferon-inducible genes1,2. The IRF family is characterized by a unique ‘tryptophan cluster’ DNA-binding region. Here we report the crystal structure of the IRF-1 region bound to the natural positive regulatory domain I (PRD I) DNA element from the interferon-β promoter1. The structure provides the first three-dimensional view of a member of the growing IRF family, revealing a new helix–turn–helix motif that latches onto DNA through three of the five conserved tryptophans. The motif selects a short GAAA core sequence through an obliquely angled recognition helix, with an accompanying bending of the DNA axis in the direction of the protein. Together, these features suggest a basis for the occurrence of GAAA repeats within IRF response elements and provide clues to the assembly of the higher-order interferon-β enhancesome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maniatis, T. et al. in Transcriptional Regulation (eds McKnight, S. & Yamamoto, K.) 1993–1220 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, (1992)).
Taniguchi, T., Harada, H. & Lamphier, M. Regulation of the interferon system and cell growth by the IRF transcription factors. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 121, 516–520 (1995).
Thanos, D. & Maniatis, T. Virus induction of human IFNβ gene expression requires the assembly of an enhanceosome. Cell 83, 1091–1100 (1995).
Miyamoto, M. et al. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to the IFN-β gene regulatory elements. Cell 54, 903–913 (1988).
Harada, H. et al. Structurally similar but functionally distinct factors, IRF-1 and IRF-2, bind to the same regulatory elements of IFN and IFN-inducible genes. Cell 58, 729–739 (1989).
Driggers, P. H. et al. An interferon-γ regulated protein that binds the interferon-inducible element of the major histocompatibility class I genes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 87, 3743–3747 (1990).
Veals, S. A. et al. Subunit of an alpha-interferon-responsive transcription factor is related to interferon regulatory factor and Myb families of DNA binding proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12, 3315–3324 (1992).
Au, W. C., Moore, P. A., Lowther, W., Juang, Y. T. & Pitha, P. M. Identification of a member of the interferon regulatory factor family that binds to the interferon-stimulated response element and activates expression of interferon-induced genes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 11657–11661 (1995).
Eisenbeis, C. F., Singh, H. & Storb, U. Pip, a novel IRF family member, is a lymphoid-specific, PU.1-dependent transcriptional activator. Genes Dev. 9, 1377–1387 (1995).
Schultz, S. C., Shields, G. C. & Steitz, T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science 253, 1001–1007 (1991).
Ramakrishnan, V., Finch, J. T., Graziano, V., Lee, P. L. & Sweet, R. M. Crystal structure of globular domain of histone H5 and its implications for nucleosome binding. Nature 362, 219–223 (1993).
Clark, K. L., Halay, E. D., Lai, E. & Burley, S. K. Co-crystal structure of the HNF-3/fork head DNA-recognition motif resembles histone H5. Nature 364, 412–420 (1993).
Harrison, S. C. & Aggarwal, A. K. DNA recognition by proteins with the helix-turn-helix motif. A. Rev. Biochem. 59, 933–969 (1990).
Ferre-D'Amare, A. R., Prendergast, G. C., Ziff, E. B. & Burley, S. K. Recognition by Max of its cognate DNA through a dimeric b/HLH/Z domain. Nature 363, 38–45 (1993).
Kawakami, T. et al. Possible involvement of the transcription factor ISGF3 gamma in virus-induced expression of the IFN-beta gene. FEBS Lett. 358, 225–229.
Aggarwal, A. K., Rodgers, D. W., Drottar, M., Ptashne, M. & Harrison, S. C. Recognition of a DNA operator by repressor of phage 434: a view at high resolution. Science 242, 899–907 (1988).
Cho, Y., Gorina, S., Jeffrey, P. D. & Pavletich, N. P. Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science 265, 346–355 (1994).
Darnell, J. E. J, Kerr, I. M. & Stark, G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signalling proteins. Science 264, 1415–1421 (1994).
Spolar, R. S. & Record, M. T. Coupling of local folding to site-specific binding of proteins to DNA. Science 263, 777–784 (1994).
Lavery, R. & Sklenar, H. The definition of generalized helicoidal parameters and of axis curvature for irregular nucleic acids. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 6, 63–91 (1988).
Falvo, J. V., Thanos, D. & Maniatis, T. Reversal of intrinsic DNA bends in the IFNβ gene enhancer by transcription factors and the architectural protein HMG I(Y). Cell 83, 1101–1111 (1995).
Ghosh, G., Van Duyne, G., Ghosh, S. & Sigler, P. B. The structure of NF-κB p50 homodimer bound to a κB site. Nature 373, 303–310 (1995).
Muller, C. W., Rey, F. A., Sodeoka, M., Verdine, G. L. & Harrison, S. C. Structure of the NF-κB p50 homodimer bound to DNA. Nature 373, 311–317 (1995).
Horvarth, C. M., Stark, G. R., Kerr, I. M. & Darnell, J. E. J Interactions between STAT and non-STAT proteins in the interferon stimulated gene factor 3 transcription complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 6957–6964 (1996).
Escalante, C. R., Yie, J., Thanos, D. & Aggarwal, A. K. Expressions, purification, and co-crystallization of IRF-1 bound to the interferon-β element PRD I. FEBS Lett. 414, 219–220 (1997).
Hendrickson, W. A. Determination of macromolecular structures from anomalous diffraction of synchrotron radiation. Science 254, 51–58 (1991).
Furey, W. Phases: A Program Package for the Processing and Analysis of Diffraction Data for Macromolecules (VA Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA, (1993)).
Brunger, A. T. X-PLOR, Version 3.1, A System for X-ray Crystallography and NMR (Yale Univ. Press, New Haven, (1992)).
Jones, A. T., Zou, J. Y., Cowan, S. W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A47, 110–119 (1991).
Uegaki, K., Shirakawa, M., Harada, H., Taniguchi, T. & Kyogoku, Y. Secondary structure and folding topology of the DNA binding domain of interferon regulatory factor 2, as revealed by NMR spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 359, 184–188 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff at CHESS for facilitating data collection, E. Jacobson, H. Viadiu and D. Wah for help with data collection, G. Mogilnitskiy for technical assistance, L. Shapiro and H. Weinstein for comments on the manuscript. Coordinates have been deposited in the Brookhaven Protein Database. Accession number 1IF1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Escalante, C., Yie, J., Thanos, D. et al. Structure of IRF-1 with bound DNA reveals determinants of interferon regulation. Nature 391, 103–106 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/34224
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/34224
This article is cited by
-
Molecular identification and functional characterization of IRF4 from common carp (Cyprinus carpio. L) in immune response: a negative regulator in the IFN and NF-κB signalling pathways
BMC Veterinary Research (2022)
-
Functional characterization of goose IRF1 in IFN induction and anti-NDV infection
Veterinary Research (2022)
-
Molecular interactions of IRF4 in B cell development and malignancies
Biophysical Reviews (2021)
-
Identification of an IRF10 gene in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) and analysis of its function in the antiviral and antibacterial immune response
BMC Veterinary Research (2020)
-
Conserved, breed-dependent, and subline-dependent innate immune responses of Fayoumi and Leghorn chicken embryos to Newcastle disease virus infection
Scientific Reports (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.