Abstract
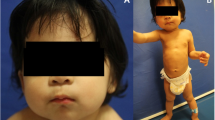
Congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV) is one of the most common musculoskeletal disorders. Genetic factors have been suggested to be an important contributor to its pathogenesis. Some genes, including PITX1, TBX4, and RBM10, have been associated with CTEV. We aimed to determine the disease-causing mutations in Chinese patients with isolated CTEV. Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood samples of a three-generation pedigree and 53 sporadic patients with CTEV. Whole-exome sequencing and Sanger sequencing were used to identify and validate disease-causing mutations, respectively. A putative pathogenic mutation c.4717G>T (p.D1573Y) in the filamin B (FLNB) gene, which co-segregated with CETV, was identified in the pedigree. Two additional novel missense mutations in the same gene [c.1897A>G (p.M633V) and c.2195A>G (p.Y732C)] were identified from the 53 sporadic patients. Plasmids expressing wild-type or mutant constructs were transfected into HEK293T cells to determine whether these amino acid substitutions affect protein activity. All three (M633V, Y732C, and D1573Y) affected FLNB protein expression and led to cytoplasmic focal accumulation. Our results provide evidence for the involvement of FLNB in the pathogenesis of isolated CTEV and have expanded the clinical spectrum of FLNB mutations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacino CA, Hecht JT (2014) Etiopathogenesis of equinovarus foot malformations. Eur J Med Genet 57:473–479. doi:10.1016/j.ejmg.2014.06.001
Bicknell LS, Morgan T, Bonafe L, Wessels MW, Bialer MG, Willems PJ, Cohn DH, Krakow D, Robertson SP (2005) Mutations in FLNB cause boomerang dysplasia. J Med Genet 42:e43. doi:10.1136/jmg.2004.029967
Bicknell LS, Farrington-Rock C, Shafeghati Y, Rump P, Alanay Y, Alembik Y, Al-Madani N, Firth H, Karimi-Nejad MH, Kim CA, Leask K, Maisenbacher M, Moran E, Pappas JG, Prontera P, de Ravel T, Fryns JP, Sweeney E, Fryer A, Unger S, Wilson LC, Lachman RS, Rimoin DL, Cohn DH, Krakow D, Robertson SP (2007) A molecular and clinical study of Larsen syndrome caused by mutations in FLNB. J Med Genet 44:89–98. doi:10.1136/jmg.2006.043687
Calvo SE, Compton AG, Hershman SG, Lim SC, Lieber DS, Tucker EJ, Laskowski A, Garone C, Liu S, Jaffe DB, Christodoulou J, Fletcher JM, Bruno DL, Goldblatt J, Dimauro S, Thorburn DR, Mootha VK (2012) Molecular diagnosis of infantile mitochondrial disease with targeted next-generation sequencing. Sci Transl Med 4:118ra10. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3003310
Coste B, Houge G, Murray MF, Stitziel N, Bandell M, Giovanni MA, Philippakis A, Hoischen A, Riemer G, Steen U, Steen VM, Mathur J, Cox J, Lebo M, Rehm H, Weiss ST, Wood JN, Maas RL, Sunyaev SR, Patapoutian A (2013) Gain-of-function mutations in the mechanically activated ion channel PIEZO2 cause a subtype of Distal Arthrogryposis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:4667–4672. doi:10.1073/pnas.1221400110
Daniel PB, Morgan T, Alanay Y, Bijlsma E, Cho TJ, Cole T, Collins F, David A, Devriendt K, Faivre L, Ikegawa S, Jacquemont S, Jesic M, Krakow D, Liebrecht D, Maitz S, Marlin S, Morin G, Nishikubo T, Nishimura G, Prescott T, Scarano G, Shafeghati Y, Skovby F, Tsutsumi S, Whiteford M, Zenker M, Robertson SP (2012) Disease-associated mutations in the actin-binding domain of filamin B cause cytoplasmic focal accumulations correlating with disease severity. Hum Mutat 33:665–673. doi:10.1002/humu.22012
de Ligt J, Willemsen MH, van Bon BW, Kleefstra T, Yntema HG, Kroes T, Vulto-van Silfhout AT, Koolen DA, de Vries P, Gilissen C, del Rosario M, Hoischen A, Scheffer H, de Vries BB, Brunner HG, Veltman JA, Vissers LE (2012) Diagnostic exome sequencing in persons with severe intellectual disability. N Engl J Med 367:1921–1929. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1206524
De Marco P, Merello E, Rossi A, Piatelli G, Cama A, Kibar Z, Capra V (2012) FZD6 is a novel gene for human neural tube defects. Hum Mutat 33:384–390. doi:10.1002/humu.21643
DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, Garimella KV, Maguire JR, Hartl C, Philippakis AA, del Angel G, Rivas MA, Hanna M, McKenna A, Fennell TJ, Kernytsky AM, Sivachenko AY, Cibulskis K, Gabriel SB, Altshuler D, Daly MJ (2011) A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet 43:491–498. doi:10.1038/ng.806
Dixon-Salazar TJ, Silhavy JL, Udpa N, Schroth J, Bielas S, Schaffer AE, Olvera J, Bafna V, Zaki MS, Abdel-Salam GH, Mansour LA, Selim L, Abdel-Hadi S, Marzouki N, Ben-Omran T, Al-Saana NA, Sonmez FM, Celep F, Azam M, Hill KJ, Collazo A, Fenstermaker AG, Novarino G, Akizu N, Garimella KV, Sougnez C, Russ C, Gabriel SB, Gleeson JG (2012) Exome sequencing can improve diagnosis and alter patient management. Sci Transl Med 4:138ra78. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3003544
Farrington-Rock C, Firestein MH, Bicknell LS, Superti-Furga A, Bacino CA, Cormier-Daire V, Le Merrer M, Baumann C, Roume J, Rump P, Verheij JB, Sweeney E, Rimoin DL, Lachman RS, Robertson SP, Cohn DH, Krakow D (2006) Mutations in two regions of FLNB result in atelosteogenesis I and III. Hum Mutat 27:705–710. doi:10.1002/humu.20348
Farrington-Rock C, Kirilova V, Dillard-Telm L, Borowsky AD, Chalk S, Rock MJ, Cohn DH, Krakow D (2008) Disruption of the Flnb gene in mice phenocopies the human disease spondylocarpotarsal synostosis syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 17:631–641. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddm188
Golan T, Yaniv A, Bafico A, Liu G, Gazit A (2004) The human Frizzled 6 (HFz6) acts as a negative regulator of the canonical Wnt. beta-catenin signaling cascade. J Biol Chem 279:14879–14888. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306421200
Gurnett CA, Alaee F, Kruse LM, Desruisseau DM, Hecht JT, Wise CA, Bowcock AM, Dobbs MB (2008) Asymmetric lower-limb malformations in individuals with homeobox PITX1 gene mutation. Am J Hum Genet 83:616–622. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.10.004
Hall JG (1997) Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita: etiology, genetics, classification, diagnostic approach, and general aspects. J Pediatr Orthop Part B 6:159–166
Honein MA, Paulozzi LJ, Mathews TJ, Erickson JD, Wong LY (2001) Impact of folic acid fortification of the US food supply on the occurrence of neural tube defects. JAMA 285:2981–2986
Hu J, Lu J, Lian G, Zhang J, Hecht JL, Sheen VL (2014) Filamin B regulates chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation through Cdk1 signaling. PLoS One 9:e89352. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0089352
Jeon GW, Lee MN, Jung JM, Hong SY, Kim YN, Sin JB, Ki CS (2014) Identification of a de novo heterozygous missense FLNB mutation in lethal atelosteogenesis type I by exome sequencing. Ann Lab Med 34:134–138. doi:10.3343/alm.2014.34.2.134
Koboldt DC, Chen K, Wylie T, Larson DE, McLellan MD, Mardis ER, Weinstock GM, Wilson RK, Ding L (2009) VarScan: variant detection in massively parallel sequencing of individual and pooled samples. Bioinformatics 25:2283–2285. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp373
Krakow D, Robertson SP, King LM, Morgan T, Sebald ET, Bertolotto C, Wachsmann-Hogiu S, Acuna D, Shapiro SS, Takafuta T, Aftimos S, Kim CA, Firth H, Steiner CE, Cormier-Daire V, Superti-Furga A, Bonafe L, Graham JM Jr, Grix A, Bacino CA, Allanson J, Bialer MG, Lachman RS, Rimoin DL, Cohn DH (2004) Mutations in the gene encoding filamin B disrupt vertebral segmentation, joint formation and skeletogenesis. Nat Genet 36:405–410. doi:10.1038/ng1319
Kruse LM, Dobbs MB, Gurnett CA (2008) Polygenic threshold model with sex dimorphism in clubfoot inheritance: the Carter effect. J Bone Joint Surg 90:2688–2694. doi:10.2106/JBJS.G.01346
Li H, Durbin R (2010) Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 26:589–595. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp698
Li BC, Hogue J, Eilers M, Mehrotra P, Hyland J, Holm T, Prosen T, Slavotinek AM (2013) Clinical report: two patients with atelosteogenesis type I caused by missense mutations affecting the same FLNB residue. Am J Med Genet A 161A:619–625. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.35792
Lochmiller C, Johnston D, Scott A, Risman M, Hecht JT (1998) Genetic epidemiology study of idiopathic talipes equinovarus. Am J Med Genet 79:90–96
Logan M, Tabin CJ (1999) Role of Pitx1 upstream of Tbx4 in specification of hindlimb identity. Science 283:1736–1739
Lu J, Lian G, Lenkinski R, De Grand A, Vaid RR, Bryce T, Stasenko M, Boskey A, Walsh C, Sheen V (2007) Filamin B mutations cause chondrocyte defects in skeletal development. Hum Mol Genet 16:1661–1675. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddm114
Lu W, Bacino CA, Richards BS, Alvarez C, VanderMeer JE, Vella M, Ahituv N, Sikka N, Dietz FR, Blanton SH, Hecht JT (2012) Studies of TBX4 and chromosome 17q23.1q23.2: an uncommon cause of nonsyndromic clubfoot. Am J Med Genet A 158A:1620–1627. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.35418
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristo MA (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303. doi:10.1101/gr.107524.110
Miedzybrodzka Z (2003) Congenital talipes equinovarus (clubfoot): a disorder of the foot but not the hand. J Anat 202:37–42
Mizuhashi K, Kanamoto T, Moriishi T, Muranishi Y, Miyazaki T, Terada K, Omori Y, Ito M, Komori T, Furukawa T (2014) Filamin-interacting proteins, Cfm1 and Cfm2, are essential for the formation of cartilaginous skeletal elements. Hum Mol Genet 23:2953–2967. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu007
Need AC, Shashi V, Hitomi Y, Schoch K, Shianna KV, McDonald MT, Meisler MH, Goldstein DB (2012) Clinical application of exome sequencing in undiagnosed genetic conditions. J Med Genet 49:353–361. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2012-100819
Pirani S, Zeznik L, Hodges D (2001) Magnetic resonance imaging study of the congenital clubfoot treated with the Ponseti method. J Pediatr Orthop 21:719–726
Skelly AC, Holt VL, Mosca VS, Alderman BW (2002) Talipes equinovarus and maternal smoking: a population-based case-control study in Washington state. Teratology 66:91–100. doi:10.1002/tera.10071
Sommer A, Blanton SH, Weymouth K, Alvarez C, Richards BS, Barnes D, Hecht JT (2011) Smoking, the xenobiotic pathway, and clubfoot. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 91:20–28. doi:10.1002/bdra.20742
Stossel TP, Condeelis J, Cooley L, Hartwig JH, Noegel A, Schleicher M, Shapiro SS (2001) Filamins as integrators of cell mechanics and signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:138–145. doi:10.1038/35052082
van der Flier A, Sonnenberg A (2001) Structural and functional aspects of filamins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1538:99–117
Wynne-Davies R (1972) Genetic and environmental factors in the etiology of talipes equinovarus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 84:9–13
Yang Y, Muzny DM, Reid JG, Bainbridge MN, Willis A, Ward PA, Braxton A, Beuten J, Xia F, Niu Z, Hardison M, Person R, Bekheirnia MR, Leduc MS, Kirby A, Pham P, Scull J, Wang M, Ding Y, Plon SE, Lupski JR, Beaudet AL, Gibbs RA, Eng CM (2013) Clinical whole-exome sequencing for the diagnosis of mendelian disorders. N Engl J Med 369:1502–1511. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1306555
Zhang D, Herring JA, Swaney SS, McClendon TB, Gao X, Browne RH, Rathjen KE, Johnston CE, Harris S, Cain NM, Wise CA (2006) Mutations responsible for Larsen syndrome cluster in the FLNB protein. J Med Genet 43:e24. doi:10.1136/jmg.2005.038695
Zheng Z, Geng J, Yao RE, Li C, Ying D, Shen Y, Ying L, Yu Y, Fu Q (2013) Molecular defects identified by whole exome sequencing in a child with Fanconi anemia. Gene 530:295–300. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.031
Zhou X, Tian F, Sandzen J, Cao R, Flaberg E, Szekely L, Cao Y, Ohlsson C, Bergo MO, Boren J, Akyurek LM (2007) Filamin B deficiency in mice results in skeletal malformations and impaired microvascular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3919–3924. doi:10.1073/pnas.0608360104
Zhu X, Petrovski S, Xie P, Ruzzo EK, Lu YF, McSweeney KM, Ben-Zeev B, Nissenkorn A, Anikster Y, Oz-Levi D, Dhindsa RS, Hitomi Y, Schoch K, Spillmann RC, Heimer G, Marek-Yagel D, Tzadok M, Han Y, Worley G, Goldstein J, Jiang YH, Lancet D, Pras E, Shashi V, McHale D, Need AC, Goldstein DB (2015) Whole-exome sequencing in undiagnosed genetic diseases: interpreting 119 trios. Genet Med. doi:10.1038/gim.2014.191
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients and their parents for consenting to participate in this study. The full-length wild-type FLNB cDNA clone was kindly provided by Dr. Philip B. Daniel (Dunedin School of Medicine University of Otago, Dunedin,New Zealand) and Dr. A. Sonnenberg (Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, The Netherlands). This study was further supported by grants from Pudong New Area of Science and Technology Development Fund (PKJ2013-Y62) and Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine Science Fund (13XJ22009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from parents or guardians of all patients in the study before blood sample collection.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Children’s Medical Center.
Additional information
H. Yang and Z. Zheng contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
439_2016_1701_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplement Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of FLNB protein indicating the frequencies of mutations underlying the AO-LS-BD-SCT spectrum. Actin-binding domains were shown as rectangle, immunoglobulin-like filamin repeats as oval, and hinge regions as thick line. Column height indicated frequency within the associated domain (actual numbers were given above the columns), while column color represented disease association as follows: AOI/III (red), LS (green), BD (yellow), SCT (dark blue) (TIFF 1993 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Zheng, Z., Cai, H. et al. Three novel missense mutations in the filamin B gene are associated with isolated congenital talipes equinovarus. Hum Genet 135, 1181–1189 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-016-1701-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-016-1701-7