Abstract.
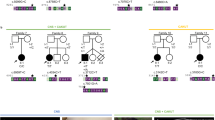
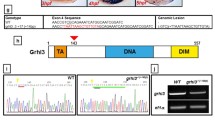
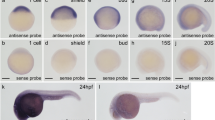
TDGF1 (CRIPTO) is an EGF-CFC family member and an obligate co-receptor involved in NODAL signaling, a developmental program implicated in midline, forebrain, and left-right axis development in model organisms. Previous studies of CFC1 (CRYPTIC), another member of the EGF-CFC family, demonstrated that normal function of this protein is required for proper laterality development in humans. Here we identify a mutation in the conserved CFC domain of TDGF1 in a patient with midline anomalies of the forebrain. The mutant protein is inactive in a zebrafish rescue assay, indicating a role for TDGF1 in human midline and forebrain development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de la Cruz, J.M., Bamford, R.N., Burdine, R.D. et al. A loss-of-function mutation in the CFC domain of TDGF1 is associated with human forebrain defects . Hum Genet 110, 422–428 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-002-0709-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-002-0709-3