Abstract.
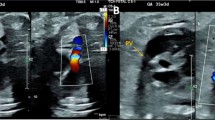
The neonatal Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominantly inherited disease with an extremely poor prognosis. This report gives a clinical and echocardiographic description of an infant with a mutation in exon 29 of the fibrillin-1 gene (FBN1), a region in which this severe form of Marfan syndrome seems to cluster. The infant died at the age of 3 months due to severe acute mitral regurgitation leading to intractable heart failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weidenbach, M., Brenner, R., Rantamäki, T. et al. Acute Mitral Regurgitation Due to Chordal Rupture in a Patient with Neonatal Marfan Syndrome Caused by a Deletion in Exon 29 of the FBN1 Gene. Pediatr Cardiol 20, 382–385 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002469900493
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002469900493