Abstract
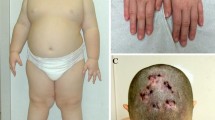
A total of 167 patients with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) was studied at the clinical and molecular level. Diagnosis was confirmed by the PW71 methylation test. Quantitative Southern blot hybridizations with a probe for the small nuclear ribonucleoprotein N were performed to distinguish between patients with a deletion (116 patient or 69.5%) and patients without a deletion (51 patients or 30.5%). These two types of patients differed with respect to the presence of hypopigmentation, which was more frequent in patients with a deletion (52%) than in patients without (23%), and to average birth weight of females and males, which was lower in patients with a deletion than in patients without. Newborns with PWS had a lower birth weight and length at term, but normal head circumference in comparison with a control group. This finding aids the identification of the neonatal phenotype. In addition, our data confirm an increased maternal age in the non-deletion group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bottani A, Robinson WP, DeLoizier-Blanchet CD, Engel E, Morris MA, Schmitt B, Thun-Hohenstein L, Schinzel A (1994) Angelman syndrome due to uniparental disomy of chromosome 15: a milder phenotype? Am J Med Genet 51:35–40
Buiting K, Dittrich B, Robinson WP, Guitart M, Abeliovich D, Lerer I, Horsthemke B (1994) Detection of aberrant methylation in unique Prader-Willi syndrome patients and its diagnostic implications. Hum Molec Genet 3:893–895 (Corrigendum Hum Molec Genet 3:2092, 1994)
Buiting K, Saitoh S, Gross S, Dittrich B, Schwartz S, Nicholls RD, Horsthemke B (1995) Inherited microdeletions in the Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes define an imprinting centre on human chromosome 15. Nature Genet 9:395–400
Butler MG, Meaney J, Palmer CG (1986) Clinical and cytogenetic survey of 39 individuals with Prader-Labhart-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet 23:793–809
Cassidy SB, Lai Li-Wen, Erickson RP, Magnuson L, Thomas E, Gendron R, Herrman J (1992) Trisomy 15 with loss of the paternal 15 as a cause of Prader-Willi syndrome due to maternal disomy. Am J Hum Genet 51:701–708
Dittrich B, Robinson W, Knoblauch H, Buiting K, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Horsthemke B (1992) Molecular diagnosis of the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes by detection of parentof-origin specific DNA methylation. Hum Genet 90:313–315
Dittrich B, Buiting K, Gross S, Horsthemke B (1993) Characterisation of a methylation imprint in the Prader-Willi region. Hum Molec Genet 2:1995–1999
Engel E (1980) A new genetic concept: uniparental disomy and its potential effect, isodisomy. Am J Med Genet 6:137–147
Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Gross S, Kaya-Westerloh S, Passarge E, Horsthemke B (1995a) DNA-methylation based testing of 450 patients suspected of having Prader-Willi syndrome. J Med Genet 32:88–92
Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Albrecht A, Passarge E, Horsthemke B (1995b) Further patient with Angelman syndrome due to paternal disomy of chromosome 15 and a milder phenotype. Am J Med Genet 56:328–329
Hassold TJ, Chiu D (1985) Maternal age-specific rates of numerical chromosomal abnormalities with special reference to trisomy. Hum Genet 70:11–17
Holm VA, Cassidy SB, Butler MG, Hanchett JM, Greenswag LR, Whitman BY, Greenberg F (1993) Prader-Willi syndrome: consensus criteria. Pediatrics 91:398–402
Keen DV, Pearse RG (1988) Weight, length, and head circumference curves for boys and girls of between 20 and 42 week's gestation. Arch Dis Child 63:1170–1172
Knoll JHM, Nicholls RD, Magenis RE, Graham JM, Lalande M, Latt SA (1989) Angelman and Prader-Willi syndrome share a common chromosome 15 deletion but differ in parental origin of the deletion. Am J Med Genet 32:285–290
Kokkonen H, Kähkönen M, Leisti J (1995) A molecular and cytogenetic study in Finnish Prader-Willi patients. Hum Genet 95:568–571
LaSalle JM, Lalande M (1995) Domain organization of allele-specific replication within the GABRB3 gene cluster requires a biparental 15q11–13 contribution. Nature Genet 9:386–393
Mascari MJ, Gottlieb W, Rogan PK, Butler MG, Waller DA, Armour JAL, Jeffreys AJ, Ladda RL, Nicholls RD (1992) The frequency of uniparental disomy in Prader-Willi syndrome. N Engl J Med 326:1599–1607
Nicholls RD, Knoll JHM, Butler MG, Karam S, Lalande M (1989) Genetic imprinting suggested by maternal heterodisomy in non-deletion Prader-Willi syndrome. Nature 342:281–285
Ouweland AMW van den, Est MN van der, Wesbey-van Swaay E, Tijmensen TSLN, Los FJ, Van Hemel JO, Hennekam RCM, Meijers-Heijboer HJ, Niemeijer MF, Halley DJJ (1995) DNA diagnosis of Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes with the probe PW71 (D15S63). Hum Genet 95:562–567
Özcelik T, Left S, Robinson W, Donlon T, Lalande M, Sanjines E, Schinzel A, Francke U (1992) Small nuclear ribonucleoproteine polypeptide N (SNRPN), an expressed gene in the PraderWilli syndrome critical region. Nature Genet 265–269
Prader A, Labhart A, Willi H (1956) Ein Syndrom von Adipositas. Kleinwuchs, Kryptorchismus und Oligophrenie nach Myatonieartigem Zustand im Neugeborenenalter. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 86:1260–1261
Purvis-Smith SG, Saville T, Manass S, Yip M-J, Lam-Po-Tang PRL, Duffy B, Johnston H, Leigh D, McDonald B (1992) Uniparental disomy 15 resulting from ‘correction’ of an initial trisomy 15. Am J Hum Genet 50:1348–1350
Reis A, Dittrich B, Greger V, Lalande M, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Anvret M, Horsthemke B (1994) Imprinting mutations suggested by abnormal methylation patterns in familial Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes. Am J Hum Genet 54:741–747
Rinchik EM, Bultmann SJ, Horsthemke B, Lee ST, Strunk KM, Spritz RA, Avidano KM, Jong MTC, Nicholls RM (1993) A gene for the mouse pink-eyed dilution locus and for human type II oculocutaneous albinism. Nature 361:72–76
Robinson WP, Bottani A, Yagang X, Balakrishnan J, Binkert F, Mächler M, Prader A, Schinzel A (1991) Molecular, cytogenetic, and clinical investigations of Prader-Willi syndrome patients. Am J Hum Genet 49:1219–1234
Robinson WP, Lorda-Sanchez I, Malcolm S, Langlois S, Schuffenhauer S, Knoblauch H, Horsthemke B, Schinzel AA (1993) Increased parental ages and uniparental disomy 15: a paternal age effect? Eur J Hum Genet, pp 280–286
Wengler SL, Hanchett JM, Steele MW, Maier BV, Golden WL (1987) Clinical comparison of 59 Prader-Willi patients with and without the 15 (Q12) deletion. Am J Med Genet 28:881–887
Wiesner GL, Bendel CM, Olds DP, White JG, Arthur DC, Ball DW, King RA (1987) Hypopigmentation in the Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet 40:431–442
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gillessen-Kaesbach, G., Robinson, W., Lohmann, D. et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation in a series of 167 deletion and non-deletion patients with Prader-Willi syndrome. Hum Genet 96, 638–643 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210291
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210291