Abstract
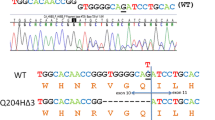
We used heteroduplex analysis to screen for mutations in the porphobilinogen deaminase gene in 21 patients with acute intermittent porphyria (AIP). Unique banding patterns were investigated by direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction products and, when indicated, sequencing of cloned DNA containing the exon of interest. Two frameshift mutations were found, a 2-bp deletion in exon 5 and a 1-bp insertion in exon 7. Both mutations generate a premature stop codon. Two point mutations, in exons 10 and 14, were also observed. The C→T mutation in exon 10 codes for an Arg173 to Trp substitution, while a G→A mutation in exon 14 changes Trp283 into a premature stop codon. This study extends the spectrum of mutations that cause AIP and demonstrates the utility of heteroduplex analysis as a screening technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bottomley SS, Bonkowsky HL, Kreimer-Birnbaum M (1981) The diagnosis of acute intermittent porphyria: usefulness and limitations of the erythrocyte uroporphyrinogen I synthase assay. Am J Clin Pathol 76:133–139
Bourgeois F, Gu X-F, Deybach JC, Te Velde MP, deRooij F, Nordmann Y, Grandchamp B (1992) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis for rapid detection of latent carriers of a subtype of acute intermittent porphyria with normal erythrocyte porphobilinogen deaminase activity. Clin Chem 38:93–95
Daimon M, Yamatani K, Igarashi M, Fukase N, Ogawa A, Tominaga M, Sasaki H (1993) Acute intermittent porphyria caused by a G to C mutation in exon 12 of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene that results in exon skipping. Hum Genet 92:549–553
Delfau MH, Picat C, deRooij F, Hamer K, Bogard M, Wilson JHP, et al (1990) Two different point G to A mutations in exon 10 of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene are responsible for acute intermittent porphyria. J Clin Invest 86:1511–1516
Delfau MH, Picat C, deRooij F, Voortman G, Deybach JC, Nordmann Y, Grandchamp B (1991) Molecular heterogeneity of acute intermittent porphyria: identification of four additional mutations resulting in the CRIM-negative subtype of the disease. Am J Hum Genet 49:421–428
Grandchamp B, Picat C, Mignotte V, Wilson JHP, Te Velde K, Sandkuyl L, et al. (1989a) Tissue-specific splicing mutation in acute intermittent porphyria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:661–664
Grandchamp B, Picat C, Kauppinen R, Mignotte V, Peltonen L, Mustajoki P, et al. (1989b) Molecular analysis of acute intermittent porphyria in a Finnish family with normal erythrocyte porphobilinogen deaminase. Eur J Clin Invest 19:415–418
Grandchamp B, Picat C, deRooij F, Beaumont C, Wilson P, Deybach JC, Nordmann Y (1989c) A point mutation G→A in exon 12 of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene results in exon skipping and is responsible for acute intermittent porphyria. Nucleic Acids Res 17:6637–6649
Gu XF, Lee J-S, Delfau MH, Grandchamp B (1991) PCR detection of a G/T polymorphism at exon 10 of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene (PBG-D). Nucleic Acids Res 19:1966
Gu X-F, deRooij F, Voortman G, Te Velde K, Nordmann Y, Grandchamp B (1992) High frequency of mutations in exon 10 of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene in patients with a CRIM-positive subtype of acute intermittent porphyria. Am J Hum Genet 51:660–665
Gu X-F, deRooij F, Lee JS, Te Velde K, Deybach JC, Nordmann Y, Grandchamp B (1993) High prevalence of a point mutation in the porphobilinogen deaminase gene in Dutch patients with acute intermittent porphyria. Hum Genet 91:128–130
Gu X-F, deRooij F, Voortman G, Te Velde K, Deybach J-C, Nordmann Y, Grandchamp B (1994) Detection of eleven mutations causing acute intermittent porphyria using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Hum Genet 93:47–52
Kappas A, Sassa S, Galbraith RA, Nordmann Y (1989) The porphyrias. In: Scriver C, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease, 6th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1305–1365
Kauppinen R (1992) Single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis applied to the diagnosis of acute intermittent porphyria. Mol Cell Probes 6:527–530
Lannfelt L, Wetterberg L, Lilius L, Thunell S, Gellerfors P (1989) ELISA for measuring porphobilinogen deaminase in human erythrocytes. Clin Chim Acta 183:227–238
Lee J-S (1991) Molecular genetic investigation of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene in acute intermittent porphyria. PhD thesis. University of Stockholm
Lee J-S, Anvret M (1991) Identification of the most common mutation within the porphobilinogen deaminase gene in Swedish patients with acute intermittent porphyria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10912–10915
Llewellyn DH, Whatley S, Elder GH (1993) Acute intermittent porphyria caused by an arginine to histidine substitution (R26H) in the cofactor-binding cleft of porphobilinogen deaminase. Hum Mol Genet 2:1315–1316
Lundin G, Wedell A, Thunell S, Anvret M (1994) Two new mutations in the porphobilinogen deaminase gene and a screening method using PCR amplification of specific alleles. Hum Genet 93:59–62
Mgone CS, Lanyon WG, Moore MR, Connor JM (1992) Detection of seven point mutations in the porphobilinogen deaminase gene in patients with acute intermittent porphyria, by direct sequencing of in vitro amplified cDNA. Hum Genet 90:12–16
Mgone CS, Lanyon WG, Moore MR, Louie GV, Connor JM (1993) Detection of a high mutation frequency in exon 12 of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene in patients with acute intermittent porphyria. Hum Genet 92:619–622
Moore MR, McColl KEL, Rimington C, Goldberg A (1987) Disorders of porphyrin metabolism. Plenum, New York
Prior TW, Papp AC, Snyder PJ, Burghes AH, Sedra MS, Western LM, Bartello C, Mendell JR (1993) Identification of two point mutations and a one base deletion in exon 19 of the dystrophin gene by heteroduplex formation. Hum Mol Genet 2:311–313
Schreiber WE, Fong F, Jamani A (1994a) Frameshift mutations in exons 9 and 10 of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene produce a crossreacting immunological material (CRIM)-negative form of acute intermittent porphyria. Hum Genet 93:552–556
Schreiber WE, Fong F, Jamani A (1994b) Molecular diagnosis of acute intermittent porphyria by analysis of DNA extracted from hair roots. Clin Chem 40:1744–1748
Scobie GA, Llewellyn DH, Urquhart AJ, Smyth SJ, Kalsheker NA, Harrison PR, Elder GH (1990) Acute intermittent porphyria caused by a C→T mutation that produces a stop codon in the porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Hum Genet 85:631–634
Yoo H-W, Warner CA, Chen C-H, Desnick RJ (1993) Hydroxymethylbilane synthase: complete genomic sequence and amplifiable polymorphisms in the human gene. Genomics 15:21–29
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schreiber, W.E., Fong, F., Nassar, B.A. et al. Heteroduplex analysis detects frameshift and point mutations in patients with acute intermittent porphyria. Hum Genet 96, 161–166 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207373
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207373