Abstract
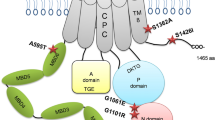
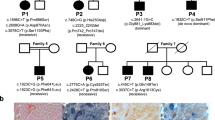
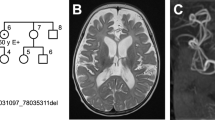
Wilson disease (WD) is an autosomal recessive disorder of copper transport, resulting in copper accumulation and toxicity to the liver and brain. The gene (WD) has been mapped to chromosome 13 q14.3. On yeast artificial chromosomes from this region we have identified a sequence, similar to that coding for the proposed copper binding regions of the putative ATPase gene (MNK) defective in Menkes disease. We show that this sequence forms part of a P–type ATPase gene (referred to here as Wc1) that is very similar to MNK, with six putative metal binding regions similar to those found in prokaryotic heavy metal transporters. The gene, expressed in liver and kidney, lies within a 300 kb region likely to include the WD locus. Two WD patients were found to be homozygous for a seven base deletion within the coding region of Wc1. Wc1 is proposed as the gene for WD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brewer, G.J. & Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan, V. Wilson Disease. Medicine 71, 139–164 (1992).
Sarkar, B. Transport of Copper. in Metal ions in biological systems, (ed. Sigel, H.) 233–281 (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1981).
Orena, S.J., Goode, C.A. & Linder, M.C. Binding and uptake of copper from ceruloplasmin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 139, 822–829 (1986).
Kagi, J.H.R. & Schaffer, A. Biochemistry of metallothionein. Biochemistry 27, 8509–8515 (1988).
Danks, D.M. Disorders of copper transport. in: Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease, (eds Beaudet, A.L., Sly, W.S. & Valle, D.) 1411–1431 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1989).
Darwish, H.M., Hoke, J.E. & Ettinger, M.J. Kinetics of Cu(II) transport and accumulation by hepatocytes from copper-deficient mice and the brindled mouse model of Menkes disease. J. biol. Chem. 258, 13621–13626 (1983).
Frydman, M. et al. Assignment of the gene for Wilson disease to chromosome 13. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 1819–1821 (1985).
Bowcock, A.M. et al. Mapping the Wilson disease locus to a cluster of linked polymorphic markers on chromosome 13. Am. J. hum. Genet. 41, 27–35 (1987).
Bowcock, A.M. et al. Eight closely linked loci place the Wilson disease locus within 13q14-q21. Am. J. hum. Genet. 43, 664–674 (1988).
Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan, V., Brewer, G.J., Boerwinkle, E. & Venta, P.J. Linkage of the Wilson disease gene to chromosome 13 in North-American pedigrees. Am. J. hum. Genet. 42, 825–829 (1988).
Farrer, L.A. et al. Predictive testing for Wilson's disease using tightly linked and flanking DNA markers. Neurology 41, 992–999 (1991).
Thomas, G.R., et al. Allelic association and linkage studies in Wilson disease. Hum. molec. Genet. 2, 1404–1405 (1993).
Houwen, R.H.J., Berger, R., Cox, D.W. & Buys, C.H.C.M. Allelic association for Wilson disease-D13S31. J. Hepatol. 16, S15 (1992).
Bull, P.C. et al. Isolation of new probes in the region of the Wilson disease locus, 13q14.2-14.3. Cytogenet. Cell. Genet. 64, 12–17 (1993).
Bull, P.C. & Cox, D.W. Long range restriction mapping of 13q14.3 focused on the Wilson disease region. Genomics 16, 593–598 (1993).
Thomas, G.R., Bull, P.C., Roberts, E.A., Walshe, J.R. & Cox, D.W. Haplotype studies in wilson disease. Am. J. hum. Genet. (in the press).
Vulpe, C., Levinson, B., Whitney, S., Packman, S. & Gitschier, J. Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease and evidence that it encodes a copper-transporting ATPase. Nature Genet. 3, 7–13 (1993).
Mercer, J.F.B. et al. Isolation of a partial candidate gene for Menkes disease by positional cloning. Nature Genet. 3, 20–25 (1993).
Chelly, J. et al. Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease that encodes a potential heavy metal binding protein. Nature Genet. 3, 14–19 (1993).
Sass-Kortsak, A. Copper metabolism. Adv. Clin. Chem. 8, 1–67 (1965).
Owen, C.A. Jr. Metabolism of radiocopper (64Cu) in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. 209, 900–904 (1965).
Rommens, J.M. et al. A transcription map of the region containing the Huntington disease gene. Hum. molec. Genet. 2, 901–907 (1993).
Goldberg, Y.P. et al. Cloning and mapping of the a-adducin gene close to D4S95 and assessment of its relationship to Huntington disease. Hum. molec. Genet. 1, 669–675 (1992).
Silver, S., Nucifora, G. & Phang, Le.T. Human Menkes X-chromosome disease and the staphylococcal cadmium resistance ATPase: a remarkable similarity in protein sequences. Molec. Microbiol. 10, 7–12 (1993).
Odermatt, A., Suter, H., Krapf, R. & Solioz, M. Primary structure of two P-type ATPases involved in copper homeostasis in Enterococcus hirae. J. biol. Chem. 268, 12775–12779 (1993).
Griffin, H.G., Foster, T.J., Silver, S. & Misra, T.K. Cloning and DNA sequence of the mercuric and organomercurial resistance determinants of plasmid pDU1358. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 3112–3116 (1987).
Nucifora, G., Chu, L., Misra, T.K. & Silver, S. Cadmium resistance from Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pl258 cadA gene results from a cadmium-efflux ATPase. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 3544–3548 (1989).
Green, N.M. & Stokes, D.L. Structural modelling of P-type ion pumps. Acta Physiol. Scand. 146, 59–68 (1993).
MacLennan, D.H., Clarke, D.M., Loo, T.W. & Skerjanc, I.S. Site-directed mutagenesis of the Ca2+ ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Acta Physiol. Scand. 146, 141–150 (1992).
Vulpe, C., Levinson, B., Whitney, S., Packman, S. & Gitschier, J. Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease and evidence that it encodes a copper transporting ATPase (Correction). Nature Genet. 3, 273 (1993).
Yarze, J.C., Martin, P., Munoz, S.J. & Friedman, L.S. Wilson Disease: current status. Am. J. Med. 92, 643–654 (1992).
Sternlieb, I. Perspectives on Wilson Disease. Hepatology 12, 1234–1239 (1990).
Yang, F., et al. Characterization, mapping, and expression of the human ceruloplasmin gene. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 3257–3261 (1986).
Sato, M. & Gitlin, J.D. Mechanisms of copper incorporation during the biosythesis of human ceruloplasmin. J. biol. Chem. 266, 5128–5134 (1991).
Gitlin, J.D., Schroeder, J.J., Lee-Ambrose, L.M & Cousins, R.J. Mechanisms of ceruloplasmin biosynthesis in normal and copper-deficient rats. Biochem. J. 282, 835–839 (1992).
O'Halloran, T.V. Transition metals in control of gene expression. Science 261, 715–725 (1993).
Scherer, S. & Tsui, L-T. Cloning and analysis of large DNA molecules. in Advanced techniques in chromosome research (ed. Adolph, K.W.) 33–72 (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1991).
Triglia, T., Peterson, M.G. & Kemp, D.J. A procedure for in vitro amplification of DNA segments that lie outside the boundaries of known sequences. Nucl. Acids Res. 16, 8186–8180 (1988).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 2nd edn 1989).
Orita, M., Suzuki, Y., Sekiya, T. & Hayashi, K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics 5, 874–879 (1989).
White, M.B., Carvalho, M., Derse, D., O'Brien, S.J. & Dean, M. Detecting single base substitutions as heteroduplex polymorphisms. Genomics 12, 301–306 (1992).
Stewart, E.A. et al. Polymorphic microsatellites and Wilson disease (WD). Am. J. hum. Genet. 53, 864–873 (1993).
Kahn, D. et al. Rhizobium melitoli fixGHI sequence predicts involvement of a specific cation pump in symbiotic nitrogen fixation. J. Bacteriol. 171, 929–939 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bull, P., Thomas, G., Rommens, J. et al. The Wilson disease gene is a putative copper transporting P–type ATPase similar to the Menkes gene. Nat Genet 5, 327–337 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1293-327
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1293-327
This article is cited by
-
First application of next-generation sequencing in four families with Wilson disease in Morocco
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2023)
-
Copper in Cancer: from transition metal to potential target
Human Cell (2023)
-
Missing heritability of Wilson disease: a search for the uncharacterized mutations
Mammalian Genome (2023)
-
A colorimetric chemosensor for distinct color change with (E)-2-(1-(3-aminophenyl)ethylideneamino)benzenethiol to detect Cu2+ in real water samples
Analytical Sciences (2023)
-
An optical chemosensor for nano-level determination of Pb2+ and Cu2+ in aqueous media and its application in cell imaging
Chemical Papers (2023)