Abstract
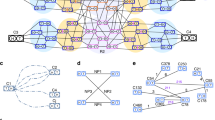
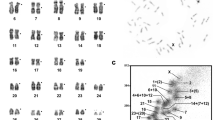
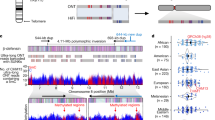
The quest for the mutation responsible for Huntington's disease (HD) has required an exceptionally detailed analysis of a large part of 4p16.3 by molecular genetic techniques, making this stretch of 2.2 megabases one of the best characterized regions of the human genome. Here we describe the construction of a cosmid and P1 clone contig spanning the region containing the HD gene, and the establishment of a detailed, high resolution restriction map. This ordered clone library has allowed the identification of several genes from the region, and has played a vital role in the recent identification of the Huntington's disease gene. The restriction map provides the framework for the detailed analysis of a region extremely rich in coding sequences. This study also exemplifies many of the strategies to be used in the analysis of larger regions of the human genome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin, J.B. & Gusella, J.F. Huntington's disease: Pathogenesis and management. New Engl. J. Med. 315, 1267–1276 (1986).
Gusella, J.F. et al. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature 306, 234–238 (1983).
Gilliam, T.C. et al. Localisation of the Huntington's disease gene to a small segment of chromosome 4 flanked by D4S10 and the telomere. Cell 50, 565–571 (1987).
Conneally, P.M. et al. Huntington's disease: no evidence for heterogeneity. Genomics 5, 304–308 (1989).
Bucan, M. et al. Physical maps of 4p16.3, the area expected to contain the Huntington's disease mutation. Genomics 6, 1–15 (1990).
Bates, G.P. et al. Defined physical limits of the Huntington disease gene candidate region. Am. J. hum. Genet. 49, 7–16 (1991).
MacDonald, M.E. et al. Recombination events suggest potential sites for the Huntington's disease gene. Neuron 3, 183–190 (1989).
Allitto, B. et al. Increased recombination adjacent to the Huntington's disease linked D4S10 marker. Genomics 9, 104–112 (1991).
Pritchard, C. et al. Recombination of 4p16 DNA markers in an unusual family with Huntington disease. Am. J. hum. Genet. 50, 1218–1230 (1992).
Bates, G.P. et al. A yeast artificial chromosome telomere clone spanning a possible location of the Huntington disease gene. Am. J. hum. Genet. 46, 762–775 (1990).
Youngman, S. et al. The telomeric 60 kb of chromosome arm 4p is homologous to telomeric regions on 13p, 15p, 21p and 22p. Genomics 14, 350–356 (1992).
Snell, R.G. et al. Linkage disequilibrium in Huntington's disease: An improved localisation for the gene. J. med. Genet. 26, 673–675 (1989).
Theilmann, J. et al. Non-random association between alleles detected at D4S95 and D4S98 and the Huntington's disease gene. J. med. Genet. 26, 676–681 (1989).
Whaley, W.L. et al. Mapping of cosmid clones in the Huntington's region of chromosome 4. Somat. Cell molec. Genet. 17, 83–91 (1991).
MacDonald, M.E. et al. Complex patterns of linkage disequilibrium in the Huntington's disease region. Am. J. hum. Genet. 49, 723–724 (1991).
Barron, L. et al. Linkage disequilibrium and recombination make a telomeric site for the Huntington's disease gene unlikely. J. med. Genet. 28, 520–522 (1991).
Snell, R.G. et al. A recombination event that redefines the Huntington disease region. Am J. hum. Genet. 51, 357–362 (1992).
Adam, S. et al. Linkage disequilibrium and modification of risk for Huntington disease. Am. J. hum. Genet. 48, 595–603 (1991).
Andrew, S. et al. Nonrandom association between Huntington disease and two loci separated by about 3 Mb on 4p16.3. Genomics 13, 301–311 (1992).
MacDonald, M.E. et al. The Huntington's disease candidate region exhibits many different haplotypes. Nature Genet. 1, 99–103 (1992).
The Huntington's Disease Collaborative Research Group. A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington's disease chromosomes. Cell 72, 971–983 (1993).
Saccone, S., De Sario, A., Della Valle, G. & Bernardi, G. The highest gene concentrations in the human genome are in telomeric bands of metaphase chromosomes. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 4913–4917 (1992).
Bates, G.P. et al. Characterization of a yeast artificial chromosome contig spanning the Huntington's disease gene candidate region. Nature Genet. 1, 180–187 (1992).
Buckler, A.J. et al. Exon amplification: A strategy to isolate mammalian genes based on RNA splicing. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 4005–4009 (1991).
Lovett, M., Kere, J. & Hinton, L.M. Direct selection: A method for the isolation of cDNAs encoded by large genomic regions. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 9628–9632 (1991).
Korn, B. et al. A strategy for the selection of transcribed sequences in the Xq28 region. Hum. molec. Genet. 1, 235–242 (1992).
Tagle, D.A., Swaroop, M., Lovett, M. & Collins, F.S. Magnetic bead capture of expressed sequences encoded within large genomic segments. Nature 361, 751–753 (1993).
Gribben, T.E. et al. Association of a mature B cell leukemia with a 4p+ chromosomal abnormality: Derivation and chacterisation of a cell line. Leukemia 3, 643–647 (1989).
Gandelman, K.Y., Gibson, L., Meyn, S. & Yang-Feng, T.L. Molecular definition of the smallest region of deletion overlap in the Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome. Am. J. hum. Genet. 51, 571–578 (1992).
Baxendale, S., Bates, G.P., MacDonald, M.E., Gusella, J.F. & Lehrach, H. The direct screening of cosmid libraries with YAC clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 6651 (1991).
Nizetic, D. et al. Construction, arraying and high-density screening of large insert cosmid libraries of the human chromosomes X and 21. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 3233–3237 (1991).
Lehrach, H. et al. Genome Analysis: Genetic and Physical Mapping Vol. 1 (eds Davies, K. E. & Tilghman, S. M.) 39–81 (Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press, New York, 1990).
Lin, C.S. et al. New DNA markers in the Huntington's disease gene candidate region. Somat. Cell molec. Genet. 17, 481–488 (1991).
Richards, J.E. et al. Chromosome jumping from D4S10 (G8) toward the Huntington's disease gene. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 6437–6441 (1988).
Smith, B. et al. Isolation of DNA markers in the direction of the Huntington's disease gene from the G8 locus. Am. J. hum. Genet. 42, 335–344 (1988).
Gilliam, T.C. et al. A DNA segment encoding two genes very tightly linked to Huntington's disease. Science 238, 950–952 (1987).
Sternberg, N., Ruether, J. & de Riel, K. Generation of a 50,000 member human DNA library with an average insert size of 75–100 kb in a bacteriophage P1 cloning vector. New Biologist 2, 151–162 (1990).
Rackwitz, H.R. et al. Analysis of cosmids using linearisation by phage lambda terminase. Gene 40, 259–266 (1985).
Zehetner, G. & Lehrach, H. A computer program package for restriction map analysis and manipulation. Nucl. Acids Res. 14, 335 (1986).
Linsay, S. & Bird, A.P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. Nature 327, 336–338 (1987).
Hoheisel, J.D. et al. High-resolution cosmid and P1 maps spanning the 14-Mb genome of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cell 73, 109–120 (1993).
Coulson, A., Sulston, J., Brenner, S. & Karn, J. Toward a physical map of the genome of the nematode Caenorabditis elegans. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 7821–7825 (1986).
Melmer, G. & Buchwald, M. Identification of genes using oligonucleotides corresponding to splice site consensus sequences. Hum. molec. Genet. 1, 433–438 (1992).
Taylor, S.A.M. et al. Cloning of the α–adducin gene from the Huntington's disease candidate region of chromosome 4 by exon amplification. Nature Genet. 2, 223–227 (1992).
Ambrose, C. et al. A novel G protein-coupled receptor kinase gene cloned from 4p16.3. Hum. molec. Genet. 1, 697–703 (1992).
Evans, G.A., Lewis, K. & Rothenberg, B.E. High efficiency vectors for cosmid microcloning and genomic analysis. Gene 79, 9–20 (1989).
Pierce, J.C., Sauer, B. & Sternberg, N. A positive selection vector for cloning high molecular weight DNA by the bacteriophage P1 system: Improved cloning efficiency. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 2056–2060 (1992).
Church, G.M. & Gilbert, W. Genomic sequencing. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 1991–1995 (1984).
Sealey, P.G., Whittaker, P.A. & Southern, E.M. Removal of repeated sequences from hybridisation probes. Nucl. Acids Res. 13, 1905–1922 (1985).
Hoheisel, J.D., Lennon, G.G., Zehetner, G. & Lehrach, H. Use of high coverage reference libraries of Drosophila melanogaster for relational data analysis; a step towards mapping and sequencing of the genome. J. molec. Biol. 220, 903–914 (1991).
Hoheisel, J.D. Ultrafast microprep protocol for large-number preparations of recombinant plasmids and cosmids. J. Meth. Cell molec. Biol. 1, 21–27 (1989).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual 2nd edn (Cold Spring Harbor Press, New York, 1989).
Mott, R., Grigoriev, A., Maier, E., Hoheisel, J. & Lehrach, H. Algorithms and software tools for ordering clone libraries: application to the mapping of the genome of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nucl. Acids Res. (in the press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baxendale, S., MacDonald, M., Mott, R. et al. A cosmid contig and high resolution restriction map of the 2 megabase region containing the Huntington's disease gene. Nat Genet 4, 181–186 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0693-181
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0693-181
This article is cited by
-
The molecular genetics of Huntington disease — a history
Nature Reviews Genetics (2005)
-
Serotonergic neurons in the median raphe nucleus regulate inhibitory avoidance but not escape behavior in the rat elevated T-maze test of anxiety
Psychopharmacology (2005)
-
A double cryptic chromosome imbalance is an important factor to explain phenotypic variability in Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome
European Journal of Human Genetics (2004)
-
Characterization of the t(4;14)(p16.3;q32) in the KMS-18 multiple myeloma cell line
Leukemia (2001)
-
Letter
European Journal of Human Genetics (2001)