Abstract
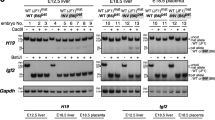
The mouse igf2 gene, coding for the insulin–like growth factor II (IGF–II) is parentally imprinted, only the gene copy derived from the father is expressed. To know whether IGF2, the human homologue, is also imprinted, we used an Apal polymorphism at the 3′ untranslated region in order to distinguish between mRNA derived from each copy of the gene in placentae from heterozygote human fetuses, studied after careful removal of the decidua. Six term and two pre–term placentae of heterozygotes were studied, and in each case the cDNA contained only one of the two alleles present in the genomic DNA. In three cases the mother was homozygous for the non–expressed allele, allowing assignment of paternal origin to the transcribed gene copy. We conclude that, as in the mouse, human IGF2 is parentally imprinted.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Surani, M.A.H., Barton, S.C. & Norris, M.L. Development of reconstituted mouse eggs suggests imprinting of the genome during gametogenesis. Nature 308, 548–550 (1984).
McGrath, J. & Solter, D. Completion of mouse embryogenesis requires both the maternal and paternal genomes. Cell 37, 179–183 (1984).
Mann, J.R. & Lovell-Badge, R.H. Inviability of parthenogenotes is determined by pronuclei, not egg cytoplasm. Nature 310, 66–67 (1984).
Cattanach, B.M. & Kirk, M. Differential activity of maternally and paternally derived chromosome regions in mice. Nature 315, 496–498 (1985).
Reik, W. Genomic imprinting and genetic disorders in man. Trends Genet. 5, 331–336 (1989).
Hall, J.G. Genomic imprinting: Review and reference to human diseases. Am. J. hum. Genet. 46, 857–873 (1990).
Henry, I. et al. Uniparental paternal disomy in a genetic cancer-predisposing syndrome. Nature 351, 665–667 (1991).
Schroeder, W.T. et al. Nonrandom loss of maternal chromosome 11 alleles in Wilms tumors. Am. J. hum. Genet. 40, 413–412 (1987).
Sapienza, C. Genome imprinting and carcinogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1072, 51–61 (1991).
Sapienza, C., Peterson, A.C., Rossant, J. & Balling, R. Degree of methylation of transgenes is dependent on gamete of origin. Nature 328, 251–254 (1987).
Swain, J.L., Stewart, T.A. & Leder, P. Parental legacy determines methylation and expression of an autosomal transgene: a molecular mechanism for parental imprinting. Cell 50, 719–727 (1987).
Pourcel, C. Maternal inhibition of hepatitis B surface antigen gene expression in transgenic mice correlates with de novo methylation. Nature 329, 454–456 (1987).
Reik, W., Collick, A., Norris, M.L., Barton, S.C. & Surani, M.A.H. Genomic imprinting determines methylation of parental alleles in transgenic mice. Nature 328, 248–251 (1987).
DeChiara, T.M., Robertson, E.J. & Efstratiadis, A. Parental imprinting of the mouse insulin-like growth factor II gene. Cell 64, 849–859 (1991).
Barlow, D.P., Stoger, R., Herrmann, B.G., Saito, K. & Schweifer, N. The mouse insulin-like growth factor type-2 receptor is imprinted and closely linked to the Tme locus. Nature 349, 84–87 (1991).
Bartolomei, M.S., Zemel, S. & Tilghman, S.M. Parental imprinting of the mouse H19 gene. Nature 351, 153–155 (1991).
Leff, S.E. et al. Maternal imprinting of the mouse Snrpn gene and conserved linkage homology with the human Prader-Willi syndrome region. Nature Genet. 2, 259–263 (1992).
DeChiara, T.M., Efstratiadis, A. & Robertson, E.J. A growth-deficiency phenotype in heterozygous mice carrying an insulin-like growth factor II gene disrupted by targeting. Nature 345, 78–80 (1990).
Gray, A. et al. Tissue-specific and developmentally regulated transcription of IGF-II. DNA 6, 283–295 (1987).
Bell, G.I., Gerhard, D.S., Fong, N.M., Sanchez-Pescador, R. & Rall, L.B. Isolation of the human insulin-like growth factor genes: insulin-like growth factor II and insulin genes are contiguous. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 6450–6454 (1985).
Reeve, A.E. et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factor-ll transcripts in Wilms tumour. Nature 317, 258–260 (1985).
Julier, C. et al. lnsulin-IGF2 region on chromosome 11p encodes a gene implicated in HLA-DR4-dependent diabetes susceptibility. Nature 354, 155–159 (1991).
Tadokoro, K., Fujii, H., Inoue, T. & Yamada, M. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for detection of Apal polymorphism at the insulin like growth factor II gene (IGF2). Nucl. Acids Res. 19, 6967 (1991).
Zhang, Y. & Tycko, B. Monoallelic expression of the human H19 gene. Nature Genet. 1, 40–44 (1992).
Sussenbach, J.S. et al. Structure and post-trancriptional regulation of expression of the human IGF-I and IGF-II genes. In Modern Concepts of Insulin-like growth factors (ed. Spencer E.M.) 639–654 (Elsevier New York, 1992).
Rachmilewitz, J. et al. A. Parental imprinting of the human H19 gene. FEBS Lett. 309, 25–28 (1992).
Hergersberg, M. Biological aspects of cytosine methylation in eukaryotic cells. Experientia 47, 1171–1185 (1991).
Haig, D. & Graham, C. Genomic imprinting and the strange case of the insulin-like growth factor II receptor. Cell 64, 1045–1046 (1991).
Polychronakos, C. The M6P/IGF-II receptor. in Molecular and cellular biology of the IGFs (eds Raizada M. & LeRoith D.) 369–379 (Plenum Press, New York, 1989).
Ozcelik, T. et al. U. Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide N (SNRPN), an expressed gene in the Prader-Willi syndrome critical region. Nature Genet. 2, 265–269 (1992).
Nicholls, R.D., Knoll, J.H.M., Butler, M.G., Karam, S. & Lalande, M. Genetic imprinting suggested by maternal heterodisomy in non-deletion Prader-Willi syndrome. Nature 342, 281–285 (1989).
Cattanach, B.M. et al. candidate mouse model for Prader-Willi syndrome which shows an absence of Snrpn expression. Nature Genet. 2, 270–274 (1992).
John, S.W.M., Weitzner, G., Rozen, R. & Scriver, C.R. A rapid procedure for extracting DNA from leukocytes. Nucl. Acids Res. 19, 408 (1991).
Chomczynski, P. & Sacchi, N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162, 156–159 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giannoukakis, N., Deal, C., Paquette, J. et al. Parental genomic imprinting of the human IGF2 gene. Nat Genet 4, 98–101 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0593-98
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0593-98
This article is cited by
-
Single-base editing in IGF2 improves meat production and intramuscular fat deposition in Liang Guang Small Spotted pigs
Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology (2023)
-
Conservation and divergence of canonical and non-canonical imprinting in murids
Genome Biology (2023)
-
Comprehensive analysis of TCGA data reveals correlation between DNA methylation and alternative splicing
BMC Genomics (2022)
-
Associations between parental type 2 diabetes risk and offspring birthweight and placental weight: a survival analysis using the Walker cohort
Diabetologia (2022)
-
Genetic causes of growth hormone insensitivity beyond GHR
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders (2021)