Abstract
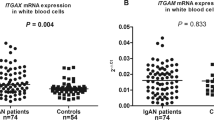
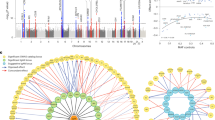
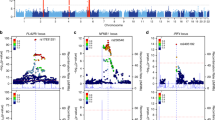
We performed a two-stage genome-wide association study of IgA nephropathy (IgAN) in Han Chinese, with 1,434 affected individuals (cases) and 4,270 controls in the discovery phase and follow-up of the top 61 SNPs in an additional 2,703 cases and 3,464 controls. We identified associations at 17p13 (rs3803800, P = 9.40 × 10−11, OR = 1.21; rs4227, P = 4.31 × 10−10, OR = 1.23) and 8p23 (rs2738048, P = 3.18 × 10−14, OR = 0.79) that implicated the genes encoding tumor necrosis factor (TNFSF13) and α-defensin (DEFA) as susceptibility genes. In addition, we found multiple associations in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) region (rs660895, P = 4.13 × 10−20, OR = 1.34; rs1794275, P = 3.43 × 10−13, OR = 1.30; rs2523946, P = 1.74 × 10−11, OR = 1.21) and confirmed a previously reported association at 22q12 (rs12537, P = 1.17 × 10−11, OR = 0.78). We also found that rs660895 was associated with clinical subtypes of IgAN (P = 0.003), proteinuria (P = 0.025) and IgA levels (P = 0.047). Our findings show that IgAN is associated with variants near genes involved in innate immunity and inflammation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
D'Amico, G. The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. Q. J. Med. 64, 709–727 (1987).
Barratt, J. & Feehally, J. IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 16, 2088–2097 (2005).
Donadio, J.V. & Grande, J.P. IgA nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 347, 738–748 (2002).
Levy, M. & Berger, J. Worldwide perspective of IgA nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 12, 340–347 (1988).
Tsukamoto, Y. et al. Report of the Asian Forum of Chronic Kidney Disease Initiative (AFCKDI) 2007. “Current status and perspective of CKD in Asia”: diversity and specificity among Asian countries. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 13, 249–256 (2009).
Hsu, S.I., Ramirez, S.B., Winn, M.P., Bonventre, J.V. & Owen, W.F. Evidence for genetic factors in the development and progression of IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 57, 1818–1835 (2000).
Hsu, S.I. Racial and genetic factors in IgA nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 28, 48–57 (2008).
Beerman, I., Novak, J., Wyatt, R.J., Julian, B.A. & Gharavi, A.G. The genetics of IgA nephropathy. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 3, 325–338 (2007).
Izzi, C. et al. Familial aggregation of primary glomerulonephritis in an Italian population isolate: Valtrompia study. Kidney Int. 69, 1033–1040 (2006).
Scolari, F. Inherited forms of IgA nephropathy. J. Nephrol. 16, 317–320 (2003).
Kiryluk, K. et al. Genetic studies of IgA nephropathy: past, present, and future. Pediatr. Nephrol. 25, 2257–2268 (2010).
Bisceglia, L. et al. Genetic heterogeneity in Italian families with IgA nephropathy: suggestive linkage for two novel IgA nephropathy loci. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 79, 1130–1134 (2006).
Gharavi, A.G. et al. IgA nephropathy, the most common cause of glomerulonephritis, is linked to 6q22–23. Nat. Genet. 26, 354–357 (2000).
Paterson, A.D. et al. Genome-wide linkage scan of a large family with IgA nephropathy localizes a novel susceptibility locus to chromosome 2q36. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 18, 2408–2415 (2007).
Cao, H.X. et al. Human leukocyte antigen DRB1 alleles predict risk and disease progression of immunoglobulin A nephropathy in Han Chinese. Am. J. Nephrol. 28, 684–691 (2008).
Fennessy, M. et al. HLA-DQ gene polymorphism in primary IgA nephropathy in three European populations. Kidney Int. 49, 477–480 (1996).
Raguénès, O., Mercier, B., Cledes, J., Whebe, B. & Ferec, C. HLA class II typing and idiopathic IgA nephropathy (IgAN): DQB1*0301, a possible marker of unfavorable outcome. Tissue Antigens 45, 246–249 (1995).
Yu, H.H. et al. Genetics and immunopathogenesis of IgA nephropathy. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 41, 198–213 (2011).
Gharavi, A.G. et al. Genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy. Nat. Genet. 43, 321–327 (2011).
Alexopoulos, E., Apostolos, K. & Papadimitriou, M. Increased glomerular and interstitial LFA-1 expression in proteinuric immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 27, 327–333 (1996).
Gupta, S.K. et al. Proteinuria, creatinine clearance, and immune activation in antiretroviral-naive HIV-infected subjects. J. Infect. Dis. 200, 614–618 (2009).
Ganz, T. Defensins: antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 710–720 (2003).
Rehaume, L.M. & Hancock, R.E. Neutrophil-derived defensins as modulators of innate immune function. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 28, 185–200 (2008).
Yokoyama, H. et al. Urinary levels of chemokines (MCAF/MCP-1, IL-8) reflect distinct disease activities and phases of human IgA nephropathy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 63, 493–499 (1998).
Stangou, M. et al. Urinary levels of epidermal growth factor, interleukin-6 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 may act as predictor markers of renal function outcome in immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton) 14, 613–620 (2009).
Saraheimo, M. et al. Increased levels of alpha-defensin (-1, -2 and -3) in type 1 diabetic patients with nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 23, 914–918 (2008).
Vordenbäumen, S. et al. Elevated levels of human beta-defensin 2 and human neutrophil peptides in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 19, 1648–1653 (2010).
Stein, J.V. et al. APRIL modulates B and T cell immunity. J. Clin. Invest. 109, 1587–1598 (2002).
Castigli, E. et al. Impaired IgA class switching in APRIL-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 3903–3908 (2004).
He, B. et al. Intestinal bacteria trigger T cell-independent immunoglobulin A2 class switching by inducing epithelial-cell secretion of the cytokine APRIL. Immunity 26, 812–826 (2007).
Neusser, M.A. et al. Intrarenal production of B-cell survival factors in human lupus nephritis. Mod. Pathol. 24, 98–107 (2011).
Ramanujam, M. et al. Similarities and differences between selective and nonselective BAFF blockade in murine SLE. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 724–734 (2006).
Maruhashi, Y. et al. Analysis of macrophages in urine sediments in children with IgA nephropathy. Clin. Nephrol. 62, 336–343 (2004).
Hei, A.L. et al. Analysis of high-resolution HLA-A, -B, -Cw, -DRB1, and -DQB1 alleles and haplotypes in 718 Chinese marrow donors based on donor-recipient confirmatory typings. Int. J. Immunogenet. 36, 275–282 (2009).
Trachtenberg, E. et al. HLA class I (A, B, C) and class II (DRB1, DQA1, DQB1, DPB1) alleles and haplotypes in the Han from southern China. Tissue Antigens 70, 455–463 (2007).
Kawabata, Y. et al. Differential association of HLA with three subtypes of type 1 diabetes: fulminant, slowly progressive and acute-onset. Diabetologia 52, 2513–2521 (2009).
Tsuchiya, N., Kobayashi, S., Hashimoto, H., Ozaki, S. & Tokunaga, K. Association of HLA-DRB1*0901–DQB1*0303 haplotype with microscopic polyangiitis in Japanese. Genes Immun. 7, 81–84 (2006).
Geetha, D. & Seo, P. Renal transplantation in the ANCA-associated vasculitides. Am. J. Transplant. 7, 2657–2662 (2007).
Berthoux, F.C. et al. HLA-Bw35 and mesangial IgA glomerulonephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 298, 1034–1035 (1978).
Berthoux, F.C., Alamartine, E., Pommier, G. & Lepetit, J.C. HLA and IgA nephritis revisited 10 years later: HLA-B35 antigen as a prognostic factor. N. Engl. J. Med. 319, 1609–1610 (1988).
Chen, J., Niaudet, P. & Levy, M. Schonlein-Henoch purpura and IgA nephropathy. in Renal Pathology (eds. C. Tisher & B. Brenner) 507–508 (Lippincott, Philadelphia, 1994).
Niaudet, P. & Levy, M. Schonlein-Henoch purpura and IgA nephropathy. in Renal Pathology (Tisher, C. & Brenner, B., eds.) 507–508 (Lippincott, Philadelphia, 1994).
Purcell, S. et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 559–575 (2007).
Price, A.L. et al. Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 38, 904–909 (2006).
Steinhaus, H. Sur la division des corps matériels en parties. Bull. Acad. Polon. Sci. (in French) 4, 801–804 (1957).
Barrett, J.C., Fry, B., Maller, J. & Daly, M.J. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21, 263–265 (2005).
R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing (Vienna, 2008).
Browning, S.R. & Browning, B.L. Rapid and accurate haplotype phasing and missing-data inference for whole-genome association studies by use of localized haplotype clustering. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 1084–1097 (2007).
de Bakker, P.I. et al. A high-resolution HLA and SNP haplotype map for disease association studies in the extended human MHC. Nat. Genet. 38, 1166–1172 (2006).
Pereyra, F. et al. The major genetic determinants of HIV-1 control affect HLA class I peptide presentation. Science 330, 1551–1557 (2010).
Howie, B.N., Donnelly, P. & Marchini, J. A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet. 5, e1000529 (2009).
Marchini, J., Howie, B., Myers, S., McVean, G. & Donnelly, P. A new multipoint method for genome-wide association studies by imputation of genotypes. Nat. Genet. 39, 906–913 (2007).
International HapMap Consortium. The International HapMap Project. Nature 426, 789–796 (2003).
1000 Genomes Project Consortium. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature 467, 1061–1073 (2010).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all the subjects and healthy volunteers who participated in this work. We thank the staff in The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University for help with sample collection, DNA extraction and sample storage; W.Y. Meah, X. Chen, H.B. Toh, C.H. Wong, P.L. Ng and I.D. Irwan for performing the genotyping; Z.X. Zhang and Z. B. Hu for providing the control samples in the validation study and R. Johnson for reviewing the manuscript and providing constructive suggestions. This work was funded by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 program) (2012CB517700-2012CB517706), Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (81130012), National Natural Science Foundation of China for Distinguished Young Scholars (30925019) and the Agency for Science & Technology and Research of Singapore (A*STAR) (to J.-J.L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.Z., Z.-H.L., M.L., X.W., J.-Q.W., J.C., R.-S.L., J.-X.W., Z.-S.L., L.Z., T.-Q.L. and X.-J.H. performed clinical characterization and recruitment of subjects and contributed samples; X.W., X.-Q.T., Z.-J.L., L.F. and W.W. prepared DNA; M.L. and X.-Y.Y. performed experiments. J.-J.L., H.-Q.L., K.-S.S. and M.L. analyzed data; Y.L., J.-N.F. and L.-D.S. contributed to analytical support and discussion; X.-Q.Y. and X.-J.Z. provided the platform and organized the study; J.-J.L., X.-Q.Y. and M.L. prepared the manuscript; J.-J.L. and X.-Q.Y. conceived and supervised the project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Tables 1–13 and Supplementary Figures 1–6 (PDF 1638 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, XQ., Li, M., Zhang, H. et al. A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies multiple susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy. Nat Genet 44, 178–182 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.1047
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.1047
This article is cited by
-
Differences of clinicopathological characteristics and outcomes of IgA nephropathy patients with and without nephrotic syndrome
International Urology and Nephrology (2024)
-
How to take advantage of easily available biomarkers in patients with IgA nephropathy: IgA and C3 in serum and kidney biopsies
Pediatric Nephrology (2023)
-
Omics are Getting Us Closer to Understanding IgA Nephropathy
Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis (2023)
-
Association of genetic polymorphisms in IL-23R and IL-17A with the susceptibility to IgA nephropathy in a Chinese Han population
Genes & Immunity (2022)
-
Single-cell RNA-sequencing reveals distinct immune cell subsets and signaling pathways in IgA nephropathy
Cell & Bioscience (2021)