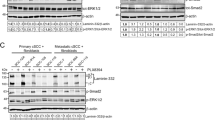
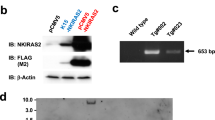
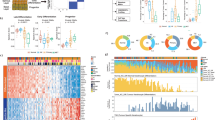
Abstract
The nuclear factor NF-κB and oncogenic Ras can alter proliferation in epidermis, the most common site of human cancer1,2. These proteins are implicated in epidermal squamous cell carcinoma in mice3,4,5, however, the potential effects of altering their function are uncertain. Whereas inhibition of NF-κB enhances apoptosis in certain tumours6, blockade of NF-κB predisposes murine skin to squamous cell carcinoma5,7. Because therapeutics inhibiting Ras and NF-κB pathways are being developed to treat human cancer8,9, it is essential to assess the effects of altering these regulators. The medical relevance of murine studies is limited, however, by differences between mouse and human skin, and by the greater ease of transforming murine cells. Here we show that in normal human epidermal cells both NF-κB and oncogenic Ras trigger cell-cycle arrest. Growth arrest triggered by oncogenic Ras can be bypassed by IκBα-mediated blockade of NF-κB, generating malignant human epidermal tissue resembling squamous cell carcinoma. Human cell tumorigenesis is dependent on laminin 5 and α6β4 integrin. Thus, IκBα circumvents restraints on growth promotion induced by oncogenic Ras and can act with Ras to induce invasive human tissue neoplasia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller, D. L. & Weinstock, M. A. Nonmelanoma skin cancer in the United States: incidence. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 30, 774–778 (1994)
Alam, M. & Ratner, D. Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 344, 975–983 (2001)
Yuspa, S. H. The pathogenesis of squamous cell cancer: lessons learned from studies of skin carcinogenesis. The thirty-third G. H. A. Clowes Memorial Award Lecture. Cancer Res. 54, 1178–1189 (1994)
Pazzaglia, S. et al. Analysis of c-Ha-ras gene mutations in skin tumors induced in carcinogenesis-susceptible and carcinogenesis-resistant mice by different two-stage protocols or tumour promoter alone. Mol. Carcinog. 30, 111–118 (2001)
van Hogerlinden, M., Rozell, B. L., Ahrlund-Richter, L. & Toftgard, R. Squamous cell carcinomas and increased apoptosis in skin with inhibited Rel/nuclear factor-κB signaling. Cancer Res. 59, 3299–3303 (1999)
Yamamoto, Y. & Gaynor, R. B. Therapeutic potential of inhibition of the NF-κB pathway in the treatment of inflammation and cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 107, 135–142 (2001)
Seitz, C. S., Lin, Q., Deng, H. & Khavari, P. A. Alterations in NF-κB function in transgenic epithelial tissue demonstrate a growth inhibitory role for NF-κB. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 2307–2312 (1998)
Karin, M., Cao, Y., Greten, F. R. & Li, Z. W. NF-κB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit. Nature Rev. Cancer 2, 301–310 (2002)
Adjei, A. A. Blocking oncogenic Ras signaling for cancer therapy. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 93, 1062–1074 (2001)
Van Antwerp, D. J., Martin, S. J., Kafri, T., Green, D. R. & Verma, I. M. Suppression of TNF-α-induced apoptosis by NF-κB. Science 274, 787–789 (1996)
Robbins, P. B. et al. In vivo restoration of laminin 5 β3 expression and function in junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 5193–5198 (2001)
Mayo, M. W. et al. Requirement of NF-κB activation to suppress p53-independent apoptosis induced by oncogenic Ras. Science 278, 1812–1815 (1997)
Cogswell, P. C., Guttridge, D. C., Funkhouser, W. K. & Baldwin, A. S. Jr Selective activation of NF-κB subunits in human breast cancer: potential roles for NF-κB2/p52 and for Bcl-3. Oncogene 19, 1123–1131 (2000)
Mitchell, C. E., Belinsky, S. A. & Lechner, J. F. Detection and quantitation of mutant K-ras codon 12 restriction fragments by capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 224, 148–153 (1995)
Seitz, C. S., Deng, H., Hinata, K., Lin, Q. & Khavari, P. A. Nuclear factor κB subunits induce epithelial cell growth arrest. Cancer Res. 60, 4085–4092 (2000)
Lazarov, M. et al. CDK4 coexpression with Ras generates malignant human epidermal tumorigenesis. Nature Med. 8, 1105–1114 (2002)
Bonni, A. et al. Cell survival promoted by the Ras–MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Science 286, 1358–1362 (1999)
Stambolic, V., Mak, T. W. & Woodgett, J. R. Modulation of cellular apoptotic potential: contributions to oncogenesis. Oncogene 18, 6094–6103 (1999)
Elenbaas, B. et al. Human breast cancer cells generated by oncogenic transformation of primary mammary epithelial cells. Genes Dev. 15, 50–65 (2001)
Watt, F. M. Role of integrins in regulating epidermal adhesion, growth and differentiation. EMBO J. 21, 3919–3926 (2002)
Mercurio, A. M. & Rabinovitz, I. Towards a mechanistic understanding of tumour invasion—lessons from the α6β4 integrin. Semin. Cancer Biol. 11, 129–141 (2001)
Savoia, P., Trusolino, L., Pepino, E. & Marchisio, P. C. Expression and topography of integrins and basement membrane proteins in epidermal carcinomas: basal but not squamous cell carcinomas display loss of α6β4 and BM-600/nicein. J. Invest. Dermatol. 101, 352–358 (1993)
Nordemar, S. et al. Laminin-5 as a predictor of invasiveness in cancer in situ lesions of the larynx. Anticancer Res. 21, 509–512 (2001)
Dajee, M., Tarutani, M., Deng, H., Cai, T. & Khavari, P. A. Epidermal Ras blockade demonstrates spatially localized Ras promotion of proliferation and inhibition of differentiation. Oncogene 21, 1527–1538 (2002)
Marinkovich, M. P., Herron, G. S., Khavari, P. A. & Bauer, E. A. Dermatology in General Medicine (ed. Freedberg, I. M.) 690–702 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1999)
Zimonjic, D., Brooks, M. W., Popescu, N., Weinberg, R. A. & Hahn, W. C. Derivation of human tumour cells in vitro without widespread genomic instability. Cancer Res. 61, 8838–8844 (2001)
Ghosh, S. & Karin, M. Missing pieces in the NF-κB puzzle. Cell 109 (Suppl.), S81–S96 (2002)
Pruitt, K. & Der, C. J. Ras and Rho regulation of the cell cycle and oncogenesis. Cancer Lett. 171, 1–10 (2001)
Wick, M., Zubov, D. & Hagen, G. Genomic organization and promoter characterization of the gene encoding the human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT). Gene 232, 97–106 (1999)
Marinkovich, M. P., Lunstrum, G. P. & Burgeson, R. E. The anchoring filament protein kalinin is synthesized and secreted as a high molecular weight precursor. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 17900–17906 (1992)
Acknowledgements
We thank H. Gladstone, M. Cooper, E. Fincher and Z. Cooper for SCC specimens; A. Anguiano for assistance with SKY-FISH; and N. Griffiths and P. Bernstein for administrative support. This work was supported by the US Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development and by grants from the NIH to P.A.K. We acknowledge the generous support of the Epidermolysis Bullosa Research Foundation and the Nu Skin Center for Research at Stanford.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dajee, M., Lazarov, M., Zhang, J. et al. NF-κB blockade and oncogenic Ras trigger invasive human epidermal neoplasia. Nature 421, 639–643 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01283
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01283
This article is cited by
-
Cooperative NF-κB and Notch1 signaling promotes macrophage-mediated MenaINV expression in breast cancer
Breast Cancer Research (2023)
-
NEMO- and RelA-dependent NF-κB signaling promotes small cell lung cancer
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
Advances in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
Nature Reviews Cancer (2023)
-
Nucleoporin downregulation modulates progenitor differentiation independent of nuclear pore numbers
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Sirtuin1 (SIRT1) is involved in the anticancer effect of black raspberry anthocyanins in colorectal cancer
European Journal of Nutrition (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.