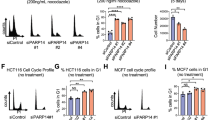
Abstract
THE division cycle of eukaryotic cells is regulated by a family of protein kinases known as the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs)1,2. The sequential activation of individual members of this family and their consequent phosphorylation of critical substrates promotes orderly progression through the cell cycle3,4. The complexes formed by CDK4 and the D-type cyclins have been strongly implicated in the control of cell proliferation during the G1 phase3–6. CDK4 exists, in part, as a multi-protein complex with a D-type cyclin, proliferating cell nuclear antigen and a protein, p21 (refs 7–9). CDK4 associates separately with a protein of Mr 16K, particularly in cells lacking a functional retinoblastoma protein9. Here we report the isolation of a human p16 complementary DNA and demonstrate that p16 binds to CDK4 and inhibits the catalytic activity of the CDK4/cyclin D enzymes. p16 seems to act in a regulatory feedback circuit with CDK4, D-type cyclins and retinoblastoma protein.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Solomon, M., J. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 5, 180–186 (1993).
Nigg, E. A. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 5, 187–193 (1993).
Motokura, T. & Arnold, A. Biochim. biophys. Acta 1155, 63–78 (1993).
Sherr, C. J. Cell 73, 1059–1065 (1993).
Matsushime, H., Roussel, M. F., Ashmun, R. A. & Sherr, C. J. Cell 65, 701–713 (1991).
Matsushime, H. et al. Cell 71, 323–334 (1992).
Xiong, Y., Shang, H. & Beach, D. Cell 71, 505–514 (1992).
Zhang, H., Xiong, Y. & Beach, D. Molec. biol. Cell 4, 897–906 (1993).
Xiong, Y., Zhang, H. & Beach, D. Genes Dev. 7, 1572–1583 (1993).
Fields, S. & Song, O. Nature 340, 245–246 (1989).
Meyerson, M. et al. EMBO J. 11, 2909–2917 (1992).
Kato, J.-Y., Matsushime, H., Hiebert, S. W., Ewen, M. E. & Sherr, C. J. Genes Dev. 7, 331–342 (1993).
Ewen, M. E. et al. Cell 73, 487–497 (1993).
Zhu, L. et al. Genes Dev. 7, 1111–1125 (1993).
Hannon, G. J., Demetrick, D. & Beach, D. Genes Dev. 7, 2378–2391 (1993).
Li, Y., Graham, C., Lacy, S., Duncan, A. M. V. & Whyte, P. Genes Dev. 7, 2366–2377 (1993).
Lukas, J., Pagano, M., Staskova, Z., Draetta, G. & Bartek, J. Oncogene (in the press).
Xiong, Y. et al. Nature 366, 701–704 (1993).
Lees, E. M. & Harlow, E. Molec. cell. Biol. 13, 1194–1201 (1993).
Zheng, X.-F. & Ruderman, J. V. Cell 75, 155–164 (1993).
Michaely, P. & Bennet, V. Trends Cell Biol. 2, 127–129 (1992).
Harlow, E. & Lane, D. Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Habor Laboratory Press, New York, 1988).
Chen, X.-S., Brash, A. R. & Funk, C. D. Eur. J. Biochem. 214, 845–852 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serrano, M., Hannon, G. & Beach, D. A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature 366, 704–707 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/366704a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/366704a0
This article is cited by
-
Differential gene expression (DGE) analysis in persons with a history of giardiasis
AMB Express (2024)
-
The CDK4/6 inhibitor revolution — a game-changing era for breast cancer treatment
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2024)
-
Obesity drives adipose-derived stem cells into a senescent and dysfunctional phenotype associated with P38MAPK/NF-KB axis
Immunity & Ageing (2023)
-
Design principles of improving the dose-response alignment in coupled GTPase switches
npj Systems Biology and Applications (2023)
-
TYMS promotes genomic instability and tumor progression in Ink4a/Arf null background
Oncogene (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.