Abstract
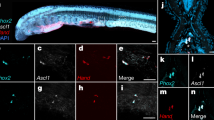
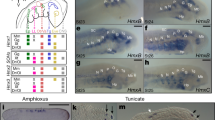
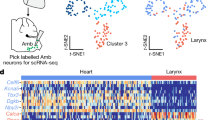
The sympathetic, parasympathetic and enteric ganglia are the main components of the peripheral autonomic nervous system1, and are all derived from the neural crest2. The factors needed for these structures to develop include the transcription factor Mash1 (refs 3,4,5), the glial-derived neurotrophic factor GNDF (refs 6,7,8) and its receptor subunits9,10,11,12, and the neuregulin signalling system13, each of which is essential for the differentiation and survival of subsets of autonomic neurons. Here we show that all autonomic ganglia fail to form properly and degenerate in mice lacking the homeodomain transcription factor Phox2b, as do the three cranial sensory ganglia that are part of the autonomic reflex circuits. In the anlagen of the enteric nervous system and the sympathetic ganglia, Phox2b is needed for the expression of the GDNF-receptor subunit Ret and for maintaining Mash1 expression. Mutant ganglionic anlagen also fail to switch on the genes that encode two enzymes needed for the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter noradrenaline, dopamine-β-hydroxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase, demonstrating that Phox2b regulates the noradrenergic phenotype in vertebrates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langley, J. N. The Autonomic Nervous System (Heffer, Cambridge, (1921).
Le Douarin, N. The Neural Crest (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge and London, (1982).
Guillemot, F.et al. Mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 is required for the early development of olfactory and autonomic neurons. Cell 75, 463–476 (1993).
Blaugrund, E.et al. Distinct subpopulations of enteric neuronal progenitors defined by time of development, sympathoadrenal lineage markers and Mash-1 -dependence. Development 122, 309–320 (1996).
Hirsch, M.-R., Tiveron, M.-C., Guillemot, F., Brunet, J.-F. & Goridis, C. Control of noradrenergic differentiation and Phox2a expression by MASH1 in the central and peripheral nervous system. Development 125, 599–608 (1998).
Moore, M. W.et al. Renal and neuronal abnormalities in mice lacking GDNF. Nature 382, 76–79 (1996).
Pichel, J. G.et al. Defects in enteric innervation and kidney development in mice lacking GDNF. Nature 382, 73–76 (1996).
Sánchez, M. P.et al. Renal agenesis and the absence of enteric neurons in mice lacking GDNF. Nature 382, 70–73 (1996).
Schuchardt, A., D'Agati, V., Larsson-Blomberg, L., Costantini, F. & Pachnis, V. Defects in the kidney and enteric nervous system of mice lacking the tyrosine kinase receptor Ret. Nature 367, 380–383 (1994).
Durbec, P. L., Larsson-Blomberg, L. B., Schuchardt, A., Costantini, F. & Pachnis, V. Common origin and developmental dependence on c-ret of subsets of enteric and sympathetic neuroblasts. Development 122, 349–358 (1996).
Cacalano, G.et al. GFRα1 is an essential receptor component for GDNF in the developing nervous system and kidney. Neuron 21, 53–62 (1998).
Enomoto, H.et al. GFRα1-deficient mice have deficits in the enteric nervous system and kidneys. Neuron 21, 317–324 (1998).
Britsch, S.et al. The ErbB2 and ErbB3 receptors and their ligand, neuregulin-1, are essential for development of the sympathetic nervous system. Genes. Dev. 12, 1825–1836 (1998).
Tiveron, M.-C., Hirsch, M.-R. & Brunet, J.-F. The expression pattern of the transcription factor Phox2 delineates synaptic pathways of the autonomic nervous system. J. Neurosci. 16, 7649–7660 (1996).
Pattyn, A., Morin, X., Cremer, H., Goridis, C. & Brunet, J.-F. Expression and interactions of the two closely related homeobox genes Phox2a and Phox2b during neurogenesis. Development 124, 4065–4075 (1997).
Morin, X.et al. Defects in sensory and autonomic ganglia and absence of locus coeruleus in mice deficient for the homeobox gene Phox2a. Neuron 18, 411–423 (1997).
Kuhlbrodt, K., Herbarth, B., Sock, E., Hermans-Borgmeyer, I. & Wegner, M. Sox10, a novel transcriptional modulator in glial cells. J. Neurosci. 18, 237–250 (1998).
Herbarth, B.et al. Mutation of the Sry-related Sox10 gene in Dominant megacolon, a mouse model for human Hirschsprung disease. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 5161–5165 (1998).
Southard-Smith, E. M., Kos, L. & Pavan, W. J. Sox10 mutation disrupts neural crest development in DOM Hirschsprung mouse model. Nature Genet. 18, 60–64 (1998).
Gavrieli, Y., Sherman, Y. & Ben-Sassoon, S. A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J. Cell Biol. 119, 493–501 (1992).
Young, H. M.et al. Asingle rostro-caudal colonisation of the rodent intestine by enteric neuron precursors is revealed by the expression of Phox2b, Ret and p75, and by explants grown under the kidney capsule or in organ culture. Dev. Biol. 202, 67–84 (1998).
Thomas, S. A., Matsumoto, A. M. & Palmiter, R. D. Noradrenaline is essential for mouse fetal development. Nature 374, 643–646 (1995).
Johnson, J. E., Birren, S. J. & Anderson, D. J. Two rat homologues of Drosophila achaete-scute specifically expressed in neuronal precursors. Nature 346, 858–861 (1990).
Lo, L., Tiveron, M.-C. & Anderson, D. J. MASH1 activates expression of the paired homeodomain transcription factor Phox2a, and couples pan-neuronal and subtype-specific components of autonomic neuronal identity. Development 125, 609–620 (1998).
Fode, C.et al. The bHLH protein NEUROGENIN2 is a determination factor for epibranchial placode-derived sensory neurons. Neuron 20, 483–494 (1998).
Blessing, W. W. in The Lower Brainstem and Bodily Homeostasis 1–18 (Oxford Univ. Press, New York, (1997).
Knittel, T., Kessel, M., Kim, M. H. & Gruss, P. Aconserved enhancer of the human and murine Hoxa-7 gene specifies the anterior boundary of expression during embryonal development. Development 121, 1077–1088 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank the following for probes: V. Pachnis (Ret), M. Wegner (Sox10), F.Guillemot (Mash1), C. Birchmeier (ErbB3); and M.-M. Portier (peripherin). This work was supported by institutional grants from the CNRS and Université de la Méditerranée and by specific grants from the European Community Biotech programme, the Association Française contre les Myopathies, the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer and Rhône-Poulenc S.A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pattyn, A., Morin, X., Cremer, H. et al. The homeobox gene Phox2b is essential for the development of autonomic neural crest derivatives. Nature 399, 366–370 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/20700
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/20700
This article is cited by
-
Loss of G9a does not phenocopy the requirement for Prdm12 in the development of the nociceptive neuron lineage
Neural Development (2024)
-
The sympathetic nervous system arose in the earliest vertebrates
Nature (2024)
-
Hirschsprung disease
Nature Reviews Disease Primers (2023)
-
Transitional care and clinical management of adolescents, young adults, and suspected new adult patients with congenital central hypoventilation syndrome
Clinical Autonomic Research (2023)
-
Chromosome 1p status in neuroblastoma correlates with higher expression levels of miRNAs targeting neuronal differentiation pathway
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.