Abstract
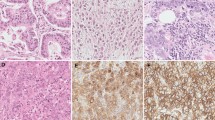
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a highly aggressive malignancy, requiring effective biomarkers for prognosis and therapeutic responsiveness. In this retrospective study of banked pathology material, we investigated the protein expression of MMP-21 in ESCC and its association with clinical significance. MMP-21 protein expression was investigated in 311 cases of ESCC by immunohistochemistry assay. Statistical analysis was utilized to evaluate the association of MMP-21 expression with clinicopathological characteristics and overall survival of patients with ESCC. Results showed that MMP-21 expression was significantly increased in ESCC (P < 0.001). It was also found that MMP-21 expression in ESCC was associated with tumor invasion (P < 0.001), lymph node metastasis (P < 0.001), distant metastasis (P < 0.001) and TNM stage (P < 0.001). Kaplan–Meier analysis showed MMP-21 expression was associated with overall survival of patients with ESCC for patients with tumors of positive MMP-21 staining tend to have worse overall survival (P < 0.001). Multivariate analysis proved that MMP-21 was an independent prognostic factor for overall survival for patients with ESCC (P < 0.001). These results suggested the potential role of MMP-21 in tumor progression and prognosis predication of human ESCC. It might also be a novel molecular target for therapeutic intervention.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2095–128. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0.
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(23):2241–52. doi:10.1056/NEJMra035010.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107.
Holmes RS, Vaughan TL. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of esophageal cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007;17(1):2–9. doi:10.1016/j.semradonc.2006.09.003.
Zhang HZ, Jin GF, Shen HB. Epidemiologic differences in esophageal cancer between Asian and Western populations. Chin J Cancer. 2012;31(6):281–6. doi:10.5732/cjc.011.10390.
Goseki N, Koike M, Yoshida M. Histopathologic characteristics of early stage esophageal carcinoma. A comparative study with gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1992;69(5):1088–93.
Blazeby JM, Brookes S, Griffin SM, Crosby T, Donovan J, Hollingworth W. Quality of life in patients with esophageal squamous cell cancer receiving surgery or definitive chemoradiotherapy: results from a randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2014;259(5):e81. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182480871.
Hou X, Wei JC, Fu JH, Wang X, Zhang LJ, Lin P, et al. Proposed modification of the seventh American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21(1):337–42. doi:10.1245/s10434-013-3265-2.
Bollschweiler E, Holscher AH. Prognosis of early esophageal cancer: differences between squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg. 2007;245(2):334. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000253072.33351.a4.
Chang AC, Ji H, Birkmeyer NJ, Orringer MB, Birkmeyer JD. Outcomes after transhiatal and transthoracic esophagectomy for cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85(2):424–9. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2007.10.007.
Kollarova H, Machova L, Horakova D, Janoutova G, Janout V. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer–an overview article. Biomedical Papers. 2007;151(1):17–20.
Melhado RE, Alderson D, Tucker O. The changing face of esophageal cancer. Cancers. 2010;2(3):1379–404. doi:10.3390/cancers2031379.
Zhang X, Wei J, Zhou L, Zhou C, Shi J, Yuan Q, et al. A functional BRCA1 coding sequence genetic variant contributes to risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34(10):2309–13. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt213.
Ye B, Feng J, Pan X, Yang Y, Ji C, Cheng M, et al. Genetic variant of single-nucleotide polymorphism is associated with risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Genet Test Mol Biomark. 2014;18(1):45–9. doi:10.1089/gtmb.2013.0336.
Markar SR, Bodnar A, Rosales J, Song G, Low DE. The impact of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy on perioperative outcomes, tumor pathology, and survival in clinical stage II and III esophageal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(12):3935–41. doi:10.1245/s10434-013-3137-9.
Xu XL, Ling ZQ, Chen W, Xu YP, Mao WM. The overexpression of VEGF in esophageal cancer is associated with a more advanced TMN stage: a meta-analysis. Cancer Biomark Sect A Dis Markers. 2013;13(2):105–13. doi:10.3233/CBM-130343.
Thrift AP, Nagle CM, Fahey PP, Russell A, Smithers BM, Watson DI, et al. The influence of prediagnostic demographic and lifestyle factors on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma survival. Int J Cancer. 2012;131(5):E759–68. doi:10.1002/ijc.27420.
Xu XL, Ling ZQ, Chen SZ, Li B, Ji WH, Mao WM. The impact of E-cadherin expression on the prognosis of esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis. Dis Esophagus Off J Int Soc Dis Esophagus/ISDE. 2014;27(1):79–86. doi:10.1111/dote.12024.
Matrisian LM. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in matrix remodeling. Trends Genet TIG. 1990;6(4):121–5.
Padmavati P, Savita S, Shivaprasad BM, Kripal K, Rithesh K. mRNA expression of MMP-28 (Epilysin) in gingival tissues of chronic and aggressive periodontitis patients: a reverse transcriptase PCR study. Dis Markers. 2013;35(2):113–8. doi:10.1155/2013/653982.
Visse R, Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res. 2003;92(8):827–39. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000070112.80711.3D.
Stetler-Stevenson WG. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2001;10(2):383–92, x.
Ahokas K, Lohi J, Lohi H, Elomaa O, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Kere J, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-21, the human orthologue for XMMP, is expressed during fetal development and in cancer. Gene. 2002;301(1–2):31–41.
Overall CM, Lopez-Otin C. Strategies for MMP inhibition in cancer: innovations for the post-trial era. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(9):657–72. doi:10.1038/nrc884.
Ahokas K, Lohi J, Illman SA, Llano E, Elomaa O, Impola U, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-21 is expressed epithelially during development and in cancer and is up-regulated by transforming growth factor-beta1 in keratinocytes. Lab Investig J Tech Methods Pathol. 2003;83(12):1887–99.
Ahokas K, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Sihvo E, Isaka K, Salo J, Saarialho-Kere U. Matrix metalloproteinases 21 and 26 are differentially expressed in esophageal squamous cell cancer. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med. 2006;27(3):133–41. doi:10.1159/000092774.
Marchenko GN, Marchenko ND, Strongin AY. The structure and regulation of the human and mouse matrix metalloproteinase-21 gene and protein. Biochem J. 2003;372(Pt 2):503–15. doi:10.1042/BJ20030174.
Skoog T, Ahokas K, Orsmark C, Jeskanen L, Isaka K, Saarialho-Kere U. MMP-21 is expressed by macrophages and fibroblasts in vivo and in culture. Exp Dermatol. 2006;15(10):775–83. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.2006.00460.x.
Huang Y, Li W, Chu D, Zheng J, Ji G, Li M, et al. Overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase-21 is associated with poor overall survival of patients with colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest Surg Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract. 2011;15(7):1188–94. doi:10.1007/s11605-011-1519-5.
Pu Y, Wang L, Wu H, Feng Z, Wang Y, Guo C. High MMP-21 expression in metastatic lymph nodes predicts unfavorable overall survival for oral squamous cell carcinoma patients with lymphatic metastasis. Oncol Rep. 2014;. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3124.
Wu T, Li Y, Lu J, Qiao Q, Bao G, Wang N, et al. Increased MMP-21 expression is associated with poor overall survival of patients with gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 2013;30(1):323. doi:10.1007/s12032-012-0323-8.
Boyd S, Virolainen S, Parssinen J, Skoog T, van Hogerlinden M, Latonen L, et al. MMP-10 (Stromelysin-2) and MMP-21 in human and murine squamous cell cancer. Exp Dermatol. 2009;18(12):1044–52. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.2009.00901.x.
Bister V, Skoog T, Virolainen S, Kiviluoto T, Puolakkainen P, Saarialho-Kere U. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases-21 and -26 and TIMP-4 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2007;20(11):1128–40. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800956.
Kuivanen T, Ahokas K, Virolainen S, Jahkola T, Holtta E, Saksela O, et al. MMP-21 is upregulated at early stages of melanoma progression but disappears with more aggressive phenotype. Virchows Archiv Int J Pathol. 2005;447(6):954–60. doi:10.1007/s00428-005-0046-8.
Conflict of interests
We declared no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Zhengwei Zhao and Lingling Yan have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., Yan, L., Li, S. et al. Increased MMP-21 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with progression and prognosis. Med Oncol 31, 91 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0091-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0091-8