Abstract
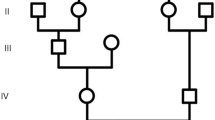
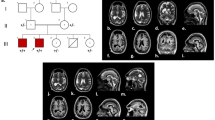
Human autosomal recessive primary microcephaly (MCPH) is a rare genetic disorder in which affected individuals are born with reduced brain size. MCPH is genetically heterogeneous, with six loci and four genes reported to date. Mutations in the ASPM gene at the MCPH5 locus appear to be the most common cause of MCPH. For this study, 33 Pakistani families with primary microcephaly were enrolled. Genotyping using microsatellite markers linked to the six known MCPH loci showed the linkage of 18 families to the MCPH5 locus, two to the MCPH2 locus, two to the MCPH4 locus, and one to the MCPH6 locus. The remaining ten families were not linked to any of the known loci. Families linked to the MCPH5 locus were further subjected to screening of the ASPM gene with direct DNA sequencing. Two previously reported variants, 3978G>A (W1326X) and 9557C>G (S3186X), were observed in five Pakistani families. Four novel nonsynonymous sequence variants, 9118insCATT, 9238A>T (L3080X), 9539A>C (Q3180P), and 1260delTCAAGTC, were found to segregate within four families, but were not observed in 200 Pakistani control chromosomes. One of the variants, 9539A>C (Q3180P), occurred in the IQ 79 domain, but its functional significance awaits definition.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woods CG, Bond J, Enard W (2005) Autosomal recessive primary microcephaly (MCPH): a review of clinical, molecular, and evolutionary findings. Am J Hum Genet 76:717–728
McCreary BD, Rossiter JP, Robertson DM (1996) Recessive (true) microcephaly: a case report with neuropathological observations. J Intellect Disabil Res 40:66–70
Mochida GH, Walsh CA (2001) Molecular genetics of human microcephaly. Curr Opin Neurol 14:151–156
Roberts E, Hampshire DJ, Pattison L, Springell K, Jafri H, Corry P, Mannon J, Rashid Y, Crow Y, Bond J, Woods CG (2002) Autosomal recessive primary microcephaly: an analysis of locus heterogeneity and phenotypic variation. J Med Genet 39:718–721
Jackson AP, McHale DP, Campbell DA, Jafri H, Rashid Y, Mannan J, Karbani G, Corry P, Levene MI, Mueller RF, Markham AF, Lench NJ, Woods CG (1998) Primary autosomal recessive microcephaly (MCPH1) maps to chromosome 8p22-pter. Am J Hum Genet 63:541–546
Roberts E, Jackson AP, Carradice AC, Deeble VJ, Mannan J, Rashid Y, Jafri H, McHale DP, Markham AF, Lench NJ, Woods CG (1999) The second locus for autosomal recessive primary microcephaly (MCPH2) maps to chromosome 19q13.1–13.2. Eur J Hum Genet 7:815–820
Moynihan L, Jackson AP, Roberts E, Karbani G, Lewis I, Corry P, Turner G, Mueller RF, Lench NJ, Woods CG (2000) A third novel locus for primary autosomal recessive microcephaly maps to chromosome 9q34. Am J Hum Genet 66:724–727
Jamieson CR, Govaerts C, Abramowicz MJ (1999) Primary autosomal recessive microcephaly: homozygosity mapping of MCPH4 to chromosome 15. Am J Hum Genet 65:1465–1469
Pattison L, Crow YJ, Deeble VJ, Jackson AP, Jafri H, Rashid Y, Roberts E, Woods CG (2000) A fifth locus for primary autosomal recessive microcephaly maps to chromosome 1q31. Am J Hum Genet 67:1578–1580
Leal GF, Roberts E, Silva EO, Costa SMR, Hampshire DJ, Woods CG (2003) A novel locus for autosomal recessive primary microcephaly maps to 13q12.2. J Med Genet 40:540–542
Bond J, Roberts E, Mochida GH, Hampshire DJ, Scott S, Askham JM, Springell K, Mahadevan M, Crow YJ, Markham AF, Walsh CA, Woods CG (2002) ASPM is a major determinant of cerebral cortical size. Nat Genet 32:316–320
Jackson AP, Eastwood H, Bell SM, Adu J, Toomes C, Carr IM, Roberts E, Hampshire DJ, Crow YJ, Mighell AJ, Karbani G, Jafri H, Rashid Y, Mueller RF, Markham AF, Woods CG (2002) Identification of microcephalin, a protein implicated in determining the size of the human brain. Am J Hum Genet 71:136–142
Bond J, Roberts E, Springell K, Lizarraga SB, Scott S, Higgins J, Hampshire DJ, Morrison EE, Leal GF, Silva EO, Costa SMR, Baralle D, Raponi M, Karbani G, Rashid Y, Jafri H, Bennett C, Corry P, Walsh CA, Woods CG (2005) A centrosomal mechanism involving CDK5RAP2 and CENPJ controls brain size. Nat Genet 37:353–355
Bond J, Scott S, Hampshire DJ, Springell K, Corry P, Abramowicz MJ, Mochida GH, Hennekam RCM, Maher ER, Fryns JP, Alswaid A, Jafri H, Rashid Y, Mubaidin A, Walsh CA, Roberts E, Woods CG (2003) Protein-truncating mutations in ASPM cause variable reduction in brain size. Am J Hum Genet 73:1170–1177
Kumar A, Blanton SH, Babu M, Markandaya M, Girimaji SC (2004) Genetic analysis of primary microcephaly in Indian families: novel ASPM mutations. Clin Genet 66:341–348
Pichon B, Vankerckhove S, Bourrouillou G, Duprez L, Abramowicz MJ (2004) A translocation breakpoint disrupts the ASPM gene in a patient with primary microcephaly. Eur J Hum Genet 12:419–421
Shen J, Eyaid W, Mochida GH, Al-Moayyad F, Bodell A, Woods CG, Walsh CA (2005) ASPM mutations identified in patients with primary microcephaly and seizures. J Med Genet 42:725–729
Mekel-Bobrov N, Gilbert SL, Evans PD, Vallender EJ, Anderson JR, Hudson RR, Tishkoff SA, Lahn BT (2005) Ongoing adaptive evolution of ASPM, a brain size determinant in Homo sapiens. Science 309:1720–1722
Chenn A, Walsh CA (2003) Increased neuronal production, enlarged forebrain and cytoarchitectural distortions in beta-catenin overexpressing transgenic mice. Cereb Cortex 13:599–606
Bond J, Woods CG (2006) Cytoskeletal genes regulating brain size. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18:95–101
Broman KW, Murray JC, Scheffield VC, White RL, Weber JL (1998) Comprehensive human genetic maps: individual and sex specific variation in recombination. Am J Hum Genet 63:861–869
Wallerman O, Eeghen AV, Kate LPT, Wadelius C (2003) Evidence for a second gene for primary microcephaly at MCPH 5 on chromosome 1. Hereditas 139:64–67
Kouprina N, Pavlicek A, Collins NK, Nakano M, Noskov VN, Ohzeki JI, Mochida GH, Risinger JI, Goldsmith P, Gunsior M, Solomon G, Gersch W, Kim JH, Barrett JC, Walsh CA, Jurka J, Masumoto H, Larionov V (2005) The microcephaly ASPM gene is expressed in proliferating tissues and encodes for a mitotic spindle protein. Hum Mol Genet 14:1–11
Bahler M, Rhoads A (2002) Calmodulin signaling via the IQ motif. FEBS Lett 513:107–113
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the members of the families for their cooperation. The work presented was funded by the Islamic Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation, Rabat, Morocco; the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Islamabad, Pakistan; the Herbert and Florence C. Wenske Foundation; the Vena E. Schaff Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Research Fund; the Abbott Labs Duane and Susan Burnham Professorship; and the Ralph and Marian Falk Medical Research Trust. Asma Gul, Muhammad Jawad Hassan, and Muhammad Salman Chishti were supported by indigenous Ph.D. fellowships from HEC, Islamabad, Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gul, A., Hassan, M.J., Mahmood, S. et al. Genetic studies of autosomal recessive primary microcephaly in 33 Pakistani families: novel sequence variants in ASPM gene. Neurogenetics 7, 105–110 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-006-0042-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-006-0042-4