Abstract
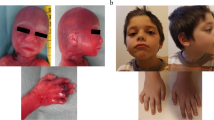
To investigate whether submicroscopic chromosomal deletions or duplications can be causative of unclear syndromic nephropathies, we analyzed ten patients with congenital abnormalities of the kidney and urinary tract or glomerulopathies combined with important extrarenal anomalies by whole-genome array-based comparative genomic hybridization. In a 14-year-old girl presenting with hematuria, proteinuria, mental retardation (MR), sensorineural hearing loss, dysmorphisms, and epilepsy, we detected a microdeletion in chromosome Xq22.3-q23. This deletion was verified and characterized by fluorescence in situ hybridization and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification analyses, found to be de novo, uniallelic and 3.3 Mb in size. Electron microscopy of a kidney biopsy showed glomerular basement membrane thinning and segmental splitting of the lamina densa compatible with Alport syndrome. Cranial magnetic resonance and diffusion tensor imaging detected a severe neuronal migration disorder with double cortex formation and pronounced reduction of the fronto-occipital tract system. Thus, in one of ten patients with unclear syndromic nephropathies we identified a previously undescribed contiguous gene syndrome at Xq22.3-q23. The microdeletion contains the X-linked Alport syndrome gene COL4A5, the MR genes FACL4 and PAK3, and parts of the X-chromosomal lissencephaly gene DCX associated with double cortex formation in girls, MR, and epilepsy. The phenotype in our patient combines features of the Alport–MR contiguous gene syndrome with lissencephaly.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Limwongse C, Cassidy SB (2003) Syndromes and malformations of the urinary tract. Avner ED, Harmon WE, Niaudet P (eds) Pediatric nephrology, 5th edn. Lippincott Raven, Philadelphia, Baltimore, New York, London
Solinas-Toldo S, Lampel S, Stilgenbauer S, Nickolenko J, Benner A, Dohner H, Cremer T, Lichter P (1997) Matrix-based comparative genomic hybridization: biochips to screen for genomic imbalances. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 20:399–407
Pinkel D, Segraves R, Sudar D, Clark S, Poole I, Kowbel D, Collins C, Kuo WL, Chen C, Zhai Y, Dairkee SH, Ljung BM, Gray JW, Albertson DG (1998) High resolution analysis of DNA copy number variation using comparative genomic hybridization to microarrays. Nat Genet 20:207–211
Müller D, Klopocki E, Neumann LM, Mundlos S, Taupitz M, Schulze I, Ropers HH, Querfeld U, Ullmann R (2006) A complex phenotype with cystic renal disease. Kidney Int 70:1656–1660
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Fiegler H, Carr P, Douglas EJ, Burford DC, Hunt S, Scott CE, Smith J, Vetrie D, Gorman P, Tomlinson IP, Carter NP (2003) DNA microarrays for comparative genomic hybridization based on DOP-PCR amplification of BAC and PAC clones. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 36:361–374
Zielinski B, Gratias S, Toedt G, Mendrzyk F, Stange DE, Radlwimmer B, Lohmann DR, Lichter P (2005) Detection of chromosomal imbalances in retinoblastoma by matrix-based comparative genomic hybridization. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 43:294–301
Fensterer H, Radlwimmer B, Strater J, Buchholz M, Aust DE, Julie C, Radvanyi F, Nordlinger B, Belluco C, Van Cutsem E, Kohne CH, Kestler HA, Schwaenen C, Nessling M, Lutz MP, Lichter P, Gress TM, EORTC Gastrointestinal (GI) Group (2007) Matrix-comparative genomic hybridization from multicenter formalin-fixed paraffin embedded colorectal cancer tissue blocks. BMC Cancer 7:58
Jiang H, van Zijl PC, Kim J, Pearlson GD, Mori S (2006) DtiStudio: resource program for diffusion tensor computation and fiber bundle tracking. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 81:106–116
Raven JC, Raven J, Court JH, Bullheller S, Häcker H (2006) Raven’s progressive matrices and vocabulary scales, 3rd edn. Harcourt Test Services, Frankfurt
Vissers LE, de Vries BB, Osoegawa K, Janssen IM, Feuth T, Choy CO, Straatman H, van der Vliet W, Huys EH, van Rijk A, Smeets D, van Ravenswaaij-Arts CM, Knoers NV, van der Burgt I, de Jong PJ, Brunner HG, van Kessel AG, Schoenmakers EF, Veltman JA (2003) Array-based comparative genomic hybridization for the genomewide detection of submicroscopic chromosomal abnormalities. Am J Hum Genet 73:1261–1270
Shaw-Smith C, Redon R, Rickman L, Rio M, Willatt L, Fiegler H, Firth H, Sanlaville D, Winter R, Colleaux L, Bobrow M, Carter NP (2004) Microarray based comparative genomic hybridisation (array-CGH) detects submicroscopic chromosomal deletions and duplications in patients with learning disability/mental retardation and dysmorphic features. J Med Genet 41:241–248
De Vries BB, Pfundt R, Leisink M, Koolen DA, Vissers LE, Janssen IM, Reijmersdal S, Nillesen WM, Huys EH, Leeuw N, Smeets D, Sistermans EA, Feuth T, van Ravenswaaij-Arts CM, van Kessel AG, Schoenmakers EF, Brunner HG, Veltman JA (2005) Diagnostic genome profiling in mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 77:606–616
Menten B, Maas N, Thienpont B, Buysse K, Vandesompele J, Melotte C, de Ravel T, Van Vooren S, Balikova I, Backx L, Janssens S, De Paepe A, De Moor B, Moreau Y, Marynen P, Fryns JP, Mortier G, Devriendt K, Speleman F, Vermeesch JR (2006) Emerging patterns of cryptic chromosomal imbalance in patients with idiopathic mental retardation and multiple congenital anomalies: a new series of 140 patients and review of published reports. J Med Genet 43:625–633
Engels H, Brockschmidt A, Hoischen A, Landwehr C, Bosse K, Walldorf C, Toedt G, Radlwimmer B, Propping P, Lichter P, Weber RG (2007) DNA microarray analysis identifies candidate regions and genes in unexplained mental retardation. Neurology 68:743–750
Kashtan CE (2008) Alport syndrome and thin basement membrane nephropathy. Geary DF, Schaefer F (eds) Comprehensive Pediatric Nephrology, 1st edn. Mosby Elsevier, Philadelphia
Alport AC (1927) Hereditary familial congenital haemorrhagic nephritis. Br Med J 1:504–506
Barker DF, Hostikka SL, Zhou J, Chow LT, Oliphant AR, Gerken SC, Gregory MC, Skolnick MH, Atkin CL, Tryggvason K (1990) Identification of mutations in the COL4A5 collagen gene in Alport syndrome. Science 248:1224–1227
Lemmink HH, Schroder CH, Monnens LAH, Smeets HJM (1997) The clinical spectrum of type IV collagen mutations. Hum Mut 9:477–499
Zhou J, Mochizuki T, Smeets H, Antignac C, Laurila P, de Paepe A, Tryggvason K, Reeders ST (1993) Deletion of the paired alpha 5(IV) and alpha 6(IV) collagen genes in inherited smooth muscle tumors. Science 261:1167–1169
Heidet L, Dahan K, Zhou J, Xu Z, Cochat P, Gould JDM, Leppig KA, Proesmans W, Guyot C, Roussel B, Tryggvason K, Grunfeld JP, Gubler MC, Antignac C (1995) Deletions of both alpha 5(IV) and alpha 6(IV) collagen genes in Alport syndrome and in Alport syndrome associated with smooth muscle tumours. Hum Mol Genet 4:99–108
Heiskari N, Zhang X, Zhou J, Leinonen A, Barker D, Gregory M, Atkin CL, Netzer KO, Weber M, Reeders S, Gronhagenriska C, Neumann HPH, Trembath R, Tryggvason K (1996) Identification of 17 mutations in ten exons in the COL4A5 collagen gene, but no mutations found in four exons in COL4A6: a study of 250 patients with hematuria and suspected of having Alport syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:702–709
Cochat P, Guibaud P, Torres R, Roussel B, Guarner V, Larbre F (1988) Diffuse leiomyomatosis in Alport syndrome. J Pediatr 113:339–343
Lane W, Robson M, Lowry RB (1994) X-linked recessive nephritis with mental retardation, sensorineural hearing loss, and macrocephaly. Clin Genet 45:314–317
Jonsson JJ, Renieri A, Gallagher PG, Kashtan CE, Cherniske EM, Bruttini M, Piccini M, Vitelli F, Ballabio A, Pober BR (1998) Alport syndrome, mental retardation, midface hypoplasia, and elliptocytosis: a new X linked contiguous gene deletion syndrome? J Med Genet 35:273–278
Piccini M, Vitelli F, Bruttini M, Pober BR, Jonsson JJ, Villanova M, Zollo M, Borsani G, Ballabio A, Renieri A (1998) FACL4, a new gene encoding long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 4, is deleted in a family with Alport syndrome, elliptocytosis, and mental retardation. Genomics 47:350–358
Vitelli F, Piccini M, Caroli F, Franco B, Malandrini A, Pober B, Jonsson J, Sorrentino V, Renieri A (1999) Identification and characterization of a highly conserved protein absent in the Alport syndrome (A), mental retardation (M), midface hypoplasia (M), and elliptocytosis (E) contiguous gene deletion syndrome (AMME). Genomics 55:335–340
Meloni I, Vitelli F, Pucci L, Lowry RB, Tonlorenzi R, Rossi E, Ventura M, Rizzoni G, Kashtan CE, Pober B, Renieri A (2002) Alport syndrome and mental retardation: clinical and genetic dissection of the contiguous gene deletion syndrome in Xq22.3 (ATS-MR). J Med Genet 39:359–360
Meloni I, Muscettola M, Raynaud M, Longo I, Bruttini M, Moizard MP, Gomot M, Chelly J, des Portes V, Fryns JP, Ropers HH, Magi B, Bellan C, Volpi N, Yntema HG, Lewis SE, Schaffer JE, Renieri A (2002) FACL4, encoding fatty acid-CoA ligase 4, is mutated in nonspecific X-linked mental retardation. Nat Genet 30:436–440
Allen KM, Gleeson JG, Bagrodia S, Partington MW, MacMillan JC, Cerione RA, Mulley JC, Walsh CA (1998) PAK3 mutation in nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation. Nat Genet 20:25–30
Bienvenu T, des Portes V, McDonell N, Carrie A, Zemni R, Couvert P, Ropers HH, Moraine C, van Bokhoven H, Fryns JP, Allen K, Walsh CA, Boue J, Kahn A, Chelly J, Beldjord C (2000) Missense mutation in PAK3, R67C, causes X-linked nonspecific mental retardation. Am J Med Genet 93:294–298
Gedeon AK, Nelson J, Gecz J, Mulley JC (2003) X-linked mild non-syndromic mental retardation with neuropsychiatric problems and the missense mutation A365E in PAK3 X-linked mild non-syndromic mental retardation with neuropsychiatric problems and the missense mutation A365E in PAK3. Am J Med Genet 120A:509–517
Peippo M, Koivisto AM, Sarkamo T, Sipponen M, von Koskull H, Ylisaukko-oja T, Rehnstrom K, Froyen G, Ignatius J, Jarvela I (2007) PAK3 related mental disability: further characterization of the phenotype. Am J Med Genet 143A:2406–2416
Gleeson JG, Allen KM, Fox JW, Lamperti ED, Berkovic S, Scheffer I, Cooper EC, Dobyns WB, Minnerath SR, Ross ME, Walsh CA (1998) Doublecortin, a brain-specific gene mutated in human X-linked lissencephaly and double cortex syndrome, encodes a putative signaling protein. Cell 92:63–72
des Portes V, Pinard JM, Billuart P, Vinet MC, Koulakoff A, Carrie A, Gelot A, Dupuis E, Motte J, Berwald-Netter Y, Catala M, Kahn A, Beldjord C, Chelly J (1998) A novel CNS gene required for neuronal migration and involved in X-linked subcortical laminar heterotopia and lissencephaly syndrome. Cell 92:51–61
Guerrini R, Marini C (2006) Genetic malformations of cortical development. Exp Brain Res 173:322–333
Matsumoto N, Leventer RJ, Kuc JA, Mewborn SK, Dudlicek LL, Ramocki MB, Pilz DT, Mills PL, Das S, Ross ME, Ledbetter DH, Dobyns WB (2001) Mutation analysis of the DCX gene and genotype/phenotype correlation in subcortical band heterotopia. Eur J Hum Genet 9:5–12
Berry-Kravis E, Israel J (1994) X-linked pachygyria and agenesis of the corpus callosum: evidence for an X chromosome lissencephaly locus. Ann Neurol 36:229–233
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the affected individuals and their families for participating in this study and Sabrina Wolf for excellent technical assistance. This paper was presented as a poster at the 14th Congress of the International Pediatric Nephrology Association, Budapest, Hungary, 2007, where it received the Schoepf-Merei Award for the excellent oral poster presentation. This work was supported by the Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung (P11/08//A137/07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. Hoischen and C. Landwehr contributed equally to this study and should both be considered as first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoischen, A., Landwehr, C., Kabisch, S. et al. Array-CGH in unclear syndromic nephropathies identifies a microdeletion in Xq22.3-q23. Pediatr Nephrol 24, 1673–1681 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1184-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1184-z