Abstract
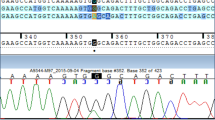
Direct DNA sequencing of the steroid 21-hydroxylase gene (CYP21) revealed two novel mutations in two patients with severe congenital adrenal hyperplasia. The nonsense mutation Trp23Stop (TGG → TGA) was found in a woman with the simple virilizing form of the disease. She was a compound heterozygote, with the previously described Ile173Asn mutation on her other allele. A boy, who developed salt-wasting in the neonatal period, carried an allele with a novel mutation of the canonical splice acceptor site in intron 1 (AG→GG). He was also a compound heterozygote, with the well-known splice mutation in intron 2 on his other allele.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 February 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lajic, S., Wedell, A. An intron 1 splice mutation and a nonsense mutation (W23X) in CYP21 causing severe congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Hum Genet 98, 182–184 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050186
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050186