Abstract
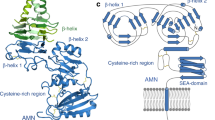
Cubilin is a 460-kDa endocytic receptor coexpressed with megalin, a multiligand receptor of the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene family, at the apical pole of epithelial cells in the renal proximal convoluted tubule, visceral yolk sac, ileum, and placenta. The structure of cubilin is unique: it lacks a transmembrane domain and requires megalin for its internalization. The accumulation of 27 interactive CUB domains provides the potential for multiple, possibly independent interactions and functions. Cubilin is involved in the intestinal absorption of vitamin B12, the catabolism of apolipoprotein A-I by the proximal convoluted tubule and more generally in renal protein reabsorption. The role of cubilin on fetomaternal interfaces is not defined but may be related to its ability to bind and internalize high density lipoproteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozyraki, R. Cubilin, a multifunctional epithelial receptor: an overview. J Mol Med 79, 161–167 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001090100193
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001090100193