Abstract
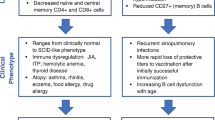
Chromosome 22q11 deletion is the most common chromosomal deletion syndrome and is found in the majority of patients with DiGeorge syndrome and velo-cardio-facial syndrome. Patients with CHARGE syndrome may share similar features. Cardiac malformations, speech delay, and immunodeficiency are the most common manifestations. The immunological phenotype may vary widely between patients. Severe T lymphocyte immunodeficiency is rare—thymic transplantation offers a new approach to treatment, as well as insights into thymic physiology and central tolerance. Combined partial immunodeficiency is more common, leading to recurrent sinopulmonary infection in early childhood. Autoimmunity is an increasingly recognized complication. New insights into pathophysiology are reviewed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kobrynski LJ, Sullivan KE (2007) Velocardiofacial syndrome, DiGeorge syndrome: the chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndromes. Lancet 370:1443–1452
Perez E, Sullivan KE (2002) Chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (DiGeorge and velocardiofacial syndromes). Curr Opin Pediatr 14:678–683
Shprintzen RJ, Higgins AM, Antshel K, Fremont W, Roizen N, Kates W (2005) Velo-cardio-facial syndrome. Curr Opin Pediatr 17:725–730
Yamagashi H, Srivastava D (2003) Unravelling the genetic and developmental mysteries of 22q11 deletion syndrome. Trends Mol Med 9:383–389
Jerome LA, Papaioannou VE (2001) DiGeorge syndrome phenotype in mice mutant for the T box gene, Tbx1. Nat Genet 27:286–291
Cooper MD, Peterson RDA, Good RA (1965) A new concept of the cellular basis of immunity. J Pediatr 67:907–908
de la Chapelle A, Herva R, Koivisto M, Aula P (1981) A deletion in chromosome 22 can cause DiGeorge syndrome. Hum Genet 57:253–256
Kelley RI, Zackai EH, Emanuel BS, Kistenmacher M, Greenberg F, Punnett HH (1982) The association of the DiGeorge anomalad with partial monosomy of chromosome 22. J Pediatr 101:197–200
Driscoll DA, Spinner NB, Budarf ML, McDonald-McGinn DM, Zackai EH, Goldberg RB, Shprintzen RJ, Saal HM, Zonana J, Jones MC (1992) Deletions and microdeletions of 22q11.2 in velo-cardio-fa-cial syndrome. Am J Med Genet 44:261–268
Matsuoka R, Takao A, Kimura M, Imamura S, Kondo C, Joh-o K, Ikeda K, Nishibatake M, Ando M, Momma K (1994) Confirmation that the conotruncal anomaly face syndrome is associated with a deletion within 22q11.2. Am J Med Genet 53:285–289
McDonald-McGinn DM, Driscoll DA, Bason L, Christensen K, Lynch D, Sullivan K, Canning D, Zavod W, Quinn N, Rome J (1995) Autosomal dominant “Opitz” GBBB syndrome due to a 22q11.2 deletion. Am J Med Genet 59:103–113
Devriendt K, Swillen A, Fryns JP (1998) Deletion in chromosome region 22q11 in a child with CHARGE association. Clin Genet 53:408–410
Yagi H, Furutani Y, Hamada H, Sasaki T, Asakawa S, Minoshima S, Ichida F, Joo K, Kimura M, Imamura S, Kamatani N, Momma K, Takao A, Nakazawa M, Shimizu N, Matsuoka R (2003) Role of TBX1 in human del22q11.2 syndrome. Lancet 362:1366–1373
Greenberg F, Valdes C, Rosenblatt HM, Kirkland JL, Ledbetter DH (1986) Hypoparathyroidism and T cell immune defect in a patient with 10p deletion syndrome. J Pediatr 109:489–492
Monaco G, Ciccimarra F, Pignata C, Garofalo S (1989) T cell immunodeficiency in a patient with 10p deletion syndrome. J Pediatr 115:330
Monaco G, Pignata C, Rossi E, Mascellaro O, Cocozza S, Ciccimarra F (1991) DiGeorge anomaly associated with 10p deletion. Am J Med Genet 39:215–216
Sullivan KE, Jawad AF, Randall P, Driscoll DA, Emanuel BS, McDonald-McGinn DM, Zackai EH (1998) Lack of correlation between impaired T cell production, immunodeficiency, and other phenotypic features in chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndromes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 86:141–146
Johnson D, Morrison N, Grant L, Turner T, Fantes J, Connor JM, Murday V (2006) Confirmation of CHD7 as a cause of CHARGE association identified by mapping a balanced chromosome translocation in affected monozygotic twins. J Med Genet 43:280–284
Gennery AR, Slatter MA, Rice J, Hoefsloot LH, Barge D, McLean-Tooke A, Montgomery T, Goodship JA, Burt AD, Flood TJ, Abinun M, Cant AJ, Johnson D (2008) Mutations in CHD7 in patients with CHARGE syndrome cause T-B + natural killer cell+ severe combined immune deficiency and may cause Omenn-like syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol 153:75–80
Carlson C, Sirotkin H, Pandita R, Goldberg R, McKie J, Wadey R, Patanjali SR, Weissman SM, Anyane-Yeboa K, Warburton D, Scrambler P, Shprintzen R, Kucherlapati R, Morrow BE (1997) Molecular definition of 22q11 deletions in 151 velo-cardio-facial syndrome patients. Am J Hum Genet 61:620–629
Edelmann L, Pandita RK, Morrow BE (1999) Low-copy repeats mediate the common 3-Mb deletion in patients with velo-cardio-facial syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 64:1076–1086
Meechan DW, Maynard TM, Gopalakrishna D, Wu Y, LaMantia AS (2007) When half is not enough: gene expression and dosage in the 22q11 deletion syndrome. Gene Expr 13:299–310
Taddei I, Morishima M, Huynh T, Lindsay EA (2001) Genetic factors are major determinants of phenotypic variability in a mouse model of the DiGeorge/del22q11 syndromes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11428–11431
Schinke M, Izumo S (2001) Deconstructing DiGeorge syndrome. Nat Genet 27:238–240
Jerome LA, Papaioannou VE (2001) DiGeorge syndrome phenotype in mice mutant for the T-box gene, Tbx1. Nat Genet 27:286–291
Guris DL, Fantes J, Tara D, Druker BJ, Imamoto A (2001) Mice lacking the homologue of the human 22q11.2 gene CRKL phenocopy neurocristopathies of DiGeorge syndrome. Nat Genet 27:293–298
Guris DL, Duester G, Papaioannou VE, Imamoto A (2006) Dose-dependent interaction of Tbx1 and Crkl and locally aberrant RA signaling in a model of del22q11 syndrome. Dev Cell 10:81–92
van Bueren KL, Papangeli I, Rochais F, Pearce K, Roberts C, Calmont A, Szumska D, Kelly RG, Bhattacharya S, Scambler PJ (2010) Hes1 expression is reduced in Tbx1 null cells and is required for the development of structures affected in 22q11 deletion syndrome. Dev Biol 340:369–380
Marfella CG, Imbalzano AN (2007) The Chd family of chromatin remodelers. Mutat Res 618:30–40
Sillibourne JE, Delaval B, Redick S, Sinah M, Doxsey SJ (2007) Chromatin remodeling proteins interact with pericentrin to regulate centrosome integrity. Mol Biol Cell 18:3667–3680
Aramaki M, Kimura T, Udaka T, Kosaki R, Mitsuhashi T, Okada Y, Takahashi T, Kosaki K (2007) Embryonic expression profile of chicken CHD7, the ortholog of the causative gene for CHARGE syndrome. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 79:50–57
Sanlaville D, Etchevers HC, Gonzales M, Martinovic J, Clément-Ziza M, Delezoide AL, Aubry MC, Pelet A, Chemouny S, Cruaud C, Audollent S, Esculpavit C, Goudefroye G, Ozilou C, Fredouille C, Joye N, Morichon-Delvallez N, Dumez Y, Weissenbach J, Munnich A, Amiel J, Encha-Razavi F, Lyonnet S, Vekemans M, Attié-Bitach T (2006) Phenotypic spectrum of CHARGE syndrome in fetuses with CHD7 truncating mutations correlates with expression during human development. J Med Genet 43:211–217
de Lonlay-Debeney P, Cormier-Daire V, Amiel J, Abadie V, Odent S, Paupe A, Couderc S, Tellier AL, Bonnet D, Prieur M, Vekemans M, Munnich A, Lyonnet S (1997) Features of DiGeorge syndrome and CHARGE association in five patients. J Med Genet 34:986–989
Markert ML, Devlin BH, Alexieff MJ, Li J, McCarthy EA, Gupton SE, Chinn IK, Hale LP, Kepler TB, He M, Sarzotti M, Skinner MA, Rice HE, Hoehner JC (2007) Review of 54 patients with complete DiGeorge anomaly enrolled in protocols for thymus transplantation: outcome of 44 consecutive transplants. Blood 109:4539–4547
Holländer G, Gill J, Zuklys S, Iwanami N, Liu C, Takahama Y (2006) Cellular and molecular events during early thymus development. Immunol Rev 209:28–46
Le Lievre CS, Le Douarin NM (1975) Mesenchymal derivatives of the neural crest: analysis of chimeric quail and chick embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol 34:125–154
Haynes BF, Heinly CS (1995) Early human T cell development: analysis of the human thymus at the time of initial entry of hematopoietic stem cells into the fetal thymic microenvironment. J Exp Med 181:1445–1458
Poliani PL, Facchetti F, Ravanini M, Gennery AR, Villa A, Roifman CM, Notarangelo LD (2009) Early defects in human T-cell development severely affect distribution and maturation of thymic stromal cells: possible implications for the pathophysiology of Omenn syndrome. Blood 114:105–108
Gill J, Malin M, Sutherland J, Gray D, Hollander G, Boyd R (2003) Thymic generation and regeneration. Immunol Rev 195:28–50
Akiyama T, Shimo Y, Yanai H, Qin J, Ohshima D, Maruyama Y, Asaumi Y, Kitazawa J, Takayanagi H, Penninger JM, Matsumoto M, Nitta T, Takahama Y, Inoue J (2008) The tumor necrosis factor family receptors RANK and CD40 cooperatively establish the thymic medullary microenvironment and self-tolerance. Immunity 29:423–437
Zuklys S, Balciunaite G, Agarwal A, Fasler-Kan E, Palmer E, Holländer GA (2000) Normal thymic architecture and negative selection are associated with Aire expression, the gene defective in the autoimmune-polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED). J Immunol 165:1976–1983
Watanabe N, Wang YH, Lee HK, Ito T, Wang YH, Cao W, Liu YJ (2005) Hassall’s corpuscles instruct dendritic cells to induce CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in human thymus. Nature 436:1181–1185
Müller SM, Kohn T, Schulz AS, Debatin KM, Friedrich W (2000) Similar pattern of thymic-dependent T-cell reconstitution in infants with severe combined immunodeficiency after human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-identical and HLA-nonidentical stem cell transplantation. Blood 96:4344–4349
Consortium ***Finnish-German APECED (1997) An autoimmune disease, APECED, caused by mutations in a novel gene featuring two PHD-type zinc-finger domains. Nat Genet 17:399–403
Bennett CL, Christie J, Ramsdell F, Brunkow ME, Ferguson PJ, Whitesell L, Kelly TE, Saulsbury FT, Chance PF, Ochs HD (2001) The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat Genet 27:20–21
Poliani PL, Vermi W, Facchetti F (2009) Thymus microenvironment in human primary immunodeficiency diseases. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 9:489–495
Writzl K, Cale CM, Pierce CM, Wilson LC, Hennekam RC (2007) Immunological abnormalities in CHARGE syndrome. Eur J Med Genet 50:338–345
Ryan AK, Goodship JA, Wilson DI, Philip N, Levy A, Seidel H, Schuffenhauer S, Oechsler H, Belohradsky B, Prieur M, Aurias A, Raymond FL, Clayton-Smith J, Hatchwell E, McKeown C, Beemer FA, Dallapiccola B, Novelli G, Hurst JA, Ignatius J, Green AJ, Winter RM, Brueton L, Brøndum-Nielsen K, Scambler PJ (1997) Spectrum of clinical features associated with interstitial chromosome 22q11 deletions: a European collaborative study. J Med Genet 34:798–804
Barber JCK, Walker JM, Barker MR, McNinch AW, Hallett RJ (1996) Repeated cytogenetic culture failure as an indicator of immunodeficiency. Lancet 348:1518
Ocejo-Vinyals JG, Lozano MJ, Sánchez-Velasco P, Escribano de Diego J, Paz-Miguel JE, Leyva-Cobián F (2000) An unusual concurrence of graft versus host disease caused by engraftment of maternal lymphocytes with DiGeorge anomaly. Arch Dis Child 83:165–169
Müller SM, Ege M, Pottharst A, Schulz AS, Schwarz K, Friedrich W (2001) Transplacentally acquired maternal T lymphocytes in severe combined immunodeficiency: a study of 121 patients. Blood 98:1847–1851
Markert ML, Alexieff MJ, Li J, Sarzotti M, Ozaki DA, Devlin BH, Sempowski GD, Rhein ME, Szabolcs P, Hale LP, Buckley RH, Coyne KE, Rice HE, Mahaffey SM, Skinner MA (2004) Complete DiGeorge syndrome: development of rash, lymphadenopathy, and oligoclonal T cells in 5 cases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 113:734–741
Janda A, Sedlacek P, Hönig M, Friedrich W, Champagne M, Matsumoto T, Fischer A, Neven B, Contet A, Bensoussan D, Bordigoni P, Loeb D, Savage W, Jabado N, Bonilla FA, Slatter MA, Davies EG, Gennery AR (2010) Multicenter survey on the outcome of transplantation of hematopoietic cells in patients with the complete form of DiGeorge anomaly. Blood 116:2229–2236
McGhee SA, Lloret MG, Stiehm ER (2009) Immunologic reconstitution in 22q deletion (DiGeorge) syndrome. Immunol Res 45:37–45
Gennery AR, Slatter MA, Grandin L, Taupin P, Cant AJ, Veys P, Amrolia PJ, Gaspar HB, Davies EG, Friedrich W, Hoenig M, Notarangelo LD, Mazzolari E, Porta F, Bredius RG, Lankester AC, Wulffraat NM, Seger R, Güngör T, Fasth A, Sedlacek P, Neven B, Blanche S, Fischer A, Cavazzana-Calvo M, Landais P, Inborn Errors Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation, European Society for Immunodeficiency (2010) Transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells and long-term survival for primary immunodeficiencies in Europe: entering a new century, do we do better? J Allergy Clin Immunol 126, 602-10.e1-11
Neven B, Leroy S, Decaluwe H, Le Deist F, Picard C, Moshous D, Mahlaoui N, Debré M, Casanova JL, Dal Cortivo L, Madec Y, Hacein-Bey-Abina S, de Saint Basile G, de Villartay JP, Blanche S, Cavazzana-Calvo M, Fischer A (2009) Long-term outcome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation of a single-center cohort of 90 patients with severe combined immunodeficiency. Blood 113:4114–4124
Cleveland WW, Fogel BJ, Brown WT, Kay HE (1968) Foetal thymic transplant in a case of DiGeorge’s syndrome. Lancet (7580), 1211–1214
August CS, Berkel AI, Levey RH, Rosen FS, Kay HE (1970). Establishment of immunological competence in a child with congenital thymic aplasia by a graft of fetal thymus. Lancet (7656):1080–1083
Markert ML, Boeck A, Hale LP, Kloster AL, McLaughlin TM, Batchvarova MN, Douek DC, Koup RA, Kostyu DD, Ward FE, Rice HE, Mahaffey SM, Schiff SE, Buckley RH, Haynes BF (1999) Transplantation of thymus tissue in complete DiGeorge syndrome. N Engl J Med 341:1180–1189
Markert ML, Devlin BH, McCarthy EA (2010) Thymus transplantation. Clin Immunol 135:236–246
Markert ML, Sarzotti M, Ozaki DA, Sempowski GD, Rhein ME, Hale LP, Le Deist F, Alexieff MJ, Li J, Hauser ER, Haynes BF, Rice HE, Skinner MA, Mahaffey SM, Jaggers J, Stein LD, Mill MR (2003) Thymus transplantation in complete DiGeorge syndrome: immunologic and safety evaluations in 12 patients. Blood 102:1121–1130
Markert ML, Alexieff MJ, Li J, Sarzotti M, Ozaki DA, Devlin BH, Sedlak DA, Sempowski GD, Hale LP, Rice HE, Mahaffey SM, Skinner MA (2004) Postnatal thymus transplantation with immunosuppression as treatment for DiGeorge syndrome. Blood 104:2574–2581
Chinn IK, Devlin BH, Li YJ, Markert ML (2008) Long-term tolerance to allogeneic thymus transplants in complete DiGeorge anomaly. Clin Immunol 126:277–281
Markert ML, Devlin BH, Chinn IK, McCarthy EA, Li YJ (2008) Factors affecting success of thymus transplantation for complete DiGeorge anomaly. Am J Transplant 8:1729–1736
Liston A, Lesage S, Wilson J, Peltonen L, Goodnow CC (2003) Aire regulates negative selection of organ-specific T cells. Nat Immunol 4:350–354
Anderson MS, Venanzi ES, Chen Z, Berzins SP, Benoist C, Mathis D (2005) The cellular mechanism of Aire control of T cell tolerance. Immunity 23:227–239
Li W, Kim MG, Gourley TS, McCarthy BP, Sant’Angelo DB, Chang CH (2005) An alternate pathway for CD4 T cell development: thymocyte-expressed MHC class II selects a distinct T cell population. Immunity 23:375–386
Choi EY, Jung KC, Park HJ, Chung DH, Song JS, Yang SD, Simpson E, Park SH (2005) Thymocyte–thymocyte interaction for efficient positive selection and maturation of CD4 T cells. Immunity 23:387–396
Junker AK, Driscoll DA (1995) Humoral immunity in DiGeorge syndrome. J Pediatr 127:231–237
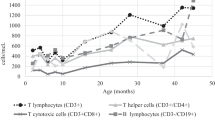
Sullivan KE, McDonald-McGinn D, Driscoll DA, Emanuel BS, Zackai EH, Jawad AF (1999) Longitudinal analysis of lymphocyte function and numbers in the first year of life in chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (DiGeorge syndrome/velocardiofacial syndrome). Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 6:906–911
Jawad AF, McDonald-Mcginn DM, Zackai E, Sullivan KE (2001) Immunologic features of chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (DiGeorge syndrome/velocardiofacial syndrome). J Pediatr 139:715–723
Cancrini C, Romiti ML, Finocchi A, Di Cesare S, Ciaffi P, Capponi C, Pahwa S, Rossi P (2005) Post-natal ontogenesis of the T-cell receptor CD4 and CD8 Vbeta repertoire and immune function in children with DiGeorge syndrome. J Clin Immunol 25:265–274
McLean-Tooke A, Barge D, Spickett GP, Gennery AR (2008) Immunological defects in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122:362–367
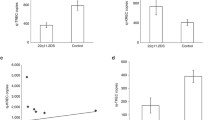
Lima K, Abrahamsen TG, Foelling I, Natvig S, Ryder LP, Olaussen RW (2010) Low thymic output in the 22q11.2 deletion syndrome measured by CCR9+ CD45RA+ T cell counts and T cell receptor rearrangement excision circles. Clin Exp Immunol 161:98–107
Piliero LM, Sanford AN, McDonald-McGinn DM, Zackai EH, Sullivan KE (2004) T-cell homeostasis in humans with thymic hypoplasia due to chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Blood 103:1020–1025
Pierdominic IM, Mazzetta F, Caprini E, Marziali M, Digilio MC, Marino B, Aiuti A, Amati F, Russo G, Novelli G, Pandolfi F, Luzi G, Giovannetti A (2003) Biased T-cell receptor repertoires in patients with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (DiGeorge syndrome/velocardiofacial syndrome). Clin Exp Immunol 132:323–331
Sedivá A, Bartůnková J, Zachová R, Poloucková A, Hrusák O, Janda A, Kocárek E, Novotná D, Novotná K, Klein T (2005) Early development of immunity in DiGeorge syndrome. Med Sci Monit 11: CR182–187
Eberle P, Berger C, Junge S, Dougoud S, Büchel EV, Riegel M, Schinzel A, Seger R, Güngör T (2009) Persistent low thymic activity and non-cardiac mortality in children with chromosome 22q11.2 microdeletion and partial DiGeorge syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol 155:189–198
Herwadkar A, Gennery AR, Moran AS, Haeney MR, Arkwright PD (2010) Association between hypoparathyroidism and defective T cell immunity in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. J Clin Pathol 63:151–155
Kung SJ, Gripp KW, Stephan MJ, Fairchok MP, McGeady SJ (2007) Selective IgM deficiency and 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 99:87–92
Finocchi A, Di Cesare S, Romiti ML, Capponi C, Rossi P, Carsetti R, Cancrini C (2006) Humoral immune responses and CD27+ B cells in children with DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion syndrome). Pediatr Allergy Immunol 17:382–388
Schubert MS, Moss RB (1992) Selective polysaccharide antibody deficiency in familial DiGeorge syndrome. Ann Allergy 69:231–238
Gennery AR, Barge D, O’Sullivan JJ, Flood TJ, Abinun M, Cant AJ (2002) Antibody deficiency and autoimmunity in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Arch. Dis Child 86:422–425
Brown JJ, Datta V, Browning MJ, Swift PJF (2004) Graves’ disease in Di George Syndrome: Patient report with a review of endocrine autoimmunity associated with 22q11.2 deletion. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 17: 1575–1579
Smith CA, Driscoll DA, Emmanuel BS, McDonald-McGinn DM, Zackai EH, Sullivan KE (1998) Increased prevalence of immunoglobulin A deficiency in patients with a chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (DiGeorge Syndrome/ Velo-Cardio-Facial Syndrome). Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 5:415–417
Davies K, Stiehm RE, Woo P, Murray KJ (2001) Juvenile idiopathic polyarticular arthritis and IGA deficiency in the 22q11 deletion syndrome. J Rheumatol 28:2326–2334
Haire RN, Buell RD, Litman RT, Ohta Y, Fu SM, Honjo T, Matsuda F, de la Morena M, Carro J, Good RA, Litman GW (1993) Diversification, not use, of the immunoglobulin VH gene repertoire is restricted in DiGeorge syndrome. J Exp Med 178:825–834
Perez EE, Bokszczanin A, McDonald-McGinn D, Zackai EH, Sullivan KE (2003) Safety of live viral vaccines in patients with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (DiGeorge syndrome/velocardiofacial syndrome). Pediatrics 112:e325
Moylett EH, Wasan AN, Noroski LM, Shearer WT (2004) Live viral vaccines in patients with partial DiGeorge syndrome: clinical experience and cellular immunity. Clin Immunol 112:106–112
Azzari C, Gambineri E, Resti M, Moriondo M, Betti L, Saldias LRG, Gelli AM, Vierucci A (2005) Safety and immunogenicity of measles-mumps-rubella vaccine in children with congenital immunodeficiency (DiGeorge syndrome). Vaccine 23:1668–1671
Waters V, Peterson KS, LaRussa P (2007) Live viral vaccines in a DiGeorge syndrome patient. Arch Dis Child 92:519–520
Davis CM, Kancherla VS, Reddy A, Chan W, Yeh HW, Noroski LM, Rosenblatt H, Shearer WT, Chinen J (2008) Development of specific T-cell responses to Candida and tetanus antigens in partial DiGeorge syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122:1194–1199
Al-Sukaiti N, Reid B, Lavi S, Al-Zaharani D, Atkinson A, Roifman CM, Grunebaum E (2010) Safety and efficacy of measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine in patients with DiGeorge syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126:868–869
Kratz CP, Niehues T, Lyding S, Heusch A, Janssen G, Gobel U (2003) Evans Syndrome in a patient with Chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome: a case report. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 20:167–172
Rasmussen SA, Williams CA, Ayoube M, Sleasman JW, Gray BA, Bent-Williams A, Stalker HJ, Zorir T (1996) Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in velo-cardio-facial syndrome: coincidence or unusual complication. Am J Med Genet 64:546–550
DePiero AD, Louire EM, Berman BW, Robin NH, Zinn EB, Hostoffer RW (1997) Recurrent immune cytopenias in 2 patients with Di George/velo cardio facial syndrome. J Paediatr 13:484–486
Verloes A, Curry C, Jamar M, Herens C, O’Lague P, Marks J, Sarda P, Blanchet P (1998) Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and del (22q11) syndrome: a non-random association. J Med Genet 35:943–947
Bach JF (2005) Infections and autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun 25(Suppl):74–80
Schurman SH, Candotti F (2003) Autoimmunity in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Curr Opin Rheumatol 15:446–453
Zemble R, Luning Prak E, McDonald K, McDonald-McGinn D, Zackai E, Sullivan K (2010) Secondary immunologic consequences in chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (DiGeorge syndrome/velocardiofacial syndrome). Clin Immunol 136:409–418
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gennery, A.R. Immunological aspects of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 69, 17–27 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0842-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0842-z