Abstract
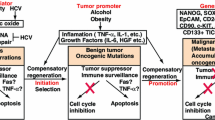
In hepatocarcinogenesis in rodents, induction of foci and nodules comprising clonally proliferated initiated cells is considered to be essential for the future development of carcinomas. Nodules in human cirrhotic liver, though known to be associated with a high hepatocellular carcinoma risk, have generally been regarded as regenerative in nature, and not the result of clonal or neoplastic cell proliferation, on a morphological basis. However, when we analyzed 83 cirrhotic nodules from 11 HBV carrier patients, utilizing hepatitis B virus (HBV) integration as a marker for clonal proliferation, we found the existence of clonal populations of more than 105 hepatocytes in 26 (31.3%) of them. Although such clonal cell populations are morphologically not discernible from neighboring hepatocytes, they may have particular histogenetic significance in human hepatocarcinogenesis and clearly deserve further investigation. Allelotype analysis of mouse hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC), induced by a single dose of diethyl nitrosaminine in C3H/MSM F1 hybrids, revealed no remarkable alterations in the original tumors when microsatellite probes were used, but loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 4 at extremely high frequency (95%) in cultured cell lines derived from these HCC. The shortest common region was about 10 cM distal to the interferon α gene, in which the p16 gene is located. The results indicated that loss of gene function, most probably including that of the p16 gene, may be essential for immortalization of cultured hepatocytes but that it may not play any role in initiation or early events in mouse hepatocarcinogenesis in vivo. The mouse HCC used for analysis in this study may be comparable with human HCC at an early stage, for which only very limited genetic alterations have so far been identified.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC :
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- HBV :
-
hepatitis B virus
- LOH :
-
loss of heterozygosity
References
Bannasch P (1986) Preneoplastic lesions as end points in carcinogenicity testing. I. Hepatic preneoplasia. Carcinogenesis (Lond) 7: 689–695
Buetow KH, Murray JC, Israel JL, London WT, Smith M, Kew M, Blanquet V, Brechot C, Redecker A, Govindarajah S (1989) Loss of heterozygosity suggests tumor suppressor gene responsible for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 8852–8856
Cairns P, Tokino K, Eby Y, Sidransky D (1994) Homozygous deletions of 9p21 in primary human bladder tumors detected by comparative multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Cancer Res 54: 1422–1424
Caldas C, Hahn SA, de Costa LT, Redston MS, Schutte M, Sevmour AB, Weinstein CL, Hruban RH, Yeo CJ, Kern SE (1994) Frequent somatic mutations and homozygous deletions of the p16 (MTS1) gene in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Nat Genet 8: 27–32
Cheng JQ, Jhanwar SC, Lu YY, Testa JR (1993) Homozygous deletions within 9p21–p22 identify a small critical region of chromosomal loss in human maligmant mesotheliomas. Cancer Res 53: 4761–4763
Ding SF, Habib NA, Dooley J, Wood C, Bowles L, Delhanty JDA (1991) Loss of constitutional heterozgosity on chromosome 5q in hrpatocellular carcinoma without cirrhosis. Br J Cancer 64: 1083–1087
Emi M, Fujiwara Y, Nakajima T, Tsuchiya E, Tsuda H, Hirohashi S, Miyaki M, Nakamura Y (1992) Frequent loss of heterozygosity for loci on chromosome 8p in hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal cancer and lung cancer. Cancer Res 52: 5368–5372
Farber E (1984) Cellular biochemistry of the stepwise development of cancer with chemicals: G.H.A. Clowes Memorial Lecture. Cancer Res 44: 5463–5474
Fujimori M, Tokino T, Hino O, Kitagawa T, Imamura T, Okamoto E, Mitsunobu M, Ishikawa J, Nakagawa H, Harada H, Yagura M, Matsubara K, Nakamura Y (1991) Allelotype study of primary hepatpcellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 51: 89–93
Hino O, Kitagawa T, Sugano H (1985) Relationship between serum and histochemical markers for hepatitis B virus and rate of viral integration hepatocellular carcinomas in Japan. Int J Cancer 35: 5–10
Holland EA, Beaton SC, Edwards BG, Kefford RR, Mann GJ (1994) Loss of heterozygosity and homozygous deletions on 9p21–22 in melanoma. Oncogene 9: 1361–1365
Kamb A, Gruis NA, Weaver-Feldhaus J, Lui Q, Harshman K, Tavitgan SV, Stochert D, Day R, Johnson BE, Skolnick MH (1994) A cell cycle regulator potentially involved in genesis of many tumor types. Science 264: 436–440
Knapek DF, Serrano M, Beach D, Trono D, Walker CL (1995) Association of rat p15INK4B/p16INK4 deletions with monosomy 5 in kidney epithelial cell lines but not primary renal tumors. Cancer Res 55: 1607–1612
Lee GH, Nomura K, Kanda H, Kusakabe M, Yoshiki A, Sakakura T, Kitagawa T (1991) Strain specific sensitivity to dietthylnitrosamime-induced carcinogenesis is maintained in hepatocytes of C3H1HeN-C57BL16N chimeric mice. Cancer Res 51: 3257–3260
Lukeis R, Irving L, Garson M, Hasthorpe S (1990) Cytogenetics of non small-cell lung cancer: analysis of consisitent non-random abnormalities. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2: 116–124
Mead LJ, Gillespie MT, Irving LB, Campbell LJ (1994) Homozygous and hemizygous deletions of 9p centromeric to the interferon genes in lung cancer. Cancer Res 54: 2307–2309
Merlo A, Gablielson E, Mabry M, Vollmer R, Baylin SB, Sidransky D (1994) Homozygous deletion on chromosome 9p and loss of heterozygosity on 9q, and 6p and 6q in primary human small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 54: 2322–2326
Moore MA, Kitagawa T (1986) Hepatoccarcinogenesis in the rat: the effect of promoters and carcinogens in vivo and in vitro. Int Rev Cytol 101: 125–173
Mori T, Miura K, Aoki T, Nishihira T, Mori S, Nakamura Y (1994) Frequent somatic mutation of the MTS1/CDK41 (multiple tumor suppressor/cyclin-dependent kinase 4 inhibitor) gene in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 54: 3396–3397
Nagayo M, Ogata T, Horisawa H, Kikuta HK (1914) Referat über Leverzirrhose. Verh Jpn Pathol Ges 4: 5–28
Nishida N, Fukuda Y, Kokuryu H, Sadamoto T, Isowa G, Honda K, Yamaoka Y, Ikenaga M, Imura H, Ishizaki K (1992) Accumulation of allelic loss on arms of chromosomes 13q, 16q and 17p in the advanced stages of human hepatocellular carc. Int J Cancer 51: 862–868
Nishimori H, Ogawa K, Tateno H (1994) Frequent deletion in chromosome 4 and duplication of chromosome 15 in liver epithelial cells derived from long-term culture of C3H mouse hepatocytes. Int J Cancer 59: 108–113
Nobori T, Miura K, Wu DJ, Lois A, Takabayashi K, Carson DA (1994) Deletions of the cyclin-dependent kinase-4 inhibitor gene in multiple human cancers. Nature 368: 753–756
Ohta M, Nagai H, Shimizu M, Rasio D, Berd D, Mastrangelo M, Singh AD, Shields JA, Shields CL, Xeoxw CM, Huebner K (1994) Rarity of somatic and germline mutations of the cyclin-dependent kinase 4 gene, CDK41, in melanoma. Cancer Res 54: 5269–5272
Olopade OI, Jenkins RB, Ransom DT, Malik K, Pomykala H, Nobori T, Cowan JM, Rowley JD, Diaz MO (1992) Molecular analysis of deletions of the short arm of chromosome 9 in human gliomas. Cancer Res 52: 2523–2529
Riet P van der, Nawroz H, Hruban RH, Corio R, Tokino K, Koch W, Sidransky D (1994) Frequent loss of chromosome 9p21–22 early in head and neck cancer progression. Cancer Res 54: 1156–1158
Sasaki T, Yoshida T (1935) Experimentelle Erzeugung des Levercarcinoms durch Fütterung mit o-Amidoazotoluol. Virchows Arch 295: 175–200
Sato K (1989) Glutathione transferases as markers of preneoplasia and neoplasia. Adv Cancer Res 52: 205–255
Simon D, Knowles BB, Weith A (1991) Abnormalities of chromosome 1 and loss of heterozygosity on 1p in primary hepatomas. Oncogene 6: 765–770
Stadler WM, Sherman J, Bohlander SK, Roulston D, Dregling M, Rukstalis D, Olopade OI (1994) Homozygous deletions within chromosomal bands 9p21–22 in bladder cancer. Cancer Res 54: 2060–2063
Tarmin L, Yin J, Zhou X, Suzuki H, Jian HY, Rhyu MG, Abraham JM, Krasna MJ, Cottrell J, Meltzer SJ (1994) Frequent loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 9 in adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the sophagus. Cancer Res 54: 6094–6096
Walker DG, Duan W, Popovic EA, Kaye AH, Tomlinson FH, Lavin M (1995) Homozygous deletions of the multiple tumor suppressor gene 1 the progression of human astrocytomas. Cancer Res 55: 20–23
Walker GJ, Hayward NK, Falvey S, Cooksley WGE (1991) Loss of somatic heterozygosity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 51: 4367–4370
Washimi O, Nagatake M, Osada H, Ueda R, Koshikawa T, Seki T, Takahashi T, Takahashi T (1995) In vivo occurrence of p16 (MTS1) and p15 (MTS2) alterations preferentially in non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Res 55: 514–517
Xu L, Sgroi D, Sterner CJ, Beauchamp RL, Pinney DM, Keel S, Ueki K, Rutter JL, Buckler AJ, Louis DN, Gusella JF, Ramesh V (1994) Mutational analysis of CDKN2 (MTS1/p16ink4) in human breast carcinomas. Cancer Res 54: 5262–5264
Yamagiwa K (1911) Zur Kenntnis des parimären paranchymatösen Leberkarzinoms (“Hepatoma”). Virchows Arch 206: 437–467
Yasui H, Hino O, Ohtake K, Machinami R, Kitagawa T (1992) Clonal growth of hepatitis B virus-integrated hepatocytes in cirrhotic liver nodules. Cancer Res 52: 6810–6814
Zhan SY, Klein-Szanto AJP, Sauter ER, Shaferenko M, Mitsunaga S, Nobiri T, Carson DA, Ridge JA, Goodrow TL (1994) Higher frequency of alterations in the p16/CDK2 gene in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines than in primary tumors of the head and neck. Cancer Res 54: 5050–5053
Zhang W, Hirohashi S, Tsuda H, Shimosato Y, Yokota J, Terada M, Sugimura T (1990) Frequent loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 16 and 4 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res 81: 108–111
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Work dedicated to Dr. Haruo Sugano on the occasion of his 70th birthday. The material of this paper was essentially presented at the 60th Anniversary Symposium of the Cancer Institute and the Cancer Institute Hospital, Tokyo, held in September 1994
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitagawa, T., Miyasaka, K., Kanda, H. et al. Hepatocarcinogenesis in rodents and humans. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 121, 511–515 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01197762
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01197762