Abstract
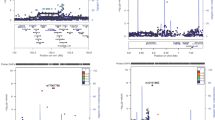
Partial exclusion mapping of the nonobese (NOD) diabetic mouse genome has shown linkage of diabetes to at least five different chromosomes. We have now excluded almost all of the genome for the presence of susceptibility genes with fully recessive effects and have obtained evidence of linkage of ten distinct loci to diabetes or the pre–diabetic lesion, insulitis, indicative of a polygenic mode of inheritance. The relative importance of these loci and their interactions have been assessed using a new application of multiple polychotomous regression methods. A candidate disease gene, interleukin–2 (Il–2), which is closely linked to insulitis and diabetes, is shown to have a different sequence in NOD, including an insertion and a deletion of tandem repeat sequences which encode amino acid repeats in the mature protein.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Todd, J.A. et al. Genetic analysis of autoimmune type 1 diabetes mellitus in mice. Nature 351, 542–5470542-547 (1991).
Jacob, H. et al. Genetic dissection of autoimmune type 1 diabetes in the BB rat. Nature Genet. 2, 56–60 (1992).
Hilbert, P. et al. Chromosomal mapping of two genetic loci associated with blood-pressure regulation in hereditary hypertensive rats. Nature 353, 521–529 (1991).
Jacob, H.J. et al. Genetic mapping of a gene causing hypertension in the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat. Cell 67, 213–224 (1991).
Rise, M.L., Frankel, W.N., Coffin, J.M. & Seyfried, T.N. Genes for epilepsy mapped in the mouse. Science 253, 669–673 (1991).
Hearne, C.M., Ghosh, S & Todd, J.A Microsatellites for linkage analysis of genetic traits. Trends Genet. 8, 288–294 (1992).
Castano, L. – Eisenbarth, G.S. Type-I diabetes: A chronic autoimmune disease of human, mouse, and rat. A. Rev. Immunol. 8, 647–79 (1990).
Todd, J.A., Bell, J.I. & McDevitt, H.O. HLA-DQβ gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature 329, 599–604 (1987).
Julier, C. et al. Insulin-IGF2 region on chromosome 11 p encodes a gene implicated in HLA-DR4-dependent diabetes susceptibility. Nature 354, 155–159 (1991).
Bain, S.C. et al. Insulin gene region-encoded susceptibility to type 1 diabetes is not restricted to HLA-DR4-positive individuals. Nature Genet. 2, 212–215 (1992).
Cornall, R.J. et al. Type 1 diabetes in mice is linked to the interleukin-1 receptor and Lsh/lty/Bcg genes on chromosome 1. Nature 353, 262–265 (1991).
Wicker, L.S. et al. Autoimmune syndromes in major histocompatibility complex (MHC) congenic strains of nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. The NOD MHC is dominant for insulitis and cyclophosphamide-induced diabetes. J. exp. Med. 176, 67–77 (1992).
Kroemer, G., Andreu, J., Gonzalo, J., Guitierrez-Ramos, J. & Martinez-A, C. Interleukin-2, autotolerance, and autoimmunity. Adv. Immunol. 50, 147–235 (1991).
Kashima, N. et al. Unique structure of murine interleukin-2 as deduced from cloned cDNAs. Nature 313, 402–404 (1985).
Degrave, W. et al. Cloning and structure of a mouse interleukin-2 chromosomal gene. Molec. Biol. Rep. 11, 57–61 (1986).
Crow, J. Basic concepts in population, quantitative, and evolutionary genetics (W. H. Freeman, New York, 1986).
Paterson, A.H. et al. Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors by using a complete linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature 335, 721–726 (1988).
Risch, N., Ghosh, S. & Todd, J.A. Statistical evaluation of multiple locus linkage data in experimental species and relevance to human studies: application to murine and human IDDM. Am. J. hum. Genet. (in the press).
Prins, J.-B. et al. Linkage on chromosome 3 of autoimmune diabetes and defective Fc receptor for IgG in NOD mice. Scienc 260, 659–698 (1993).
Garchon, H., Bedosa, P., Eloy, L. & Bach, J.-F. Identification and mapping to chromosome 1 of a susceptibility locus for periinsulitis in non-obese diabetic mice. Nature 353, 260–262 (1991).
Matesanz, F., Alcina, A. & Pellicer, A. A new cDNA sequence for the murine interleukin-2 gene. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1132, 335–336 (1992).
Matesanz, F., Alcina, A. & Pellicer, A. Existence of at least five interleukin-2 molecules in different mouse strains. Immunogenetics (in the press).
Riggins, G. et al. Human genes containing polymorphic trinucleotide repeats. Nature Genet. 2, 186–191 (1992).
The Huntington's Disease Collaborative Research Group. A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Hunting-ton's disease chromosomes. Cell 72, 971–983 (1993).
Flemming, C.L., Russell, S.J. & Collins, M.K.L. Mutation of Asp20 of human interleukin-2 reveals a dual role of the p55 a chain of the interleukin-2 receptor. Eur. J. Immunol. 23, 917–921 (1993).
Zurawski, S.M., Mosmann, T.R., Benedik, M. & Zurawski, G. Alterations in the amino-terminal third of mouse interleukin 2: effects on biological activity and immunoreactivity. J. Immunol. 137, 3354–3360 (1986).
De Gouyon, B. et al. Genetic analysis of diabetes and insulitis in an interspecific cross of the nonobese diabetic mouse with Mus spretus. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 1877–1881 (1993).
Morton, N.E., Shields, D.C. & Collins, A. Ann. hum. Genet. 55, 301–314 (1991).
Dietrich, W. et al. SSLP Genetic map of the mouse (Mus musculus) 2N=40. in Genetic Maps-Locus Maps of Complex Organisms 6th edn (ed. O'Brien, S.J.) (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1993).
Dietrich, W. et al. A genetic map of the mouse suitable for typing intraspecific crosses. Genetics 131, 423–447 (1992).
Love, J.M., Knight, A.M., McAleer, A.M. & Todd, J.A. Towards construction of a high resolution map of the mouse genome using PCR-analysed microsatellites. Nucl. Acids Res. 18, 4123–4130 (1990).
Hearne, C.M. et al. Additional microsatellite markers for mouse genome mapping. Mamm. Genome. 1, 273–282 (1991).
Cornall, R.J., Aitman, T.J., Hearne, C.M. & Todd, J.A. The generation of a library of PCR-analyzed microsatellite variants for genetic mapping of the mouse genome. Genomics 10, 874–881 (1991).
Cornall, R.J., Friedman, J.M. & Todd, J.A. Mouse microsatellites from a flow-sorted 4:6 Robertsonian chromosome. Mamm. Genome 3, 620–624 (1992).
Aitman, T.J., Hearne, C.M., McAleer, M.A. & Todd, J.A. Mononucleotide repeats are an abundant source of length variants in mouse genomic DNA. Mamm. Genome 1, 206–210 (1991).
McAleer, M.A. et al. Linkage analysis of 84 microsatellite markers in intra- and interspecific backcrosses. Mamm. Genome 3, 457–460 (1992).
Poustka, A., Rackwitz, H.-R., Frischauf, A.-M., Hohn, B. & Lehrach, H. Selective isolation of cosmid clones by homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci.U.S.A. 81, 4129–4133 (1984).
Dixon, W. BMPD Statistical Software (University of California Press, Berkeley, 1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S., Palmer, S., Rodrigues, N. et al. Polygenic control of autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Nat Genet 4, 404–409 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0893-404
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0893-404
This article is cited by
-
Low-dose IL-2 reduces IL-21+ T cell frequency and induces anti-inflammatory gene expression in type 1 diabetes
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Genetic interaction between two insulin-dependent diabetes susceptibility loci, Idd2 and Idd13, in determining immunoregulatory DN T cell proportion
Immunogenetics (2018)
-
TCR transgenic mice reveal the impact of type 1 diabetes loci on early and late disease checkpoints
Immunology & Cell Biology (2016)
-
Idd13 is involved in determining immunoregulatory DN T-cell number in NOD mice
Genes & Immunity (2014)
-
Congenic mice reveal genetic epistasis and overlapping disease loci for autoimmune diabetes and listeriosis
Immunogenetics (2014)