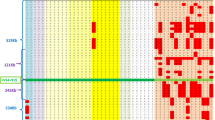
Abstract
Menkes disease is a lethal–X linked recessive disorder associated with copper metabolism disturbance. We have recently mapped two chromosome breakpoints related to this disease in a 1 megabase yeast artificial chromosome contig at Xq13.3. We now report the construction of a phage contig and the isolation of candidate partial cDNAs for the Menkes disease gene. The candidate gene expresses an 8 kb message in all investigated tissues, and deletions were detected in 16% of 100 unrelated Menkes patients. The deduced partial protein sequence shared the GMTCXXC motif with bacterial metal resistance operons, suggesting a potential heavy metal binding protein. These findings should lead to more accurate prenatal diagnosis of this severe disease and a better understanding of the cellular homeostasis of essential heavy metals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Menkes, J.H., Alter, M., Steigleder, G., Weakley, D.R. & Sun, J.H. A sex-linked recessive disorder with retardation of growth, peculiar hair and focal cerebral and cerebellar degeneration Pediatrics 29, 764–779 (1962).
Danks, D.M. Herditary disorders of copper metabolism in Wilson's disease and Menkes' disease. In The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Diseases, (eds Scriver, J.R.et al.) 1422–1431 (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1989).
Horn, N. Copper metabolism in Menkes' disease In Metabolism of Trace Metals in Man (eds Rennert. O.M. & Chan,W.-Y.) 25–52 (CRC Press, 1984).
Horn, N., Tønnesen, T. & Tümer, Z. Menkes disease: An X-linked neurological disorder of the copper metabolism. Brain Pathol. 2, 351–362 (1992).
Scheinberg, I.H. and Collins, J.C. Menkes' disease: A disorder of zinc metabolism? Lancet i, 619 (1989).
Horn, N., Stene, J., Mollekaer, A.M. & Friedrich, U. Linkage studies in Menkes' disease. The Xg blood group system and C-banding of the X chromosome. Ann. hum. Genet. 48, 161–172 (1984).
Wienker, T.F. et al. Evidence that the Menkes locus maps on proximal Xp. Hum. Genet. 65, 72–73 (1983).
Wieacker, P. et al. Menkes kinky hair disease: A search for closely linked restriction fragment length polymorphism. Hum. Genet. 64, 139–147 (1983).
TØnnesen, T., Petterson, A., Kruse, T.A., Gerdes, A.-M. & Horn, N. Multipoint linkage analysis in Menkes disease. Am. J. hum. Genet. 50, 1012–1017 (1992).
Yang, H-M. et al. Exclusion mapping of 12 X linked disease loci and 10 DNA probes from the long arm of the X-chromosome. Clin. Genet. 38, 94–104 (1990).
Davisson, M.T. X-linked genetic homologies between mouse and man. Genomics 1, 213–227 (1987).
Davies, K.E., Mandel, J.-L., Monaco, A.P., Nussbaum, R.L. & Willard, H.F. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X chromosome. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 58, 853–966 (1991).
Kapur, S., Higgins, J.V., Delp, K. & Rogers, B. Menkes syndrome in a girl with X-autosome translocation. Am. J. med. Genet. 26, 503–510 (1987).
Verga, V. et al. Localization of the translocation breakpoint in a female with Menkes syndrome to Xq13.2–q13.3 proximal to PGK-1. Am. J. hum. Genet. 48, 1133–1138 (1991).
Tümer, Z. et al. Mapping of the Menkes locus to Xq13.3 distal to the X-inactivation center by an intrachromosomal insertion of the segment Xq13.3–q21.2. Hum. Genet. 88, 668–672 (1992).
Tümer, Z. et al. Characterization of a 1.0 Mb YAC contig spanning two chromosome breakpoints related to Menkes disease. Hum. molec. Genet. 1, 483–489 (1992).
Korn, E. Biochemistry of actomyosin-dependent cell motility (a review). Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 588–599 (1978).
Kozak, M. An analysis of 5′ -noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucl. Acids Res. 15, 8125–8148 (1987).
Kyte, J. & Doolittle, R.F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. molec. Biol. 157, 105–132 (1982).
Altschul, S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W. & Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignement search tool. J. molec. Biol. 215, 403–410 (1990).
Laddaga, R.A., Chu, L., Misra, T.K. & Silver, S. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the mercurial-resistance operon from Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pl258. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 5106–5110 (1987).
Silver, S. & Walderhaug, M. Gene regulation of plasmid- and chromosome determined inorganic ion transport in bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 56, 195–228 (1992).
Nucifora, G., Chu, L., Misra, T.K. & Silver, S. Cadmium resistance from Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pl258 cadA gene results from a cadmium—efflux ATPase. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 3544–3548 (1989).
Kahn, D. et al. Rhizobium meliloti fixGHI sequence predicts involvement of a specific cation pump in symbiotic nitrogen fixation. J. of Bacteriol. 171, 929–939 (1989).
Brown, N.L., Ford, S.J., Pridmore, R.D. & Fritzinger, D.C. Nucleotide sequence of a gene from the Pseudomonas Transposon Tn501 encoding mercuric reductase Biochemistry 22, 4089–4095 (1983).
Inoue, C., Sugawara, K. & Kusano, T. The merR regulatory gene in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans is spaced apart from the merstructural genes. Molec. Microbiol. 5, 2707–2718 (1991).
Yoon, K.P. & Silver, S. A second gene in the Staphylococcus aureus cadA cadmium resistance determinant of plasmid pl258. J. Microbiol. 173, 7636–7642 (1991).
Herd, M.S. et al. Uptake and efflux of copper—64 in Menkes'—disease and normal continuous lymphoid cell lines. Biochem. J. 247, 341–347 (1987).
Noojen, J.L. et al. Trace element studies in three patients and a fetus with Menkes' disease. Effect of copper therapy. Pediatr. Res. 15, 284–289 (1981).
Yazaki, M. Study on abnormal copper metabolism in Menkes' kinky hair disease and Wilson's disease. Nagoya med. Journal. 25, 169–186 (1981).
Vulpe, C., Levinson, B., Whitney, S., Packman, S. & Gitschier, J. Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease and evidence that it encodes a copper-transporting ATPase. Nature Genet. 3, 7–13 (1993).
Tønnesen, T. & Horn, N. Prenatal diagnosis of Menkes disease, an inherited disorder of copper metabolism. J. Inher. metab. Dis. 1, 207–214 (1989).
Graeber, M.B., Monaco, A.P., Chelly, J. & Müller, U. Isolation of DNTR repeats from yeast artificial chromosomes encompassing loci PGK1 and DXS56. Hum. Genet., (in the press).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 2nd ed (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1989).
Feinberg, A.P. & Vogelstein, B. A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal. Biochem. 132, 6–13 (1983).
Church, M.C. & Gilbert, W.G. Genomic sequencing. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 81, 1991–1995 (1984).
Monaco, A.P. et al. Detection of deletions spanning the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus using a tightly linked DNA segment. Nature 316, 842–845 (1985).
Seed, B. An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. Nature 329, 840–842 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chelly, J., Tümer, Z., Tønnesen, T. et al. Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease that encodes a potential heavy metal binding protein. Nat Genet 3, 14–19 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0193-14
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0193-14
This article is cited by
-
Pharmacokinetics of CuGTSM, a Novel Drug Candidate, in a Mouse Model of Menkes Disease
Pharmaceutical Research (2021)
-
Copper is an essential regulator of the autophagic kinases ULK1/2 to drive lung adenocarcinoma
Nature Cell Biology (2020)
-
Identification of novel ATP7A mutations and prenatal diagnosis in Chinese patients with Menkes disease
Metabolic Brain Disease (2017)
-
Heavy metal contamination, sources, and pollution assessment of surface water in the Tianshan Mountains of China
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment (2015)