Summary
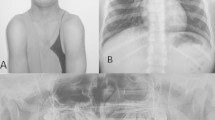
Neuropathologic study of eight cases of thanatophoric dysplasia (dwarfism) reveals developmental abnormalities including hypoplasia of posterior fossa, megalencephaly, cerebral gyral disorganization, hippocampal malformation, neuronal heterotopia, nuclear dysplasia, and abnormal axonal bundles. There are no noticeable differences in CNS abnormalities between thanatophoric dysplasia with and without cloverleaf skull (Kleeblattschädel). The CNS abnormalities, likely the result of abnormal neuronal migration and cytoarchitectonic disarrangement, are apparently not caused by skeletal abnormalities. The observation suggests that CNS abnormalities represent a characteristic and distinct manifestation of thanatophoric dysplasia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J (1976) Experimental reorganization of the cerebellar cortex. VII. Effects of late-x-irradiation schedules that interfere with cell acquisition after stellate cells are formed. J Comp Neurol 165:65–76
Beiley OT (1936) Relation of glioma of the leptomeninges to neuroglial nests. Report of a case of astrocytoma of the leptomeninges. Arch Pathol 21:584–601
Bailey P, Bucy PC (1931) The origin and nature of meningeal tumors. Am J Cancer 15:15–35
Bloomfield JA (1970) Cloverleaf skull and thanatophoric dwarfism. Aust Radiol 14:429–434
Brun A (1965) Marginal glioneural heterotopias of the central nervous system. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 65:221–233
Caviness VS, Jr, Evrard P, Lyon G (1978) Radial neuronal assemblies, ectopia and necrosis of developing cortex: A case analysis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 41:67–72
Caviness VS, Sidman RL (1973) Time of orgin of corresponding cell classes in the cerebral cortex of normal and reeler mutant mice. An autoradiographic analysis. J Comp Neurol 148:141–152
Choi BH, Lapham LW, Amin-Zaki L, Saleem T (1978) Abnormal neuronal migration, deranged cerebral cortical organization, and diffuse white matter astrocytosis of human fetal brain: A major effect of methylmercury poisoning in utero. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 37:719–733
Cooper IS, Kernohan JW (1951) Heterotopic glial nests in the subarachnoid space: Histopathologic characteristics, mode of origin and relation to meningeal gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 10:16–29
Danes BS (1974) Achondroplasia and thanatophoric dwarfism. A study in cell culture. Birth Defects 10:37–42
Dvorak K, Feit J, Jurankova Z (1978) Experimentally induced focal microgyria and status verrucous deformis in rats: Pathogenesis and interrelation. Histological and autoradiographical study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 44:121–129
Friede RL (1975) Developmental neuropathology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 351–355
Goutieres F, Aicardi J, Bargeton E (1971) Une malformation cerebrale particulière associée au narisme thanatophore. Rev Neurol 125:435–440
Hicks SP, D'Amato CJ, Coy MA, O'Brien ED, Thurston JS, Joftes DL (1968) Migrating cells in the developing central nervous system studied by radiosensitivity and tritiated thymidine uptake. Bookhaven Symp Biol 14: 246–304
Ho KL (1983) Concurrence of subependymoma and heterotopic leptomeningeal neuroglial tissue. Arch Pathol Lab Med 107:136–140
Hori A, Friede RL, Fisher G (1983) Ventricular diverticles with localized dysgenesis of the temporal lobe in cloverleaf skull anomaly. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 60:132–136
Horton WA, Harris DJ, Collins DL (1983) Discordance for the Kleeblattschädel anomaly in monozygotic twins with thanatophoric dysplasia. Am J Med Genet 15:97–101
Huguenin M, Godard C, Ferrier PE, Bamatter F (1968) Two different mutations within the same sibship: thanatophoric dwarfism and Ullrich-Feichtiger syndrome. Helv Paediatr Acta 24:239–245
Iannacione G, Gerline (1974) The so-called “cloverleaf skull syndrome”. Pediatr Radiol 2:175–184
Keats TE, Riddervold HO, Michaelis LL (1970) Thanatophoric dwarfism. Am J Roentgenol 108:473–480
Klatzo I (1975) Pathophysiologic aspects of cerebral ischemia. In: Tower DB (ed) The nervous system, vol. 1: The basic neurosciences. Raven Press, New York, pp 313–332
Langman J, Schimada M (1971) Cerebral cortex of mouse after prenatal chemical insults. Am J Anat 132:355–374
Levine DN, Fisher MA, Caviness VS, Jr (1974) Porencephaly with microgyria: A pathologic study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 29:99–113
Maroteaux P, Lamy M, Robert JM (1967) Le nanisme thanatophore. Presse Med 75:2519–2524
Martinelli B, Campailla E, Ferrari G (1975) Malformation cerebrale particulière et nanism thanatophore. Arch Fr Pediatr 32:455–460
McBride MC, Kemper TL (1982) Pathogenesis of four layered microgyric cortex in man. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 57:93–98
Partington MW, Gonzales-Crussi F, Khakee SG, Wollin DG (1971) Cloverleaf skull and thanatophoric dwarfism. Arch Dis Child 46:656–664
Rakic P, Sidman RL (1970) Histogenesis of cortical layers in human cerebellum, particularly the lamina dissecans. J Comp Neurol 139:473–500
Rakic P (1974) Neurons in rhesus monkey visual cortex: Systematic relation between time of origin and eventual disposition. Science 183:425–427
Rakic P (1972) Mode of cell migration to the superficial layers of fetal monkey neocortex. J Comp Neurol 145:61–84
Richman DP, Stewart RM, Cavines US (1974) Cerebral microgyria in a 27-week fetus: An architectonic and topographic analysis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 33:374–384
Sabry A (1974) Thanatophoric dwarfism in triplets. Lancet II:533
Saldino RM (1971) Lethal short-limbed dwarfism: Achondrogenesis and thanatophoric dwarfism. Am J Roentgenol 112:185–197
Sato D, Hosokawa Y, Nakamura Y, Mukae T, et al. (1981) Thanatophoric dysplasia of identical twins. Acta Pathol Jpn 31:895–902
Sewell AC, Spranger JW, Pennock CA (1977) Epiphyseal cartilage chemistry in thanatophoric dwarfism. Lancet I:854
Shah K, Astley R, Cameron AH (1973) Thanatophoric dwarfism. J Med Genet 10:243–252
Shimada M, Abe Y, Yamano T, Ohta S, Yaniazaki S, Ohya N (1982) The pathogenesis of abnormal cytoarchitecture in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of the mouse treated transplacentally with cytosine arabinoside. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 58:159–167
Sidman RL, Rakic P (1973) Neuronal migration, with special reference to developing human brain: A review. Brain Res 62:1–35
Sillence DO, Horton WA, Rimoin DL (1979) Morphologic studies in the skeletal dysplasia. A review. Am J Pathol 96:813–860
Singh SC (1980) Deformed dendrites and reduced spine numbers on ectopic neurons in the hippocampus of rats exposed to methylazoxymethanol acetate. A Golgi-Cox study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 49:193–198
Spranger JW, Langer LO, Wiedemann H-R (1974) Bone dysplasia. An atlas of constitutional disorders of skeletal development. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 38–40
Thompson FH, Parmley TH (1971) Obstetric features of thanatophoric dwarfism. Am J Obstet Gynecol 109:396–401
Volpe JJ, Adams RD (1972) Cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome of Zellweger: An inherited disorder of neuronal migration. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 20:175–198
Webster W, Shimada M, Langman J (1973) Effects of fluorodenoxyridine on developing neocortex of the mouse. Am J Anat 137:67–81
Wolbach SB (1907) Congenital rhabdomyoma of the heart. Report of a case associated with multiple nests of neuroglial tissue in the meninges of the spinal cord. J Med Res 16:495–520
Wongmongkolrit T, Bush M, Roessmmann U (1983) Neuropathological findings in thanatophoric dysplasia. Arch Pathol Lab Med 107:132–135
Yang SS, Heidelberger KP, Brough AJ, Corbett DP, Berstein J, (1976) Lethal short-limbed chondrodysplasia in early infancy. In: Rosenberg HS, Bolande RP (eds) Perpectives in pediatric pathology, vol 3. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago, pp 1–40
Young RS, Pochaczevsky R, Leonidas JC, Wexler IB, Rather H (1973) Thanatophoric dwarfism and cloverleaf skull (“Kleeblattschädel”). Pediatr Radiol 106:401–405
Zellweger H, Taylor B (1965) Genetic aspects of achondroplasia. Lancet I:8–16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ho, K.L., Chang, C.H., Yang, S.S. et al. Neuropathologic findings in thanatophoric dysplasia. Acta Neuropathol 63, 218–228 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00685248
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00685248